* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids (Vocabulary)
Survey
Document related concepts
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Nanochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Thermal conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force velocimetry wikipedia , lookup
Thermoelectric materials wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
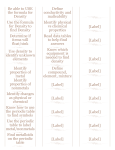
Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids (Vocabulary) Periodic Table of Elements A table in which all the known elements are arranged by properties and are represented by one or two letter chemical symbols. Metals Elements which have physical properties such as good conductivity, shiny luster, malleability and ductility. Nonmetals Elements which have physical properties such as no conductivity (an insulator), dull luster, and brittleness (will break). Metalloids Elements which can have both properties of metals and nonmetals. Also may be called a semiconductor. Luster The way a substance reflects light; Examples Shiney Dull Metalic Waxy Malleability How well it can be hammered into thin sheets. Examples Flattened penny Aluminum can Tin foil Aluminum foil Brittle The tendency to break, snap, or crack without first bending or changing shape as a result of application of little force. Conductivity How well it allows electricity to move through. Ductility Can be stretched into wire. Magnetism Attracted to or repelled by a magnet. Sonorous An object that produces a sound when struck by another object. Conductor a material that conducts or transmits heat, electricity, or sound Insulator A substance that does not allow the heat or sound to pass through Semiconductor A substance that can conduct electricity or heat under some conditions but not others Density Formula D = mass/volume (I density) Water Displacement A method used to calculate the volume of an irregular shaped object. Volume Formula V =LxWxH