* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hubble Deep Field Image
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Structure formation wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
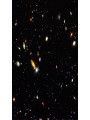
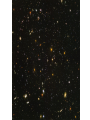
Hubble Deep Field Daniel Hazard Background The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is a composite picture of 342 different images. The HDF covers an area of 144 arc seconds. Taken by the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) over a period of 10 consecutive days in December of 1995. Taken by the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2. Total exposure time was more than 100 hours. … the telescope and its origins Astronomer Lyman Spitzer calls for space-based observatory in 1946; designing of HST begun in 1978; launched in 1990. NASA and ESA funded, NASA built. Named after astronomer Edwin Hubble. Total costs to date have been estimated to be close to $14,000,000,000. May be replaced by James Webb Space Telescope in 2013. Selecting the HDF HDF is but a tiny, tiny portion of the sky seen in the Northern Hemisphere; more specifically: a small section which lies within the Ursa Major constellation. Field was selected by the following criteria Needed to be outside of the Milky Way’s disk of dust Could not contain very bright objects or anything that emitted too much infrared, x-ray, or UV In addition, field could never be occulted by the Earth or Moon. … HDF within the sky Describing the HDF As a result of the field’s size, it is thought to display less than 10 stars from our galaxy. Most of the objects seen are distant galaxies--nearly 3,000 of them. There are also a number of bluish objects and regions. They might be: Regions of intense star formation Faint quasars White dwarfs Initial implications of HDF HDF looks into space, and, in effect, back in time Large number of galaxies with unforeseen redshift values; prior to the HDF no galaxies with a redshift value higher than 1 Helped in debate over the missing mass of the universe. Prior to the HDF there were theories of faint yet massive objects in the outer regions of galaxies such as red dwarves and planets making up this missing, non visible mass. The HDF proved that this wasn’t the case, as these proposed faint objects did not exist. Thus, the mass must exist in other non visible forms such as dark matter and dark energy. A second HDF Named Hubble Deep Field South (HDF- S); very similar to original HDF, now named Hubble Deep Field North (HDFNorth). Same criteria, only now in Southern Hemisphere, within the Tucana constellation. Taken over in 1998 over 10 days. Content of HDF-S Remarkably similar to HDF-N. One major difference is the existence of a known quasar. Implications of HDF-S In general, HDF-S confirmed many findings of HDF-N. Evidence for cosmological principle: correlations between HDF-N and HDF-S help support the idea that the universe is homogenous and isotropic. … one more image Hubble Ultra Deep Field (HUDF) is appropriately titled: taken over a period of several months in 2003 and 2004, the HUDF is the deepest image ever taken in visible light. Taken within the constellation of Fornax Also looks back into time: 13 billion years Evidence for Big Bang, and finite age of universe Contains perhaps as many as 10,000 galaxies Works Cited http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hubble_ Deep_Field http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hubble_ Space_Telescope http://oposite.stsci.edu/pubinfo/PR/9 7/hdf-key-findings.html