* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TUTORIAL 4 WORK, ENERGY AND POWER An escalator is used to
Survey
Document related concepts
Hooke's law wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Continuously variable transmission wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
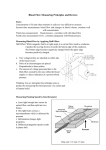
TUTORIAL 4 WORK, ENERGY AND POWER 1. An escalator is used to move 20 passengers every minute from the first floor of a department store to the second. The second floor is located 5.20 meters above the first floor. The average passenger's mass is 54.9 kg. Determine the power requirement of the escalator in order to move this number of passengers in this amount of time 2. A student with a mass of 80.0 kg runs up three flights of stairs in 12.0 sec. The student has gone a vertical distance of 8.0 m. Determine the amount of work done by the student to elevate his body to this height. Assume that her speed is constant. 3. If a spring is stretched 2.0 cm by a suspended object having a mass of 0.55 kg? a) What is the force constant of the spring b) How much work done by the spring as it stretched through this distance 4. A 2m x 2m x’ B C 10 m Determine the gravitational potential energy of an object of mass 2 kg placed at A, B & C if the reference level at which u = 0 A D B 20 m 10 m C 7m Figure 1 5. A 2 kg sphere slides down a smooth and curvy surface as shown in Figure 1. The sphere is initially at rest. Calculate: a) The potential energy at A, B, C, and D. b) The velocity of the sphere as it passes point B. Use the conservation of energy. 6. A 2 kg sphere slides down a smooth and curvy surface as shown in Figure 1. The sphere is initially at rest. Calculate: a) The potential energy at A, B, C, and D. b) The velocity of the sphere as it passes point B. Use the conservation of energy. 7. A 90 kg mountain climber is at the final ascent stage of the 4101 m high Mount Kinabalu. Calculate the change in the potential energy as the climber gains the last 200 m. Let U = 0 be: a) At sea level b) At the top of the peak 8. A spring is extended by 5 cm when it is stretched by an external force of 1 N. If the spring is extended by 10 cm, what is the elastic potential energy stored in the spring? 9. A 1.5 x 103 kg car needs to pass a slow moving lorry. The velocity of a car changes from 15.2 m s-1 to 19.5 m s-1 in 3.5 s. Calculate the minimum power required for this pass. F R 60o Friction = μR mg 10. A tourist drags his luggage of mass 22 kg with a force F at a constant velocity across the floor as shown. The coefficient of static friction between the rollers of the luggage and the floor is 0.40. Calculate the work done by the force F after the luggage is dragged 25 m along the floor. 11. 120 kg 3.5 m Force A worker uses a pulley to lift a load of 120 kg. He pulled the rope with a force of 1500N. The load is raised through a height of 3.5 m at constant speed. Calculate a) the work done by the worker b) the work output c) the efficiency of the pulley system 12. An inextensible rope over a rough pulley is used to raise a load of 36N through a height of 2.0 m. To raise the load at a constant speed, a force of 40N is required. What is the efficiency of the pulley? 40 N 2.0 m 13. An inextensible rope over a rough pulley is used to raise a load of 36N through a height of 2.0 m. To raise the load at a constant speed, a force of 40 N is required. What is efficiency of the pulley? 40N 36 N 2.0 m 40N 36 N 14. A pump is used to raise water through a height of 100 m at a rate of 3.0 kg s -1. What is the power of the pump if The velocity of water entering and leaving the pump can be neglected and The velocity of water entering the pump can be neglected, but water is leaving the pump at 3.0 m s-1 15. A worker uses a pulley to lift a load of 120 kg. He pulled the rope with a force of 1500N. The load is raised through a height of 3.5m at a constant speed. Calculate: a) the work done by the worker b) the work output c) the efficiency of the pulley 16. A ball is released from rest from a height of 2.0m. It bounces back to a height of 1.8m. a) what is the velocity of the ball b) what is the velocity when it bounces off the floor?