* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Unit 1 The Agricultural Transition and Early Complex Societies
Survey
Document related concepts
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Romania wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Protestantism and Islam wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
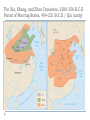
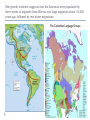
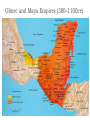
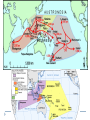
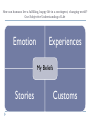
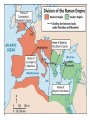
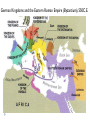
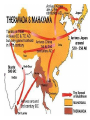
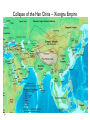
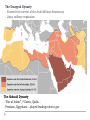
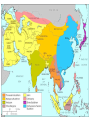
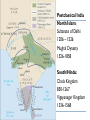
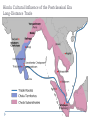
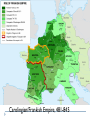
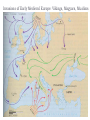
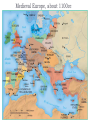
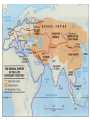
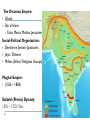
AP Unit 1 The Agricultural Transition and Early Complex Societies Reese Mesopotamia Cuneiform Ziggurat at UR Bantu Migrations, 2000B.C.E. Harappa, 2000 B.C.E “The fourfold divisions of castes was created by me according to the appointment of qualities and duties… distinguished according to the qualities born of nature… Performing the duty prescribed by nature… one should not abandon a natural duty though tainted with evil” – The Bhagavad Gita The Xia, Shang, and Zhou Dynasties, 2200-256 B.C.E Period of Warring States, 404-221 B.C.E / Qin (unity) New genetic evidence suggests that the Americas were populated by three waves of migrants from Siberia: one large migration about 15,000 years ago, followed by two lesser migrations. Pre-Columbian Language Groups Olmec and Maya Empires (300–1100ce) Olmecs, 1200-100B.C.E. Teosinte to Maize San Lorenzo Head, 900B.C.E Jade Knife Teotihuacan, 200 B.C.E. – 750C.E. The City of the Gods Mayan Empire, 300 – 1100 C.E. Tikal Kukulacan at Chichen Itza Mayan Alphabet Mayan Calendar “Birth is misery; old age is misery; disease is misery; death is misery; sorrow… grief… to wish for what one cannot have is misery… This , O Priests, is called the noble truth of misery… The Ear, the nose, the tongue, the body… the mind is delightful and agreeable to men; there desire springs up and grows, there it settles and takes root.” - the Four Noble Truths “Every man intent on his own respective duties obtains perfection. Listen, now, how one intent on one’s on duty obtains perfection. Worshiping, by the performance of his own duty, him from whom all thins proceed, and by whom all this is permeated, a man obtains perfection… One who is self-restrained, whose understanding is unattached” – The Bhagavad Gita Plato’s Allegory of the Cave How can humans live a fulfilling, happy life in a contingent, changing world? Our Subjective Understanding of Life Emotion Experiences My Beliefs Stories Customs Which world proves you meaning? My World Subjective Emotional Personal Belief Myth Why? The World Objective Logical Universal Fact Science How? German Kingdoms and the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantium), 550C.E. The Silk Roads, 200 BCE – 300CE Collapse of the Han China – Xiongnu Empire "All praise is due to Allah, so we praise Him, and seek His pardon and we turn to Him. We seek refuge with Allah from the evils of ourselves and from the evil consequences of our deeds…His is the sovereignty and to Him is due all praise. He grants life and causes death and is Powerful over everything. There is no God but Allah” - The Sermon of The Holy Prophet (Muhammad) on His Final Pilgrimage to Ka'aba Teachings of Islam: Umma The Five Pillars (Hajj) “Seal of the Prophets” Caliph - Sunni and Shi’a Jihad: To Struggle - Internal struggle of faith - “Just moral-social order” - struggle to defend Islam Qur'an and Shari’a Law (Rituals, Morals, Social Conduct) Islamic Institutions: Hadith Madrasas Ulama and Qadis Expansion: Sufi Missionaries Merchants Camels/Empires Compass, Lateen Sails… “You know that every Muslim is the brother of another Muslim.You are all equal… I leave behind me two things, the Qur'an and my example, the Sunnah and if you follow these you will never go astray.” The Umayyad Dynasty - Favored the interest of the Arab Military Aristocracy - Jizya; military expansion The Abbasid Dynasty - “Dar al Islam” / Ulama, Qadis… - Persians, Egyptians… played leading roles in gov Postclassical India North/Islam: Sultanate of Delhi 1206 – 1526 Mughal Dynasty 1526-1858 South/Hindu: Chola Kingdom 850-1267 Vigayanagar Kingdom 1336-1568 Hindu Cultural Influence of the Postclassical Era Long-Distance Trade Khmer Empire/ Kingdom of Angkor, 802-1431 Angkor Wat-”Temple City” to Vishnu Carolingian/Frankish Empire, 481-845 Fealty,(allegiance) Homage (submission), Fiefs (land) -The Nobility, Clergy and the bonds of the Peasantry Invasions of Early Medieval Europe: Vikings, Magyars, Muslims Medieval Europe, about 1100ce Classical and Postclassical Nomadic Invasions: Europe: Huns, Franks,Vandals… (450-850) Vikings, Muslims, Magyars (793-1066*) Ottoman Turks: Collapse of Byzantium (1453) Southwest Asia: Ottoman Empire (1443 -1919) Safavid (Persia) Dynasty (1501 – 1722) South Asia: Turks – Sultanate of Delhi (1206 – 1526) Mughal Dynasty (1526 – 1858) East Asia: Xiongnu – Han Collapse (220) Mongols – Yuan Dynasty (1279 – 1368) The Ottoman Empire: Ghazis Dar al Islam: - Cairo, Mecca, Medina, Jerusalem Social-Political Organization: Devshirme System/ Janissaries Jizya / Dhimmi Millets (Ethnic/ Religious Groups) Mughal Empire: (1526 – 1858) Safavid (Persia) Dynasty 1501 – 1722/ Shia Mansa Musa/ Mali Empire Trans-Saharan Trade Routes Gold Mines The Summa Theologica,Thomas Aquinas The Existence of God can be proved in five ways. The first and more manifest way is the argument from motion. It is certain, and evident to ours senses, that in the world some things are in motion. Now whatever is moved is moved by another… Therefore, whatever is moved must be moved by another… it is necessary to arrive at a first mover, moved by no other; and this everyone understands to be God. The second way is from the nature of efficient cause. In the world of sensible things we find there is an order of efficient causes. There is no case known (neither is it, indeed, possible) in which a thing is found to be the efficient cause of its self; for so it would be prior to itself, which is impossible. The third way is taken from possibility and necessity , and runs thus. We find in nature things that are possible to be and not to be… Therefore, if at one time nothing was in existence, it would have been impossible for anything to have begun to exist; and thus even now nothing would be in existence – which is absurd. The fourth way is taken from the gradation to be found in things. Among beings there are some more and some less good, true, noble, and the like. But more and less are predicated of different things according as they resemble in their different ways something which is the maximum,… Therefore there must also be something which is to all beings the cause of their being, goodness, and every other perfection; and this we call God. Great Chain of Being