* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Military history of the United Kingdom during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Operation Torch wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
The War That Came Early wikipedia , lookup
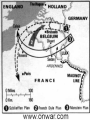
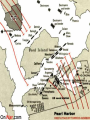
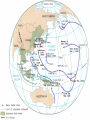
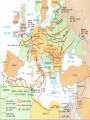
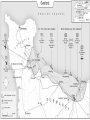
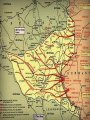
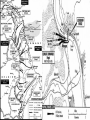
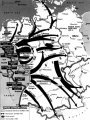
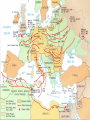
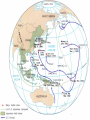
World War II 1940-1945 Causes World War I didn’t settle differences Harsh terms of Treaty of Versailles Especially on Germany Economic instability following First World War Italy and Germany look to Fascist dictators Solve Problems Return to Glory Aggressions of Axis Powers Italy, Germany, Japan formed Axis Powers by 1940 Italy conquered Ethiopia (1936) Albania (1939) Hitler repeatedly violated Treaty of Versailles (1934-1938) Germany annexed Austria (1938) Tripartite Pact Conquered Czechoslovakia and Poland (1939) Hitler also broke Munich and NaziSoviet Non-Aggression Pacts Japan invaded Manchuria (1932) China (1937) French Indochina (1940) Bombed U.S. Pacific Fleet at Pearl Harbor (1941) Wake Island (1941) Allied Nations Great Britain France (until 1940) United States (1941) Soviet Union (1943) China (1943) Italy joins in 1943 Many smaller nations Weaponry Improvements made to: Aircraft used more effectively: Tanks Machine guns/rifles Artillery Submarines Battleships & Destroyers German Luftwaffe British Royal Air Force U.S. Army Air Corps Imperial Japanese Naval Air Force Air Craft Carriers By 1942, dominated naval warfare Blitzkrieg German word for “Lightning War” Fast moving tanks (Panzers) and ground forces Mixed with air cover Luftwaffe Effectively used against: Czechoslovakia Poland Holland Denmark Norway Belgium France Soviet Union War Time Leaders Great Britain: Prime Minister Winston Churchill United States: President Franklin D. Roosevelt Free-French Forces: General Charles De Gaulle and General Henri Giraud Soviet Union: Premier Joseph Stalin Nationalist China: General Chiang Kai-chek Germany: Adolf Hitler Italy: Benito Mussolini Japan: Emperor Hirohito & Prime Minister Hideki Tojo 1940 April 9: Germany invades Denmark and Norway May 10: Germany invades Holland, Belgium, Luxembourg September: U.S. begins military draft Begins building air and naval fleet Begins aiding Allies Japan joins Axis (Tripartite Pact): Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis formed November: President Franklin Roosevelt elected to third term Germany Conquers France Invades on June 5, 1940 German Blitzkrieg goes around French Maginot Line Invades through Belgium Splits Allied lines in two Manstein Plan Half of Allied forces fled to Dunkirk Along French-German border Churchill has them rescued Rest of Allied forces surrender within days Including Paris June 14 French government flees to Bordeaux Germans install French Vichy government in the south Lasts until Allied liberation in August of 1944 Battle of Britain Lasts from August through September 1940 Fought in skies over Britain Original plan: Luftwaffe gets bored Begins bombing London and major cities Luftwaffe bombs RAF spitfires on the ground Then bomb RAF radar towers Then bomb major British cities Force British to surrender without invasion Causes much damage & loss of life Winston Churchill wills his people to “never surrender” British RAF holds off Luftwaffe Forces Hitler to abandon plans of invasion Moral victory for British Bombing would continue intermittently through out war Battle of Atlantic Lasts from 1940-1945 British and U.S. Navy (Atlantic Fleet) square off against German fleet Used battleships, destroyers, submarines Aircraft Carriers make an appearance later in war Allied forces eventually prevail 1941 March 11: Lend-Lease Act passed U.S. would lend and lease used ships and planes to British Proposed by Roosevelt Passed by Congress Helped U.S. economy August 14: Atlantic Charter proposed Endorsed by Churchill and Roosevelt At Atlantic Conference Met off coast of Newfoundland Vision of post-war world Led to creation of United Nations in 1945 8 Points of Atlantic Charter No territorial gains were to be sought by the United States or the United Kingdom. Territorial adjustments must be in accord with the wishes of the peoples concerned. All peoples had a right to self-determination. Trade barriers were to be lowered. There was to be global economic cooperation and advancement of social welfare. Freedom from want and fear. Freedom of the seas. Disarmament of aggressor nations, postwar common disarmament. Germany invades Soviet Union Blitzkrieg begins early on the morning of June 22, 1941 Violated the non-aggression pact September: German forces had reached the gates of Leningrad in the north Called Operation Barbarossa Smolensk in the center and Dnepropetrovsk in the south German units reached the outskirts of Moscow in early December Yet after months of campaigning, the German army was exhausted Germans expected a rapid Soviet collapse Planners failed to equip their troops for winter warfare Speedy German advance had caused the forces to outrun their supply lines Like Napoleon, Hitler’s forces got trapped in a Russian Winter In December, the Soviet Union launched a major counterattack against the center of the front Driving the Germans back from Moscow in chaos Japan bombs Pearl Harbor December 7, 1941 Plan was to knock out U.S. Pacific Fleet First wave attacked at 7:53AM Would allow Japan to expand into Central and South Pacific Second wave at 9AM Japanese sunk USS Arizona, Oklahoma, Utah, West Virginia and other battleships Bombed planes at nearby Hickam Field and other air fields Third wave wasn’t launched because Japanese felt element of surprise was gone Failed to hit oil tanks Failed to hit U.S. aircraft carriers: Lexington, Hornet, Enterprise Were at sea U.S. and Great Britain declares war on Japan on December 8 Germany declare war on U.S. on December 9 Japanese also captured Guam on December 7th 1942 Pacific January 7-April 9: Battle of Bataan February 27: Battle of Java Sea American-Filipino forces hold on for months against Japanese invasion FDR demands that Allied Commander Douglas MacArthur evacuate to Australia Allied troops finally surrender in April Prisoners are taken on Bataan Death March through the jungle Many die along way to Camp O’Donnell Japanese try to invade Dutch East Indies Allied forces intercept Japanese convoy Allies forced to retreat 1st encounter with Japanese since Pearl Harbor May 6: Corregidor falls to Japanese Island fortress in Manila Bay American signal station there Japanese occupy Philippines Allies Turn The Tide in the Pacific April 18: Doolittle Raid U.S. bombers attack military and industrial targets around Tokyo Showed Japanese were vulnerable to air attack May 7-8: Battle of Coral Sea--indecisive 1st battle completely fought by aircraft carriers Japanese sink more ships than Allies But Allies force Japanese to abandon plan to invade Australia June 3-6: Battle of Midway Retaliation for Pearl Harbor U.S. learns of Japanese plan to invade Midway Island Sink 4 Japanese carriers Turning point of war for U.S. Navy June 6-7: Allies begin campaign to retake Aleutians from Japanese August 21: Battle of Guadalcanal Begins Allied strategy of “island hopping” begins Japanese had taken island to build airbase there for Australian invasion Japanese hold on for six months against Allied invasion One of bloodiest battles of Pacific theatre Allies take island on February 9, 1943 Begins Allies Solomon Island Campaign 1942 Europe August 21-February 2, 1943: Battle of Stalingrad October 23-November 5: Battle of El-Alamein Hitler’s forces try and take the strategic city on the Volga River Then would march south into the oil fields of the Middle East Germans have success in early months Soviets get reinforcements By February, Soviets force German army to retreat 1st large-scale defeat for Germans in Europe Rommel’s Afrika Korps tries to take Egypt and Suez Canal from British British under General Bernard Montgomery hold off Germans and secure Egypt November 8: Operation Torch--U.S. forces land in North Africa North African Campaign begins U.S. troops to aid British in liberating Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia 1943 Europe January 12-24: Casablanca Conference February 20-22: Battle of Kasserine Pass Allies liberate from Axis control September 3: Allies land at Reggio di Calabria End of the North African Campaign July 9-August 17: Allied invasion of Sicily Rommel’s Afrika Korps defeats Allied forces May 13: Allied victory in Tunisia Churchill and Roosevelt meet Discuss Sicilian and Italian Campaigns Italian campaign begins Southern Italy surrenders to Allies; Northern Italy remains in Axis control September 9: 1st wave lands at Paestum September 10: Allies land at Salerno September 12-14: 2nd wave lands at Paestum October 1: Allies land at Naples October 13: Italy declares war on Germany November 28-December 1: Allied leaders meet at Tehran Conference Joseph Stalin meets with Churchill and Roosevelt for the first time Stalin demanded a Second Front be opened Discuss Allied invasion of western Europe 1943 Pacific November 1: Battle of Empress August Bay November 1-December 24: Battle of Bougainville U.S. Navy victorious Secures landings at Bougainville Allied forces liberate the island Ends the Solomon Islands Campaign November 21-24: Battles of Tarawa and Makin atolls Tarawa one of the bloodiest conflicts U.S. Marines invasion helps liberate island Allies liberate Gilbert Islands 1944 Europe January 22: Allied invasion of Anzio Beach February 14-March 31: Battle of Anzio May 11-18: Battle of Monte Cassino Allies pinned down on beach for weeks Finally force Axis retreat Germans take refuge in ancient monastery Allies bomb and cause major destruction June 4: Allies liberate Rome D-Day: June 6th Allied invasion of Normandy, France Paratroopers “jumped” in behind German lines the night before Troops came ashore before 7AM Landings at Omaha, Utah, Sword, Gold, and Juno beaches Helped secured beach landings Bombardment from armada before landings Called “Operation Overlord” Heaviest opposition and casualties at Omaha Beach Allies finally come ashore and take coastal region and towns Takes them several months to “breakout” from coast Many regard D-Day as most important event of 20th Century August 15: Allied invasion of Southern France Operation Anvil/Dragoon Allies liberate France and march toward German border August 25: Allies liberate Paris Operation Market Garden Allied invasion of Holland Allied plan to invade Germany through Holland Allied paratroopers make “jump” into occupied territory Initially a success September 17-25 Allies capture Waal Bridge at Nijmegen Eventually failed Allied plan to advance across Rhine at Arnhem had to be abandoned Battle of the Bulge December 16-January 31, 1945 Also known as Battle of the Ardennes Germans launch massive offense against Allied lines in Belgium Near town of Bastogne Cause a “bulge” in Allied lines Allies get reinforcements Within weeks, drive Germans back Force German retreat Last German offensive of war 1944 Pacific February 1-8: Allies take Kwajalein February 18-23: Allies take Truk and Eniwetok April 22: Allies take Hollandia, New Guinea Also known as the “Marianas Turkey Shoot” U.S. Naval forces victorious over Japanese July 21-August 10: Allies retake Guam July 24-August 1: Allies retake Tinian Allies liberate New Guinea on September 17 June 15-July 9: Allies retake Saipan June 19-20: Battle of Philippine Sea Ends Marshall Islands Campaign End of Mariana Islands campaign October 23-26: Battle of Leyte Gulf Last major naval encounter in Pacific Victory allows Allies to land in Philippines Campaign would last until May 8, 1945 1945 Europe February 4-11: Allies leaders meet at Yalta February-March: Allies liberate Belgium, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands March 7: Allies secure the Ludendorff Bridge at Remagen Harry S. Truman becomes president April 29: Italian Campaign ends in Allied victory April 30: Hitler commits suicide May 2: Berlin surrenders Last standing span over the Rhine Allies cross the Rhine River April 12: President Roosevelt dies Last time Roosevelt would meet with Churchill and Stalin Discuss plan for end of the European war Getting the Soviets involved in Pacific war May 4: Germany surrenders May 8: V-E Day July 17-August 2: Allied leaders meet at Potsdam Conference Truman and British Prime Minister Atlee meet Joseph Stalin for 1st time Discuss ending Post-war Europe and war in Pacific 1945 Pacific February 19-March 16: Allies take Iwo Jima March: Allies begin massive firebombing of Japanese cities March 3: Allies liberate Manila April 1-June 21: Allies take Okinawa May 8: Philippines Campaign ends August 1: Soviet Union declares war on Japan Invades Manchuria and Korea August 6: U.S. drops atomic bomb on Hiroshima August 9: U.S. drops an atomic bomb on Nagasaki August 15: Japan surrenders Last major conflict of Pacific theatre V-J Day September 2: Treaty ending war in the Pacific signed on board USS Missouri in Tokyo Bay