* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Italian Renaissance - World History and Honors History 9
Survey
Document related concepts
Spanish Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Northern Mannerism wikipedia , lookup
Art in early modern Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Waddesdon Bequest wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance philosophy wikipedia , lookup
French Renaissance literature wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance in Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Italian Renaissance painting wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance music wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
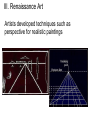
Chapter 15 - Renaissance and Reformation Vitruvian man by Leonardo da Vinci, 1492 Section 1 - The Italian Renaissance Section 1 - The Italian Renaissance Main Idea In Italy the growth of wealthy trading cities and new ways of thinking helped lead to a rebirth of the arts and learning. This era became known as the Renaissance. Reading Focus • What changes in society and in cities stimulated the beginning of the Renaissance? • What ideas formed the foundation of the Italian Renaissance? • What contributions did artists make to the Renaissance? I. The Beginning of the Renaissance Result of changes caused by Black Death and renewed interest in ancient Greece and Rome I. The Beginning of the Renaissance Began in Italy – city-states became centers of trade and manufacturing I. The Beginning of the Renaissance Florence, Venice and Milan grew in power; came to symbolized the Italian Renaissance Skyline of Florence with the Duomo cathedral I. The Beginning of the Renaissance A wealthy merchant class – bankers and traders - promoted cultural rebirth I. The Beginning of the Renaissance The wealthy became patrons of the arts; played a major role by sponsoring artists I. The Beginning of the Renaissance Medici family of Florence very important richest bankers and merchants in Europe Botticelli's "The Adoration of the Magi" (1476) with the Medici family and friends I. The Beginning of the Renaissance Lorenzo Medici – patron who supported the most talented poets, artists and philosophers Raphael's Lorenzo de' Medici II. Renaissance Ideas Renaissance = rebirth; a change in the way people viewed themselves and their world Auguste Rodin - The Thinker (1902) II. Renaissance Ideas Thinkers explored life with a secular, or worldly, focus rather than just a spiritual one II. Renaissance Ideas Secular writers wrote in the vernacular; included Castiglione and Machiavelli Baldassare Castiglione Niccolò Machiavelli II. Renaissance Ideas Scientists included Nicholas Copernicus, first to suggest a heliocentric theory of the universe (Zwolteh) II. Renaissance Ideas Humanism - focused on classic subjects and individual achievement II. Renaissance Ideas Based on study of classical culture: grammar, rhetoric, poetry, and history II. Renaissance Ideas Believed education should stimulate an individual’s creative powers III. Renaissance Art Renaissance art reflected humanist ideas The Birth Of Venus by Sandro Botticelli (1485) III. Renaissance Art Artists developed techniques such as perspective for realistic paintings Medieval Art – Not Realistic III. Renaissance Art Architect of Rome Donato Bramante designed St. Peter’s Basilica III. Renaissance Art The most celebrated artists were Leonardo da Vinci The Last Supper Mona Lisa Michelangelo The Pieta David The Creation of Adam Raphael Raphael’s School of Athens is famous for depicting figures of the Classical past with the features of his Renaissance contemporaries The Crucifixion Donatello Donatello's bronze statue of David (c. 1425–1430) Donatello's equestrian statue at Padua, the first example of such a monument since ancient times (1445–1450)