* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download electromagnetism
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
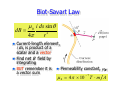
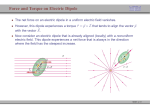
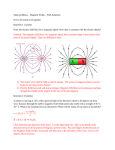
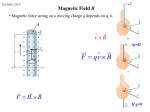
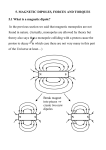
Electric Motor z What happens if we put a loop of wire carrying a current in a B field ? z FB on opposite sides of the loop produce a torque on the loop causing it to rotate. Electric motor – a commutator reverses the direction of the current every half turn to that the torque is always in the same direction. Electric Motor z z z Define normal n to plane using right-hand rule Torque tends to rotate loop to align n with B field Torque for single loop τ = iAB sin θ where A is the area of the loop and θ is between n and B z Replace single loop with coil of N loops or turns τ = ( NiA) B sin θ Magnetic Dipole • Define magnetic dipole moment μ = NiA τ = ( NiA) B sin θ = μB sin θ z The direction of the magnetic dipole moment is the same as the normal vector to the plane. r r μ =n z The torque becomes r τ = μ×B r r Magnetic Dipole z z z A magnetic dipole in a magnetic field has a magnetic potential energy, U Lowest energy when dipole moment lined up with B field Highest energy when dipole moment directed opposite B field r U = −μ • B r Magnetic Dipole • Magnetic dipole moment μ has Torque r τ = μ×B r z r Potential Energy r U = −μ • B r Remember electric dipole moment p Torque r r τ = p× E r Potential Energy r r U = −p•E B Fields from Currents z Calculate B field produced by distribution of currents z Similar to finding E from distribution of charges 1 dq dE = 4πε 0 r 2 z B fields, like E fields, can be superimposed to find net field Biot-Savart Law μ 0 i ds sin θ dB = 2 4π r z z z Current-length element, i ds, is product of a scalar and a vector Find net B field by integrating BUT remember it is z Permeability constant, μ0 a vector sum −7 μ 0 = 4 π × 10 T ⋅ m A Biot-Savart Law μ0 ids sin θ dB = 2 4π r z Rewrite in vector form r r r μ0 ids × r dB = 3 4π r z Known as Biot-Savart Law