* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (AVNRT)
Survey
Document related concepts
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
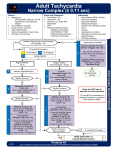
Patient Information AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (AVNRT) BACKGROUND INFORMATION • • • • • • • A heart rhythm condition where the heart rate can become abnormally fast A type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). This is related to a “short circuit” in the electrical connections of the heart located in the region of the AV node (part of the normal electrical conduction system of the heart). Episodes of fast heart rates tend to be brief, usually minutes in duration. Generally not dangerous (this will not cause a cardiac arrest), but certainly can be associated with very bothersome symptoms. Can occur in patients of all ages. Not necessarily associated with other heart problems. SYMPTOMS • • • • Palpitations; perception of a fast or forceful heart beat Chest discomfort Shortness of breath Lightheadedness DIAGNOSTIC TESTS • • • EKG Heart rhythm monitor (Holter or Event monitor) Electrophysiologic (“EP”) study; an invasive catheter based procedure where the doctor can “map” out the electrical system of the heart TREATMENT • • • Vagal maneuvers (bearing down, forceful coughing) can stop episodes of fast heartbeats. Medications that slow down the heart rate (beta blockers, calcium channel blockers) Radiofrequency ablation; most often curative. Involves essentially cauterizing inside the heart at the site of the “short circuit”. Part of the EP study, see above. FOR MORE INFORMATION or to make an appointment at URMC Cardiology at Highland Hospital, please call (585) 341-6780 or visit us online at www.highlandheart.urmc.edu Page 1 Rev 2.0