* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Grid energy storage wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
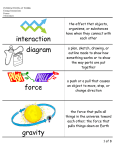
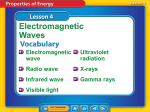
7.P.2.1 (Energy) C.Notes What is energy Ability to cause change Types of energy Mechanical energy – ability to do work (sum of potential & kinetic energy) Form of energy involved in the operation of simple machines Potential energy – stored energy in an object due to its position (energy at rest) Kinetic energy – energy in motion Amount of kinetic energy depends on mass & speed Electrical energy - energy carried by electric current Natural forms (green energy): lightning, solar energy, water power, wind power o Doesn’t create extra pollutants Geothermal energy – form of heat energy generated inside Earth Hydroelectric energy – potential energy of water transformed into electrical energy Energy is created by dams Chemical energy – energy stored in chemical bonds between atoms Food you eat has stored chemical energy Light energy – energy carried by light and other kinds of electromagnetic waves Can be absorbed, reflected or transmitted Thermal energy – energy that comes from heat Warmer substance is , more thermal energy Can be transferred by conduction, convection & radiation Solar energy – limitless energy source from the sun Sound energy - energy made by vibrations that travel in waves Energy transfers from one system to another Thermally – warm object & cool object Ice cube melting Mechanically – push or pull over distance Electrically – when an electrical source such as a battery or generator is connected in a complete circuit to an electrical device Electromagnetic waves – caused by the vibration of an electric charge Waves seen after an explosion **when energy transfers from one system to another, HEAT is ALWAYS involved** Batteries – store energy and transfer energy to components in a circuit Energy comes from chemical reactions Electricity – important because it is used for so many things To produce electricity, a heat source is ALWAYS required o Methods to produce electricity: burning of fossil fuels, water power, wind power Mechanical energy Potential (PE) vs. Kinetic Energy (KE) 7.P.2.1 (Energy) C.Notes Objects with mechanical energy are able to do work Energy involved with operation of simple machines Potential Energy Energy at rest Doesn’t use energy until it moves Kinetic Energy Energy in motion Conservation of Energy Energy cannot be created nor destroyed Energy only changes forms Different forms of energy Motion & heat Different ways for energy to travel Light, sound, electricity Circuit Definition - The complete path around which electric current flows Require a complete loop through which an electrical current can pass Example: Charging your cell phone needs a complete loop or cell phone doesn’t charge Types of circuits Series circuit - electrical circuit in which the electricity flows in one path If there is a break in the path of electricity the entire circuit will not work 7.P.2.1 (Energy) C.Notes Parallel circuit - electrical circuit in which the electricity flows in more than one direction A break in one branch will not affect the other branches or appliances Describe mechanical energy Kinetic vs. potential energy transfer (explain, illustrate (video) Various forms of energy Ways energy travels Cosmos video Energy Circuits/batteries 7.P.2.1 (Energy) C.Notes