* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Relevance of the Business-to-Business/Consumer
Survey
Document related concepts
Customer satisfaction wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Theory of the firm wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Market environment wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Social marketing wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
History of marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
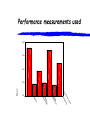
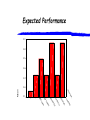
Profiling Contemporary Marketing Practice Jaqueline Pels, Universidad Torcuato Di Tella 1- Overview 2- Cross-National Results 2000 3 - Incorporating e-Marketing 4 - Cross-National Results 2001 Market Orientation & Performance 5- Conclusions and Implications 1- Contemporary Marketing Practice (CMP) Research Programme CMP research project was started in NZ in 1996 extended to Canada, Finland, Sweden, Ireland, Argentina, Thailand, UK, Germany, USA, SE Asia, Africa… Objective? “profile marketing practice in a contemporary environment, and to examine the relevance of relational marketing in different organizational, economic and cultural contexts” Synthesis of: European, North American, Australasian & Latin thinking qualitative and quantitative methods Contrasting Views of How Firms Relate to their Markets Transactional (AMA 1985) “….the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods and services to create exchange, and satisfy individual and organizational objectives”. Relational (e.g. Berry 1983) “attracting, maintaining and …enhancing customer relationships” … need for a richer framework that incorporates both transactional and relational aspects of marketing Developing Pluralistic View of Marketing Practice (Coviello, Brodie and Munro 1997) Classification scheme developed from an extensive review of North American and European literature Transaction Marketing (TM) managing the 4P’s to attract and satisfy customers Database Marketing (DM) using technology-based tools to target and retain customers Interaction Marketing (IM) developing interpersonal relationships between individual buyers and sellers Network Marketing (NM) positioning the firm in a connected set of inter-firm relationships Aspects of Marketing - Relational Exchange Dimensions Transaction Database Interaction Network Focus Economic transaction Information & economic transaction Relationships between a buyer and seller Relationships between firms Parties Involved A firm in the general market A firm in a specific target market Individual sellers and buyers Sellers, buyers, and other firms Communication Pattern Firm “to” market Firm “to” individual Individuals “with” individuals Firms “with” firms Type of Contact Arms’ length, impersonal Personalised Face-to-face, interpersonal Impersonalinterpersonal Duration Discrete Discrete yet over time Continuous Continuous Formality Formal Formal (personalised via technology) Formal and informal Formal and informal Balance of Power Active seller – passive buyers Active seller – less passive buyers Seller/buyer mutually active/adaptive All firms active and adaptive Aspects of Marketing - Managerial Dimensions Transaction Database Interaction Network Managerial Intent Customer attraction Customer retention Interaction Co-ordination Decision Focus Product or brand Product/brand and customers Relationships between individuals Relationships between firms Managerial Investment Internal marketing assets Internal marketing assets External maktg assets External mktg assets Managerial Level Functional marketers Specialist marketers All managers/ employees General manager Time Frame Short term Longer term Short or long term Short or long term Research Questions? At a general level... To what extent are transactional and relational marketing practiced across countries? More specifically… Do the findings generalize for economies that are either similar or different in terms of: economic development Method participants required to fulfill the questionnaire as part of course work structured survey instrument measuring marketing practices feedback sessions to ensure validity of results instrument administered in English to participants from executive management programs pre-tested to ensure questions understood controls for demographic differences Sample Group 1: Advanced Economies [New Zealand (185), Canada (94), Finland /Sweden (51)] economies well developed Group 2: Transition Economies [Argentina (96), Thailand (55)] economies in transition firms range in size, age, growth rate, ownership, level of export activity, use of technology, and sector consumer goods (15-28%), consumer services, (15-25%), B2B goods (22-38%), B2B services (26-43%) 2- Cross National Results,2000 Aspects of Marketing Practiced (Firms with Medium to High Levels) Transaction Mktg NZ 80.5% Canada 75.5% Fin/Swe 70.6% Argentina Thailand 74.0% 83.6% Database Mktg 77.8% 79.8% 80.4% 57.3% 83.6% Interaction Mktg 91.8% 91.5% 88.2% 75.0% 90.9% 7474.1% 79.8% 74.5% 61.4% 85.5% Network Mktg Which Combinations? Transaction Marketing Database Marketing Network Marketing Interaction Marketing Are There Differences Across Firm Types? • 3 clusters • Transactional (T), Tranasactional/Relational (TR), Relational (R) • BUT all types of firms have membership in all three clusters and 40% of all firms fall into the TR cluster • some country specific differences e.g. tendency for more firms from Argentina to be in the T cluster Which Combinations? higher %’s of consumer goods firms in T cluster Transaction Marketing Database Marketing Network Marketing Interaction Marketing Which Combinations? higher %’s of consumer service firms in T and TR clusters Transaction Marketing Database Marketing Network Marketing Interaction Marketing Which Combinations? higher %’s of B2B goods and service firms in R and TR clusters Transaction Marketing Database Marketing Network Marketing Interaction Marketing 3- Incorporating Interactive eMarketing into the CMP Framework Ongoing conceptual development/refinement: instrument now has a 5th aspect e-Marketing eM interactive technologies to create and mediate dialogues testing of the new instrument in UK, NZ and Germany “Interactive”: The Early Views As discussed by Blattberg and Deighton (1991) used synonymously with the term ‘database’ marketing builds on traditional approaches available through the mail, telephone, and sales force a medium for 2-way conversation: the consumer ‘speaks’ through purchases and the manufacturer employs artificial intelligence to reply (e.g. loyalty programs) More Recent Views the ability to address an individual, gather and remember the response of that individual, and address the individual once more in a way that takes into account his/her unique response (Deighton 1996) a form of marketing with the following qualities (Iacobucci 1998) Content: technology, intrinsic motivation, use of interactive marketing information, real time Structural: private, truly interactive, interactions among groups (incl. customers), networked networks “...the use of information from the customer rather than about the customer.” (Day 1998, p.47) often discussed in the context of the Internet Relational Exchange Dimensions (adapted from Coviello et al 1997, Milley 1998) Database INTERACTIVE Interaction Focus Information & economic transaction Relationships between a buyer and seller Relationships between a buyer and seller Parties Involved A firm in a specific target market A firm to many individual buyers Individual sellers and buyers Communication Pattern Firm “to” individual Firm “with” individuals Individuals “with” individuals Type of Contact Personalised (yet distant) Personalised (close) Face-to-face, interpersonal (close) Duration Discrete yet over time Continuous Continuous Formality Formal (personalised via technology) Formal (personalized via technology) Formal and informal Balance of Power Active seller – less passive buyers Active seller/buyer (seller more powerful) Seller/buyer mutually active/adaptive Managerial Dimensions (adapted from Coviello et al 1997, Milley 1998) Database INTERACTIVE Interaction Managerial Intent Customer retention Interaction Interaction Decision focus Product/brand and customers Relationships between the firm and individuals Relationships between individuals Managerial Investment Internal marketing assets Internal marketing assets External Internal operational assets mktg assets Managerial Level Specialist marketers Specialist marketers Technology Specialists All managers/employees All managers/ employees Time frame Longer term Longer term Short or long term 4 - Cross-National Results 2001 Market Orientation & Performance 48 New Zealand, 84 UK & 61 Argentine Firms vary in size, age, growth rate, type of product offered, type of market served, use of technology, export level, ownership structure As before partial correlations show very clear relationships DM practiced with TM IM practiced with NM Interactive Marketing provide linkage between DM and IM/NM Overview: Aspects of Marketing Practice 2001 Transaction NZ UK ARG Low 19 37 14 Medium 60 45 54 High 21 18 32 Total 100% 100% 100% Index Value Database NZ UK ARG 23 55 27 28 34 66 29 11 7 100% 100% 100% e-Marketing NZ UK ARG 63 85 52 29 8 41 8 7 7 100% 100% 100% Interaction NZ UK ARG 8 24 13 40 30 37 52 46 50 100% 100% 100% Network NZ UK ARG 17 39 29 42 30 56 42 31 15 100% 100% 100% Which Combinations? Transaction Marketing Database Marketing e-Marketing Moderate positive relationship Strong positive relationship Moderate negative relationship Network Marketing Interaction Marketing Table 4: Partial Correlations Between Indices by Country a. Transactional Marketing & Relational Marketing Transaction Marketing with Database Marketing Transaction Marketing with Interaction Marketing Transaction Marketing with Network Marketing b Relational Marketing. Database Marketing with Interaction Marketing Database Marketing with Network Marketing Interaction Marketing with Network Marketing ** = p<.01, * = p<.05 USA New Zealand .39** Argentina -.18** -.05 -.03 .09 .62** .41** .15 .39* .31** .66** .67** Transaction mktg Database mktg network mktg e-mktg interaction mktg New Zealand UK Transaction mktg Database mktg network mktg e-mktg Argentina interaction mktg Market Orientation Table 7: Groups by Market Orientation Pluralistic Traditional B2B Low Marketing Total MO 1 .7254 .7252 .6744 .7122 MO 2 .7022 .6497 .6295 .6648 MO 3 .7167 .6939 .6344 .6874 ce an rm rfo io Pe ct fa er th ti s O Sa er m to us C ow gr th re ed haai n t Sr g ke e ar m M sto cu y n l it ti o bi en i ta et of R Pr er m to us ew C N s le Sa 2.5 Mean Performance measurements used 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 r su ea m rm fo er rp tis he sa ot st cu g in it ev of hi pr ac s de g in cu in nt ta at re r cu t g in ke in ar ta m re s de g rin om cu st se cu w ne s g le in in sa d ga re si de in ta at 3.1 Mean Expected Performance 3.7 3.6 3.5 3.4 3.3 3.2 Table 8: Clusters by Type of Performance Measurement Used and Expected Performance Pluralistic Traditional B2B Low Marketing Used Expected Used Expected Used Expected Sales Growth 4.42 3.08 4.36 3.10 4.50 2.86 New Customer Gained 3.67 3.08 3.55 3.11 2.63 3.83 Market Share 3.09 3.30 3.64 4.25 2.63 4.00 Customer Retention 3.33 4.00 4.00 4.36 2.50 3.83 Profitability 4.25 3.18 4.27 3.36 3.88 2.86 Customer Satisfaction 3.33 3.90 3.91 4.20 2.63 4.00 Summary of Key Findings managers of all types of organisations are placing an emphasis on managing marketing relationships need to focus more on issues and trends which are shaping the future understanding of the IT in supporting, enhancing and transforming dangers of focusing too much on traditional dichotomous thinking ie Goods vs Services, Consumer vs B2B, transactional vs relational the distinction between goods and services is not the point service aspect of products provide competitive advantage The Argentine Sample Product/Service Ownership Mis sing 1.8 38.2 38.6 Not for Profit Totally foreign owned B2B Servic es Consumer Packaged Go 12.7 Consumer Durables 7.3 Consumer Services 20 Industrial Goods 20 Totally domestically Domestic/foreign AGEORG 49.1 more than 10 yrs 5yrs or less 21.1 6-10 yrs 29.8 38.6 22.8