* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How to Calculate Kinetic Energy
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
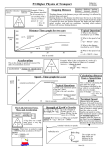
Buggé: Energy 5 How to Calculate Kinetic Energy 5.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) In a car crash testing facility, engineers evaluate the reaction of a car to an impact on its front. To create such an impact, a rod pushes a 1000 kg block on wheels over a distance d. This causes the block to accelerate from an initial to a final velocity. To measure the smashing potential of this block, let’s determine the change in the block’s kinetic energy after the piston pushes it a distance d. The initial and final states of the process are pictured to the right. a) Draw a force diagram for the block. Use it to find an expression for the force that the piston exerts on the block in terms of its mass m and acceleration a. b) Use a kinematics equation to convert the acceleration a in the equation from part (a) into an expression involving the block’s initial and final speeds vi and vf. Substitute this into the expression for force from part (a). c) Substitute the expression for force from part (b) into the expression for work when the force is parallel to the displacement, W = Fd, and then simplify. d) Using a work-energy bar chart, develop a mathematical representation of this process in terms of work, initial kinetic energy, and final kinetic energy. Compare this expression to the one from part (c). e) What characteristics of an object do you expect kinetic energy to depend on? Its mass? Velocity? Acceleration? Height? f) By comparing your answers from parts (c) and (d), do you see a term that could represent kinetic energy and that depends on the characteristics that you think kinetic energy should depend on? g) Show that the units of this quantity are equal to the units for energy, joules. Buggé: Energy 5 Kinetic Energy: K = ½ mv2 For each of the following energy problems, use the problem solving strategy. Include sketches, your system, and bar charts in your answers. 5.2 Regular Problem If you drop a 0.3 kg baseball from a window 20 m above the ground, how fast will the ball be moving the instant before it hits the ground? 5.3 Practice If a stretched slingshot has 100 J of elastic potential energy, how fast will a 0.5 kg softball be moving right after the launcher fires it? 5.4 Regular Problem A crane lifts a 50-kg crate so that the crate’s speed increases from 0 m/s to 5.0 m/s over a vertical distance of 10.0 m. Draw a bar chart representing this process. What is the force that the crane exerts on the crate? Specify the system, its initial and final states, and any assumptions you made. Explain how these assumptions affect your answer. 5.5 Regular Problem A man throws a 0.4-kg softball vertically into the air with an initial speed of 10 m/s. How fast will it be traveling when it passes 1/3 of its maximum elevation? 5.6 Equation Jeopardy Write a problem and draw an energy bar chart that would require the mathematical equation below to solve it.