* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WORK: Work is done when the force produces motion. Def: WORK is
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
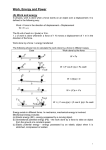
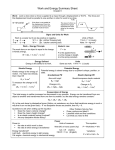
WORK: Work is done when the force produces motion. Def: WORK is said to be done only when a constant force Acting on the body produces a displacement in the body in the same direction as the force applied. Work is a scalar quantity, Work done = Force x Displacement. UNITS OF WORK: W=Fxs S I Unit is JOULE (J) =1 Nm and CGS UNIT: erg, 1 erg = 1 dyne. 1cm The name joule is given in honour of the British scientist James Prescott joule WORK done is said to be 1 joule only when a force of 1 Newton displaces a body by 1metre in the direction of force applied. WORK done is said to be 1 erg only when a force of 1 dyne displaces a body by 1centimetre in the direction of force applied. 1 joule = 107 ergs Some other larger units of work: (1) 1 killojoule = 1000 joule =103 joule (2) 1 megajoule = 1000 killojoule = 106 joule (3) 1gigajoule = 1000 magajoule = 109 joule Work done when the force is applied at an angle with the horizontal line of displacement. Applied force 𝛉 θ W=horizontal component of force x displacement W= f cosθ x s = f.s.cosθ Where θ is the angle between the direction of motion and direction of the applied force There are 4 cases 1)when the displacement of a body is in the direction of the force applied: W=fscosθ = f.s cos 0° W = f.s as cos 0° =1 Here work done is positive For eg: work done by collie when he is lifting a heavy box on his head, winning team of tug off war, kick the football, 2) when the displacement of a body is perpendicular to the direction of the force applied: W=fscosθ = f.s cos 90° W=0 as cos 90° =0 Here work done is zero For eg: when a stone attached to a rope is rotated in the horizontal circular direction, a man walking on a road with some weight on his head, suitcase in his hand, work done by earth on the moving satellites in circular path around the earth, 3) when the displacement of a body is in the direction opposite to the force applied: W=fscosθ = f.s cos180° W = −f.s as cos 180° =−1 Here work done is negative Horizontal component of force For eg:in tug off war work done by losing team,when the object lifted upward then the work done by gravity,work done by the frictional force, 4) when the displacement of a body is zero even when the force applied: W=fscosθ = f.0. cos θ° W = 0 as S =0 Here work done is zero For eg. Try to Push the wall, Work done is a scalar quantity even though we can measure it as positive ‘negative or zero II)) Work done against gravity:(thrown or lifted upward) When the work is done against the gravity ,The amount of work done is always equal to the product of weight of a body and vertical distance through which the body is lifted. Work done in lifting body=weight of a body x vertical distance(height) W= m.g.h as weight of a body = m.g For eg. The stone thrown upward, climbing of steps(staircase),lifting an object ENERGY : Anything which is able to do work is said to possess energy. Def; The energy is the ability to do work./capacity to do work. The amount of energy possessed by the body is equal to the amount of work it can do when its energy is released. The process of doing work: A body that possesses energy can exert a force on an object. In this process some of the energy of the body is transferred to the object, By gaining this energy the object moves. Energy is a scalar quantity. Unit of energy; S I Unit is JOULE (J) CGS UNIT: erg The other units of energy are watt hour and kilowatt hour 1 watt hour = 3600 J 1 kilowatt hour = 3.6 × 106 J The electrical energy is measured in Unit(electrical bill 250 units) and 1unit=1kilowatt hour. Heat energy is measured in calories 1 calrolie = 4.18 J 1kilocalorie = 4.18 ×103 J A very small unit of energy is electron volt 1eV = 1.6 ×10−19 J FORMS OF ENERGY: 1)Heat energy;(Thermal energy):the energy possessed by the body due to its temperature. when we burn coal, wood or gas, heat energy is released ,steam also possess heat energy, sun also radiates heat energy. Light energy: it gives us the sensation of vision, an electrical bulb emits light, natural source is sun. Sound energy; The energy of the vibrating body producing sound. Eg .flute, sitar, whistle, tuning fork Chemical energy: the energy released in chemical reactions .the energy possessed by fuels (petrol, diesel, gas), food Electrical energy:the energy of moving electrons in a conductor(charged body ,electrical cell) Nuclear energy: The energy released when two nuclei of light elements combine to each other to form a heavy nucleus (called as nuclear fusion)or when the heavy nucleus breaks into two light nuclei .( called as nuclear fission) Solar energy: The energy radiated from the sun . Magnetic energy:When the current is passed through the coil it stores magnetic energy. Mechanical energy: The energy possessed by the body due to its rest, state of motion or configuration.It is the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy. Kinetic energy: The energy possessed by the body by virtue of its motion is called kinetic energy. For eg. A moving car, flowing water, wind, moving ball Consider the body of mass m is at rest.let the force f be applied on it so that it attains the velocity v and travels a distance s Work done w= F.s W = ma.s as f=ma But using equation of motion we can write , 2as = 𝑣 2 − 𝑢2 2 𝑣 – 0 =2as 𝑣2 ∴ W= m. a. 1 𝑣2 2𝑎 2 S = 2𝑎 W=2 𝑚𝑣 This work done is equal to the kinetic energy. 1 K.E. = 2 𝑚 𝑣 2 The amount of KE of a moving body depends on: 1)Mass of body (kg) 2) Velocity (m/s ) Work done by a body when the body is changing its velocity form u to v,then 1 1 W = 2 𝑚 𝑣 2− 2 𝑚 𝑢2 Total work done is the change in kinetic energy of the body. When either mass or velocity of moving body is increased, KE will also increase. The KE of gas increases with increase in temperature as speed of gas molecules increases with the increase in its temperature. And vice versa. Potential Energy: The energy possessed by the body by virtue of its position/configuration is called potential energy. For eg:1) water stored in a dam, a stone lying at the top of hill, mountain has PE due to its position. A stretched or compressed spring, a wound spring of a watch, a stretched bow and arrow has PE due to its shape Gravitational PE: When the body is lifted from the ground to certain height then the work is done against the force of gravity,then the amount of work done is stored in the form of gravitational PE . Gravitational PE depends on the difference in vertical heights from initial and final position of a body but independent of the path followed by the body from initial and final position. Let the object of mass m is raised at height h Against the force of gravity g ,then the force acting on the body is F=mg A A ∴Work done = force × Displacement W = f.h A1 A2 W= mgh that is . EP = PE= mgh B B Transformation of energy: In the hydroelectric plants the PE of the stored water in the dam (reservoir) gets converted into the KE of the falling water at the bottom of the dam KE is transformed to the KE of the blades of the turbine this KE gets converted to the electrical energy. Transformation of energy in nature: The sun is the ultimate source of all types of energy. Plants absorb solar energy and undergo the process of photosynthesis chemical energy of the food gets converted into the muscular energy stored in man and animals which can be used for work done by them. Examples of energy changes Mechanical energy Heat energy Light energy Human activities /gadget Generation of electricity by dynamo Production of sound by vibrations Rubbing two pieces of stone to generate fire Steam engine Solar cell Preparation of chemical compounds by heat Photoelectric cell Decomposition of silver salts in the photographic plate Photosynthesis Transformation of energy Mechanical energy to electrical energy Mechanical energy to sound energy Mechanical energy to heat energy Heat energy to Mechanical energy heat energy to electrical energy heat energy to chemical energy Light energy to electrical energy Light energy to chemical energy Light energy to chemical energy of food