* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science Success Academy
Discovery of Neptune wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Galilean moons wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Naming of moons wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
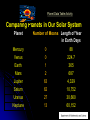
Our Solar System Grade 5 Big Idea 5: Earth in Space and Time SC.5.E.5.1, SC.5.E.5.2, SC.5.E.5.3 Does This Matter to Me? PSELL Big Idea 5 Student Book p. 160 This picture, courtesy of NASA, our national space program, is an artist's rendering of the planned Space Launch System as a rocket lifts off with the Orion spacecraft atop. The Orion spacecraft is already built and ready at Cape Canaveral in Florida. The Space Shuttle program provided successful low-Earth orbit missions, but NASA's heavy-lift launch vehicle will provide a new capability for human exploration beyond low-Earth orbit. The Space Launch System, shown here with Orion on it, is designed to be flexible for launching spacecraft for crew and cargo missions that will go far beyond to the moon again, to explore asteroids, and even to go to Mars. It will be people who are your age right now, maybe even you, who will be the ones to go on these exciting missions. Talk about these questions in your group: 1. How is our view of our Sun different from our view of other stars? 2. How and why does the moon's appearance change over the course of a month? 3. Why do the positions of the moon, stars, and planets change in the night sky? Our solar system is located in a galaxy known as The Milky Way. p. 167 What is a Galaxy? A galaxy is a group of solar systems, dust, and gas held together by gravity. Let’s read to learn more: In a Galaxy, Far, Far Away… What did you learn? How have astronomers learned about space? Sun and Stars pp. 167-168 Stars come in all different sizes. Our Sun is the standard used for comparing all other star sizes. The biggest stars are called supergiants. Some are 500 times larger than the Sun. Some of the smallest stars are white dwarfs. Many are 1/100 the size of the Sun roughly the size of Earth What do we know about the Sun? Click on SC.3.E.5.2; SC.3.E.5 Sun - Size and Appearance The sun is the closest star to Earth. The sun is a big ball of hot gases. The sun gives off two kinds of energy: light and heat. This is called solar energy. All eight planets orbit, or revolve, around the sun. The sun is so large that more than a million Earths could fit inside it. Solar System Let’s Explore Your Place In Space: Our Solar System Resource Link: http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link=/our_solar_system/solar_system.html What objects orbit the sun? pp. 169-170 Planets orbit the sun. What is a planet? A planet is a large ball of rock or gas that follows a path round the sun. What else orbits the sun? moons, drawf planets, comets, asteroids What are the eight planets? Having trouble remembering them? Try this mnemonic device: My Very Educated Mother Just Showed Us Neptune! Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Inquiry 10: Modeling the Solar System (SC.5.E.5.3) Student Resource pp. 173-181 Question: How can we model the distances of planets from the Sun and from each other? Make a Prediction: In a model of the solar system, the Sun and Mercury (the closest planet to the Sun) are 14 inches apart. How far do you think it is from the Sun to the farthest planet, Neptune? 120 inches 90 feet 300 feet How are the Planets grouped? What characteristics do they share? Inner Planets Size: Small Rocky and Solid Few or no moons Temperature: Hot to warm . Mercury Venus Earth (one moon) Mars Outer Planets Size: Large Composed of gas and dust Many moons Temperature: Cool to cold Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Planet Data Table Activity Comparing Planets in Our Solar System Planet Number of Moons Length of Year in Earth Days Mercury Venus 0 0 88 224.7 Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn 1 2 63 62 365 687 4,329 10,752 Uranus Neptune 27 13 30,660 60,152 Planet Characteristics Planet Size Length of Its Orbit Composition of Planet Mercury Small Shortest Rocky No moons Venus small Longer than Mercury but shorter than Earth’s Rocky Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune small small Largest Planet Large Large Large Longer than Venus but shorter than Mar’s Longer than Earth but shorter than Jupiter’s Longer than Mars but shorter than Neptune’s Longer than Jupiter but shorter than Uranus’s Longer than Saturn but shorter than Neptune’s Longer than Uranus No moons Rocky One moon Rocky No moons Gases and dust Many moons Gases and dust Many moons Gases and dust Many moons Gases and dust Many moons Accountable Talk Interactive Notebook Reflection Complete the sentences below to compare and contrast planet characteristics. 1. ________________ are different from ______________ in that ____________________ are ________________ than the ________________. 2. ___________ is/are similar to ______________________in that ______________________. Solar System Review Inner Planets Outer Planets Accountable Talk Interactive Notebook Reflection Complete the sentences below to compare and contrast planet characteristics. 1. ________________ are different from __________________ in that ____________________ are ________________ than the ________________. 2. ___________ is/are similar to _________________________in that ______________________. How does Earth differ from other planets? Earth is the 3rd planet from the sun. It is called the “Rocky Planet,” because it is made of rocks. Sometimes Earth is called the “Water Planet,” because about 70% of its surface is covered with the water. Earth orbits or revolves around the sun in 365 days, or one Earth year. While it is orbiting the sun, it also spins like a top! It spins 1 time in 24 hours, and that is why Earth’s day lasts for 24 hours. Earth is the only known planet where plants and animals live. It has one moon. SC.4.E.5.4