* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nutrition PP - St. Clair Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Malnutrition wikipedia , lookup
Food studies wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Food politics wikipedia , lookup
Obesity and the environment wikipedia , lookup
Dietary fiber wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
Fat acceptance movement wikipedia , lookup
Adipose tissue wikipedia , lookup
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Body fat percentage wikipedia , lookup
Overeaters Anonymous wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Food choice wikipedia , lookup
Childhood obesity in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
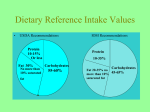
Nutrition—Eating Habits and Essential Nutrients UNIT 3 Eating Habits A difference between hunger and appetite Hunger the physiological need to eat Few of us have experienced the type of hunger that threatens survival Appetite psychological; the desire to eat Why do we eat? Physiological need (hunger) To obtain the energy and nutrients required for daily living Eating Habits Why do we eat? Appetite Personal preferences taste, texture, color, etc. Habit familiarity, comfort Ethnicity or tradition Social interaction eating can be a very social experience Availability, convenience, economy Emotional comfort Values religious, spiritual, political, environmental Body image Nutrition Eating Habits—Definitions Nutrition the science that investigates the relationship between physiological function and the essential elements of foods eaten Nutrients the constituents of food that sustain physiologically: proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water Calorie a unit of measure that indicates the amount of energy obtained from a particular food Eating Habits Most diet-related diseases result from excessive calorie and fat consumption Serving sizes vs. portion sizes Serving = amount recommended (USDA) Portion = amount chosen by individual Eat a variety Nutrient-dense foods Get the most from the food you eat Nutrients Water the most essential nutrient (5060% of body weight) Bathes cells Aids fluid and electrolyte balance Maintains pH balance Transports molecules and cells Major component of blood Nutrients How much water is enough? 6-8 glasses = 64 oz. Water in food, too Urine should be clear, light or bright yellow Dark yellow urine is a sign of dehydration Nutrients Protein the second-most abundant substance in the human body Necessary for development and repair of: Bone Muscle Skin Blood Aid antibody production & hormone formation Aid transport of iron, oxygen and nutrients Supply energy after body has used carbohydrate and fat 4 calories per gram Nutrients Protein continued… Made of amino acids 9 essential amino acids Must come from diet Complete proteins contain all 9 essential aminos Meat sources Soy bean products Incomplete proteins (plant sources) can be combined to provide all essential amino acids Nutrients Carbohydrates basic nutrients that supply energy Easily converted to energy (glucose) 4 calories per gram Complex carbohydrates Provide sustained energy source Starches stored as glycogen for sudden energy needs Polysaccharides Found in grains, green leafy and yellow fruits and vegetables, beans and potatoes Nutrients Carbohydrates continued… Simple carbohydrates Disaccharides and monosaccharides Glucose, fructose, sucrose, lactose, galactose Found in fruits, honey, milk Fiber (Polysaccharide) Two forms: soluble and insoluble Soluble fiber Found in oat bran, dried beans, fruits/vegetables Lowers blood cholesterol levels Insoluble fiber Found in bran, whole-grains, fruits/vegetables Aids digestion Nutrients Fiber continued… Benefits of fiber Protection Protection Protection Protection Protection Protection Protection against against against against against against against colon and rectal cancer breast cancer constipation diverticulosis heart disease diabetes obesity Nutrients Fats basic nutrient composed of carbon & hydrogen 9 calories per gram Excess calories are stored as triglycerides (95% of total body fat) Other 5% is cholesterol Plaque accumulation causes artherosclerosis HDL transports cholesterol to liver for elimination LDL transports cholesterol to cells Regular aerobic exercise raises levels of HDL ARTICLE 9: “The trouble with Trans fat” Trans fat (trans unsaturated fatty acids) are naturally found in small amounts in meat and dairy products.) Hydrogenation: Converts healthy vegetable oil into unhealthy trans fat. HOW? Heat and bubble hydrogen though it WHY? Longer Shelf life, cheaper, stays solid at room temperature. “Trans fat both raises LDL and lowers HDL- the worst possible combination.” “Harvard School of Public Health researchers estimate that hydrogenated fat is responsible for at least 30,000 premature heart disease deaths annually in the US.” “…increased waist size in men- another risk factor for heart disease.” “There’s also evidence that trans fat contributes to insulin resistance, raising the risk of type 2 diabetes.” “One of the most important things people can do to improve their health is to avoid trans fat.” ARTICLE 11: The trouble with Trans fat” Website Searching Wendy’s: http://www.wendys.com/w-1-0.shtml Arby’s: http://www.arbys.com/ KFC: http://www.kfc.ca/ Subway: http://www.subway.com/subwayroot/index.aspx McDonalds: http://www.mcdonalds.ca/en/index.aspx http://www.kentuckyfriedcruelty.com/anderson-vid.asp\ Group Project What is a usual meal you might purchase at this restaurant? What is the best meal you can order? What are the calories? What is the fat content? What is the trans fat? What is the total sodium? How much fiber is in your meal? What are the calories? What is the fat content? What is the trans fat? What is the total sodium? How much fiber is in your meal? What is the worst meal you can order in your restaurant? What are the calories? What is the fat content? What is the trans fat? What is the total sodium? How much fiber is in your meal? Nutrition— Vitamins/Minerals and Food Guidelines Essential Nutrients—Vitamins Vitamins are essential organic compounds that promote growth and reproduction and help maintain life and health Help maintain nerves and skin Produce blood cells Build bones and teeth Heal wounds Convert food energy to body energy Do not contain calories Vitamins Fat soluble Are absorbed through intestinal tract with help of fats Vitamins A, D, E, K Overuse can lead to hypervitaminosis Water soluble Easily dissolved in water B vitamins and vitamin C Essential Nutrients—Minerals Minerals are inorganic, indestructible elements that aid physiological processes Aid absorption of vitamins Are readily excreted Not usually toxic Macrominerals are needed in large amounts Trace minerals are required in small doses Possible harm if deficient or overused Minerals—Macrominerals Sodium Regulates blood and body fluids Regulates transmission of nerve impulses Regulates heart activity Regulates certain metabolic functions Only 500-1000 mg needed per day Average American consumes 6000-12000 mg Many packaged foods contain 100% or more of recommended daily allowance per serving Excessive amounts may lead to hypertension and may increase loss of calcium in urine Macrominerals Calcium Most Americans do not consume enough calcium per day Plays a vital role in 1200 mg recommended Building strong bones and teeth Muscle contraction Regulating heartbeat and fluid balance within cells Sources include dairy products, fortified orange juice, broccoli, cauliflower, peas and beans Phosphoric acid in soft drinks lowers calcium levels Stress can lower calcium levels Aid calcium absorption by getting sun (increasing vitamin D in body) and consuming foods containing vitamin C Macrominerals Other macrominerals: Phosphorus—animal sources Magnesium—nuts, legumes, whole grains, seafood, chocolate Potassium—meats, milk, fruits, vegetables Chloride—salt, soy sauce Trace Minerals Iron Iron deficiency is the most common nutrient deficiency Anemia results Inability to produce oxygen-carrying hemoglobin 10 mg/day for men, 18 mg/day for women Sources are beef, fish, poultry, eggs, peas and nuts Trace Minerals Others Zinc—meats, fish, poultry, grains, vegetables Manganese—most foods Copper—meats, drinking water Iodine—iodized salt, seafood Food Guide Pyramid The new pyramid = MyPyramid http://www.usda.gov/cnpp/pyramid.html http://www.mypyramid.gov/ Dietary Guidelines Alcohol in moderation Limit hydrogenated polyunsaturated fats 1-2 drinks per day Linked to higher levels of HDL More than 1-2 drinks increases risk of serious health problems Margarine and shortening Supplements are no substitute for food variety Use sugar and salt sparingly Weight should not increase with age Determining Nutritional Needs Recommended Daily Allowances (RDAs) Average daily intakes of energy and nutrients considered adequate to meet the needs of most healthy people % Daily Values represent nutrient needs of the typical consumer 2 reference values Reference Daily Intake reflects average daily allowances for proteins, vitamins, and minerals Daily Reference Values reflect nutrients with no established RDA, such as fiber and fat, but correlate with health Article 10: 10 Myths That Won’t Quit Article 11: “What Does Science Say You Should Eat?” Brad Lemley “…44 million people are clinically obese compared with 30 million a decade ago.” Walter Willett, chairman of the department of nutrition at the Harvard School of Public Health Eating Plan: Featuring abundant fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, chicken, and vegetable oils. Evidence: 121,700 participants over 2 decades of research “I call it “the Snack well revolution”. “The problem with overeating refined carbohydrates such as white flour and sucrose (table sugar) is that amylase, an enzyme, quickly converts them into the simple sugar called glucose. That goads up the pancreas to overproduce insulin, the substance that conducts glucose into the cells.” Problems? Syndrome X (Coined by Gerald Reaven) and involves the health problems associated with insulin resistance. Type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, hypertension, non-alcoholic-type liver disease, polycystic ovary syndrome, cancer Article 13: “What Does Science Say You Should Eat?” Brad Lemley Willett’s Plan “Good carb, good fat.” “…eating vegetables in abundance, consuming alcohol in moderation, and taking a daily multivitamin to coyer nutritional gaps.” Problems with the food guide pyramid? Eat Eggs- Eat fish Article 13: “What Does Science Say You Should Eat?” Brad Lemley Three Day Food Log Starting today and due Tuesday, October 3rd . Typed food log. Write down everything that you consume during the next three days. Need to include everything consumed! 1. Type of food (and brand if available) 2. Amount of Food consumed (oz, large apple, cups..) 3. What time of day you consumed the food 4. Water and drinks need to be included 5. What exercise (if any) was performed on each day