* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 Atoms Properties of Matter Intensive vs. Extensive
Bell test experiments wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum group wikipedia , lookup
Quantum entanglement wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
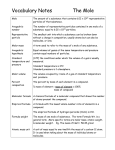
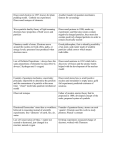
Chapter 1 Atoms Properties of Matter o Intensive vs. Extensive, physical vs. chemical Chemical Change Physical Change Mixtures and Pure Substances Elements and Compounds o Group or Family o Period or Row o Metals o Nonmetals o Metalloids Chapter 2 Scientific Method SI Units of Measurements Prefixes used in SI base units Derived Units Conversion Factor or Dimensional analysis Accuracy vs. Precision Significant Figures (precise and estimated) Scientific Notation Direct and Inverse or Indirect proportionality Dependent and Independent Variables Chapter 3 Law of conservation of mass Law of definite proportions Law of multiple proportions Subatomic particles J.J. Thompson’s (Lord Kelvin) Cathode Ray Experiment and Outcome Milliken’s Oil Drop Experiment and Outcome Rutherford’s Experiment and Outcome Mass Number Atomic Number Nuclide Isotope’s definition Average atomic mass Avogadro’s Number Mole Molar Mass Chapter 4 Electromagnetic Radiation o Particles and Wave Properties of Light o Speed, Frequency, Wavelength o Energy of a photon Plank’s Constant Ground Vs. Excited State Electrons Absorption Spectrum Line-Emission Spectrum Bohr’s Model of Hydrogen Atom Quantum Theory Quantum Numbers o Principal Quantum Number o Angular Momentum Quantum Number o Magnetic Quantum Number o Spin Quantum Number Orbitals Electron Configuration o Aufbau Principal o Hund’s Rule o Pauli’s Exclusion Principal o Nobel-gas configuration Formula Mass and Molar Mass Mole to Mass and Mass to Mole Conversion Mole to Particles and Particles to Mole Conversion Mass to Particles and Vice Versa Conversion Percent Composition Empirical Formula and Molecular Formula Chapter 8 Physical Indicators of a Chemical reaction Symbols used to write chemical equations Balancing Chemical Equations Types of Chemical Reactions o Synthesis o Decomposition Electrolysis o Displacement o Single o Double o Combustion Activity Series of Elements Chapter 9 Stoichiometry Limiting Reactants and Percent Yield




















![PROBLEM 1 [25 PTS] A system consists of N distinquishable](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006063913_1-e1778e5c6114fd66466f556bb5f30c03-150x150.png)
