* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Surface (topology) wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terms of location wikipedia , lookup
Conic section wikipedia , lookup
Plane of rotation wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Projective plane wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
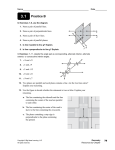
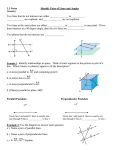
Name ______________________ Date _______ Block______ Example/Diagram Conclusion B A ∠ABC = ∠B = ∠1 1 Two rays: BA and BC C Vertex is point B Geometry Terms: Angle: 2 rays with a common endpoint Bisect: to divide into two equal parts A B Coplanar: points/ lines that are in the same plane € = BC AB C D A Collinear: points that lie on the same line € ∠ABD = ∠DBC C € B • A Pt A and pt B are on the same line. • B € A l Line l and line m are co-planar. They are both in plane A. m Corollary: a statement that follows directly from a theorem EX: The acute angles of a right triangle are complimentary. Mention only .. . . . . Intersect: to meet or cross; the set of points figures have in common T Line: a series of points extending in both directions ; has no thickness Line Segment: part of a line with definite endpoints. The two lines cross at point X They have point X in common. N X P Since sum of angles = 180 and 180 -90 =90, The sum of the acute angles must be 90. R Line MN is represented M A as N B € MN Segment AB is represented by € AB Ordered Pair: (x,y) used to locate points y 3 1 x The point is (3,1). Over to the right 3 and up 1. Parallel: do not intersect l Plane: a flat surface that extends in all directs – has no thickness O Point: a definite location in space; has no size (•A) A m The box represents a plane called O. The walls the floor and the ceiling all represent planes. Point B is in plane A B Postulate: accepted statement of fact; relationship between terms Ray: has one endpoint and continues in one direction; part of a line. Skew: neither parallel nor intersecting; not in the same plane Space: set of all points Theorem: a conjecture or conclusion that has been, or can be proven Lines l and m are parallel: l // m • EX: Through any two points, there is exactly one line. A We know it to be true because we cannot prove it untrue. B B Ray AB = AB C A D AB is skew to DH F G H Boundless and three dimensional so cannot€be drawn. 1 2 € Will contain points, lines, and angles. Example: Two parallel lines cut by a transversal form alternate interior congruent angles ∠1 ≅ ∠2 On A Separate Piece of Paper: Draw a coordinate plane and label the x and y axes, origin, and quadrants. Describe how to plot a point on a coordinate plane, for example (5,-2) Y II I (-,+) (+ , + ) Origin (0,0) X 1 23 4 5 2 •(5,-2) 4 III (-,-) IV (+,-) Go over from the origin 5 places to the right. Then go down two spaces. Geometry Terms: Angle: Bisect: Collinear: Coplanar: Corollary: Intersect: Line: Line Segment: Ordered Pair: Parallel: Name ______________________ Date _______ Block______ Example/Diagram Conclusion Plane: Point: Postulate: Ray:. Skew: Space: Theorem: On A Separate Piece of Paper: Draw a coordinate plane and label the x and y axes, origin, and quadrants. Describe how to plot a point on a coordinate plane, for example (5,-2)