* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download COMPUTATION AND ESTIMATION Kindergarten: •Represent
Survey
Document related concepts
History of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical calculator wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Elementary arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
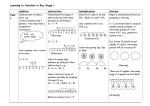
COMPUTATION AND ESTIMATION Kindergarten: •Represent addition and subtraction problems with objects, fingers, mental images, drawings, sounds (e.g. claps), acting out situations, verbal explanations, expressions, or equations. •Find the missing addend in combinations up to 10. •Estimate the number of objects in a set up to 20. Discuss the reasonableness of those estimates with assistance. Grade 1: •Solve addition and subtraction facts up to 10. •Continue to develop addition and subtraction facts up to 20. •Use strategies such as counting on, making ten (8+6=8+2+4, 10+4=14), decomposing a number leading to ten (13-4=13-3-1, 10-1=9); using the relationship between addition and subtraction (if you know 8+4=12 then you know 12-8=4) and creating equivalent but easier or known sums (6+7 by creating the known equivalent 6+6+1=12+1, OR 13). •Demonstrate fluency in using the following U.S. Algorithms: 1-digit Addition & Subtraction using horizontal and vertical notation 2-digit Addition & Subtraction without regrouping •Estimate objects up to 100. •Estimate sums and differences with numbers < 20. •Recognize when an estimation is or is not a reasonable answer. Grade 2: •Use various strategies to develop fluency such as: fact families, doubles, doubles + 1, doubles + 2, doubles - 1, doubles - 2, etc. •Solve addition and subtraction combinations through 20. •Add and subtract single and double digit numbers with and without regrouping using both vertical and horizontal notation. •Add and subtract 3- and 4-digit numbers without regrouping using both vertical and horizontal notation. •Use the dollar sign and decimal point OR cents sign when adding and subtracting. •Demonstrate fluency in using the U.S. Algorithm: 2-digit Addition & Subtraction with regrouping 3-digit and 4-digit Addition & Subtraction without regrouping Multiplication equations using factors from 0 through 5 •Estimate values, sums, and differences of quantities and determine the reasonableness of those estimates. •Introduce rounding 2-digit numbers to the nearest ten. •Use manipulatives and write corresponding multiplication equations as repeated addition. Grade 3: •Use concrete models and examples to solve x and ÷ equations (arrays, cups, cubes, etc.). •Solve problems involving multiplication through the nines tables through 9 x 5. (M3.A.3.1.2) •Solve multiplication and division equations with products and dividends to 100. •Solve problems involving multiplication facts through 9 x 5. •Solve single-and double-digit addition and subtraction problems with and without regrouping in vertical and horizontal form. (M3.A.3.1.1) •Solve triple-digit addition and subtraction problems without regrouping in vertical and horizontal form. (M3.A.3.1.3) •Solve addition and subtraction problems involving money or decimals through tenths. •Demonstrate fluency in using the following U.S. Algorithms: 3-digit and 4-digit Addition & Subtraction with regrouping 2-digit x 1-digit Multiplication with and without regrouping •Estimate sums and differences of quantities; round 2-digit numbers to the nearest ten, and 3-digit numbers to the nearest hundred; before computing (limit to 2 numbers). (M3.A.3.2.1) Grade 4: •Solve problems involving multiplication facts through 12 x 12. •Solve problems involving division facts through 9 x 9. •Solve addition or subtraction problems involving decimals through hundredths (decimal numbers must have the same number of places). (M4.A.3.2.1) •Solve addition or subtraction problems with fractions with like denominators (denominators to 10-no simplifying necessary). (M4.A.3.2.2) •Demonstrate fluency in using the following U.S. algorithms: 2-, 3-, & 4-digit x 1-digit Multiplication with regrouping 2-digit x 2-digit Multiplication with regrouping 2-digit & 3-digit x 1-digit Division Addition & Subtraction of decimals (through hundredths) Multiply & Divide decimals by 1-digit whole number (through hundredths) Addition & Subtraction of fractions (with like denominators of 10 or less) •Round whole numbers to the nearest ten, hundred, thousand, ten-thousand, or hundredthousand. (M4.A.3.1.1) •Round amounts of money to the nearest dollar. (M4.A.3.1.2) •Estimate the answer to addition, subtraction, and multiplication problems using whole numbers through six digits (for multiplication, no more than 2 digits times 1 digit excluding powers of 10). (M4.A.3.1.3) Grade 5: •Solve problems involving +, -, x, ÷ of whole numbers (multipliers up to 2 digits, divisors or one digit) and decimals including money (answers through hundredths; no divisors with decimals). (M5.A.2.1.1) •Solve problems involving + and – of fractions through sixteenths for like and unlike denominators – for unlike denominators, the LCD must be one of the given denominators). (M5.A.2.1.2) •Use +, -, x, ÷ to compute without a calculator (multipliers up to 2-digits, 1-digit divisors or multiples of10; whole numbers through thousands and decimals through hundredths; no divisors with decimals). (M5.3.2.1) •Use mental math to complete +.-, x, ÷ of whole numbers, benchmark decimals to hundredths, fractions (1/2, ¼, 1/10, ⅕). •Demonstrate fluency in using the following U.S. Algorithms: 3-Digit and 4-Digit Multiplication (Whole Numbers) 4-Digit by 1-Digit Division (Whole Numbers) 4-Digit by 2-Digit Division (using multiples of 10) Addition and Subtraction of fractions through sixteenths (like or unlike denominators, LCD is one denominator) •Use the mathematical terms: addend, sum, factor, product, difference, remainder, divisor, dividend and quotient when performing the operation. •Represent and interpret the remainder as a whole number remainder, a fraction. •Use models to demonstrate x of fractions using denominators up to 12. •Use estimation to solve problems involving whole numbers and/or decimals (up to 2digit multipliers, 1-digit divisors or multiples of 10; whole numbers through thousands and decimals through hundredths; no divisors with decimals). (M5.A.3.1.2) •Round whole numbers through millions and decimals through hundredths. (M5.A.3.1.1)