* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FINAL REVIEW
Survey
Document related concepts
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus modality wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Broca's area wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Spinal cord wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
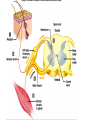
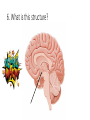
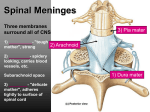
FINAL REVIEW YOU GOT THIS! Spinal Cord • Part of the CNS but connects PNS with the brain • Neuron vs Nerve vs Plexus • Ends around T12-L3 • Conus medullaris vs cauda equina • White matter vs. Gray matter • Gray horns – dorsal, lateral, ventral • Meninges – dura mater, arachnoid, pia • Know the meningeal spaces as well • Know the plexus nerves (i.e. brachial, lumbosacral, etc) 1. The presence of ________ gives white matter it’s whitish color. 2. Sensory information is relayed through which horn of the spinal cord? 3. CSF is concentrated in which part of the meninges? What is the function of CSF? 4. The axillary nerve belongs to which plexus? 5. Why are spinal nerves considered to be “mixed” nerves? Brain • Must be able to LABEL and know FUNCTIONS of the regions • • • • • • Cerebrum Diencephalon thalamus and hypothalamus Mesencephalon superior/inferior colliculi and the auditory-visual reflex Pons Medulla Oblangata Cerebellum arbor vitae, cerebellar nuclei • Sulcus vs. Gyrus • Precentral Gyrus vs Postcentral Gyrus • What is the brain stem? • Meninges • Stabilizing extensions of the dura matter • Draining Sinuses – sagittal and transverse • Choroid plexus in the ventricles produces CSF • 4 ventricles and WHERE they are located (i.e. 3rd ventricle is diencephalon) • Pathway of CSF flow • Know where the corpus callosum is and what it’s function it • Broca’s area vs Wernicke’s area • Fornix Limbic system (emotions/memory) 6. What is this structure? Which structure of the endocrine system does it connect to? 7. A patient has suffered damage to Broca’s area. What kind of speech deficit would you expect to see? 8. What area of the brain does higher cognitive functioning (i.e. impulse control, logic) occur? What do you call it when some neural functions tend to be more dominant in one hemisphere than the other? And, what structure allows crosscommunication between these hemispheres? Lateralization and Corpus Callosum 9. What is the function of the dural sinuses? 10. What structures make up the brain stem? GOOD LUCK! Remember to also review the slides on the ear and eye! This will show up on the exam as well