* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name:
History of Eastern Christianity wikipedia , lookup
History of the Eastern Orthodox Church wikipedia , lookup
History of the Byzantine Empire wikipedia , lookup
History of Eastern Orthodox theology wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Angelos dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Heraclian dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine art wikipedia , lookup
Decline of the Byzantine Empire wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine music wikipedia , lookup
East–West Schism wikipedia , lookup
Monothelitism wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine economy wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Papacy wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Isaurian dynasty wikipedia , lookup
History of the East–West Schism wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine flags and insignia wikipedia , lookup
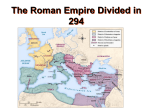
Name: Date: Period: Topic: The Byzantine Empire: Constantinople and Justinian I (Pages 61-63) (313 CE, 330 CE, Byzantium, Constantinople, Emperor, legalized, Rome, western) Section 6.1 (pg 61) and Constantine was the Roman ___________ who ___________ Christianity in the section 3.2 (pg 32) Who was Constantine? year ________. Christianity became the official religion of the Roman Empire What two important things after his death in 395 CE. In ________ he moved the capital of the Empire from did he do? ___________ to the city of ________________. _____________ later came to be known as _____________________. This shift strengthened the eastern half of the empire and weakened the _____________________. Section 6.2 Why was Constantinople ideally located to be the capital of the Byzantine Empire? What were some of Constantinople’s main features? (bread, chain, chariot, crossroads, defend, east, Greek, harbor, orphanages, poverty, public works, sea, sewer system, three, trade, wall, water, watch towers) Constantinople was easy to ________ and it lay at the _________of many ______ and overland ___________ routes linking ________ and west. Constantinople was surrounded by ________on _______sides and fortified by miles of ________with ____________ and gates. A large ________ protected the mouth of its harbor. The city had a ________________, hospitals, homes for the elderly, and ___________. What was daily life like in Constantinople? Life in Constantinople was more advanced than in western Europe. The city’s language was ___________, but traders and visitors spoke many languages. Most people lived in ____________. Many people attended ________ races. The emperor gave _________to the unemployed, who did ___________ in exchange. Section 6.3 What event forced Justinian to rebuild parts of Constantinople? (City, Hagias Sophia, Hippodrome, hospitals, property, public baths, rioting, roads, women) Large parts of the___________ were ruined when fighting in the ______________ spilled into the streets and escalated into a ____________. What were some of the improvements made to Constantinople as a result of Justinian’s public works projects? New bridges, ____________, parks,_____________, and ____________ were built. In addition, the ________________, a grand cathedral, was built. How has Justinian’s Code Justinian’s Code is the basis for many ____________ in the western world, and affected the modern was one of the first to extend_____________ rights to _________________. world? Summary: Describe Constantinople. What was good about it? What problems did it have? and how did Emperor Justinian I deal with those problems? ____________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Name: Date: Period: Topic: The Byzantine Empire: The Eastern Orthodox Church and the Great Schism (Pages 64-67) (church, emperor ,government, head, Monasteries, poor, represent, sick) Section 6.4 What was the relationship between religion and government in the Byzantine Empire? Religion and _______________were closely linked. The __________was believed to be both the __________of the government and the ________________ Jesus Christ on Earth. How did the Eastern Orthodox Church play a central role in the daily life of Byzantines? Most people attended ___________ regularly and received sacraments at every stage of their lives. _____________________and convents, homes for monks and nuns, cared for the __________ and __________. Section 6.5 (800 CE, 1054 CE , Eastern Orthodox Church, Charlamegne, excommunicated, icons, Leo III, patriarch, prayer, Roman Catholic Church, schism, western worshiping) ____________ are religious art used in religious services and ___________ Emperor __________believed that people were wrongly ________________ the icons themselves. Leo II ordered icons to be destroyed. Pope Gregory III ____________ the emperor (kicked him out of the church). Why did Byzantine emperor Leo III forbid the use of icons in 730? How did the pope react to Leo’s order? What event in 800 increased tensions between the east and west? In __________, Pope Leo crowned ________________, the king of the Franks, as Holy Roman emperor. This outraged the Byzantines, who felt they were the rightful rulers of the Roman Empire. How did the relationship between the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Roman Catholic Church change in 1054? In _________, the _________ of Constantinople closed down churches that worshiped in the _______________ style. In response, the Pope excommunicated the Patriarch. This created a permanent _____________ a schism, or formal division, resulted in the ____________________________ and the ______________________________ becoming two separate Christian churches. Summary: Describe the Eastern Orthodox Church and the reasons it split from the Roman Catholic Church. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________