* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
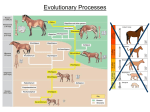
Evolution Natural Selection Microevolution Macroevolution Is evolution really taking place? Hardy – Weinberg Equilibrium 1. Large population 2. Random mating 3. No mutations 4. No migration 5. No natural selection If these conditions are true than there is NO Evolution. NO change in gene frequency from generation to generation. To prove this they developed the: Hardy-Weinberg Equation p+q=1 p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 Where p = Dominant Allele and q = Recessive Allele By knowing the number of Dominant and Recessive alleles of a gene in the population you can predict the phenotype of the members of the population and visa versa. If the conditions of the Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium are maintained then the population should remain constant generation after generation. Natural selection The natural process that results in the adaptation of a population to the living and nonliving factor in a region. Darwin believed this was the mechanism for all of evolution. Steps of natural selection: Over production Competition Variation Adaption Speciation Darwin didn’t understand the genetic component behind this process. Microevolution • Evolution that occurs on the population and species level • Caused by: » » » » » Gene Mutations Genetic Drift Founder Effect Bottleneck Effect Non-random Mating Microevolution Gene mutation • Directional Selection • Stabilizing Selection • Disruptive Selection What defines a species? Two organisms that can reproduce in nature and produce offspring that are fertile and can reproduce are the same species. Gene Mutation A sudden change in the genetic sequence of an organism Point mutation: Where a single nitrogenous base in a gene is altered effecting one amino acid the protein. Example: sickle cell anemia is only one base different than normal hemoglobin Frames Shift mutation: Deletion of a base which causes a change in the overall sequence of amino acids in a protein Genetic Drift New population is started with just a few members of original population so the gene pool is limited. The only variations that show up in future generations are those found on those limited number of genes. Original Population Migration New Population Offspring Genetic Drift - Bottleneck Effect A barrier, over hunting or habitat loss prevents the interaction of a new populations with the original population limiting genetic diversity. MacroEvolution • Evolution that occurs on the community level effecting many different species. • • • • Prezygotic – Before a zygote forms Postzygotic – After the zygote forms Allopatric Speciation – “ Other Country” Sympatric Speciation – “ Same Country” Prezygotic – Factors that prevent an organism from mating and having offspring. These can include habitat isolation, temporal isolation, mechanical isolation and behavioral isolation Postzygotic – Mating takes place and a zygote is formed but it doesn’t produce any new offspring. This can include zygote mortality, hybrid sterility Allopatric - Part of a population is separated from the original population and geographically isolated from it leading to reproductive isolation. Variations occur due to genetic drift and mutations with each population Synpatric – Groups within a population become reproductively isolation from each other. This can be the result of mating behaviors, habitat and food preferences. Changes occur due to genetic drift and natural selection. Adaptive Radiation When new organisms comes into to a region where there are many unoccupied niche the organisms will spread out and find a niche that offers the least competition with its neighbors. Over time the population will adapt to that niche and only interact with similar members of the population occupying that niche.