* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine Lesson 2 Monday, March 12
Bovine somatotropin wikipedia , lookup
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
Norepinephrine wikipedia , lookup
Progesterone wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
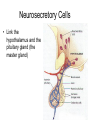
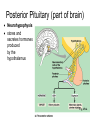
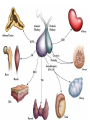
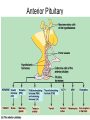
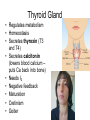
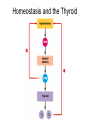
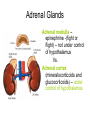
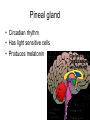
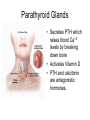
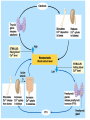
Endocrine Lesson 2 Monday, March 12 AIM: Where are hormones synthesized, and what is their effect? DO NOW: What is the difference between a steroid and a peptide hormone? HW: Memorize hormones/finish flash cards Multiple choice packet on hormones (Ch. 45) Neurosecretory Cells • Link the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland (the master gland) Hypothalamus • integrates endocrine and nervous function. • Produces releasing hormones (or inhibitory hormones) that act on anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) • Produces hormones ADH and oxytocin that are stored in the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) BE CAREFUL! • The hypothalamus produces releasing hormones that stimulate the anterior pituitary to produce stimulating hormones. • DO NOT CONFUSE OR EQUATE RELEASING HORMONES WITH STIMULATING HORMONES. Posterior Pituitary (part of brain) Neurohypophysis stores and secretes hormones produced by the hypothalamus Fig. 45.6a Anterior Pituitary GH • • • • • Growth hormone Gigantism Acromegaly Dwarfism Genetic engineering Prolactin • Peptide hormone • Milk production FSH, LH • Follicle stimulating hormone • Luteinizing hormone • Have effects on testes (testosterone) and ovaries (estrogen and progesterone) Female Hormones • Estrogen and progesterone -- produced in the ovary • Progesterone = the pregnancy hormone • Estrogen secondary sex characteristics • Both are involved in the menstrual cycle Male Hormones (Androgens) • Testosterone • Spermatogenesis • Secondary sex characteristics Thyroid Gland • Regulates metabolism • Homeostasis • Secretes thyroxin (T3 and T4) • Secretes calcitonin (lowers blood calcium – puts Ca back into bone) • Needs I2 • Negative feedback • Maturation • Cretinism • Goiter Homeostasis and the Thyroid Adrenal Glands Adrenal medulla – epinephrine -(fight or flight) – not under control of hypothalamus Vs. Adrenal cortex (mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids) – under control of hypothalamus Adrenal Medulla • Catecholamines – Adrenalin (epinephrine), norepinephrine • Amines • Fright, flight, fight hormones Adrenal Cortex • Target of ACTH from ant. pituitary • Steroid hormones • Glucocorticoids (cortisol) – increase blood sugar • Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) –increase reabsorption of sodium in CD and hence water— also increase bp via vasoconstriction Pineal gland • Circadian rhythm • Has light sensitive cells • Produces melatonin Endorphins • Natural opiates • euphoria Parathyroid Glands • Secretes PTH which raises blood Ca+2 levels by breaking down bone • Activates Vitamin D • PTH and calcitonin are antagonistic hormones.