* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quantum Reality
Quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Second quantization wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Quantum entanglement wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chaos wikipedia , lookup
Quantum potential wikipedia , lookup
Quantum tunnelling wikipedia , lookup
Wave packet wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantum gravity wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Supersymmetry wikipedia , lookup
Higgs mechanism wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Topological quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Technicolor (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chromodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
AdS/CFT correspondence wikipedia , lookup
Quantum logic wikipedia , lookup
Quantum gravity wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Uncertainty principle wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
An Exceptionally Simple Theory of Everything wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Relational approach to quantum physics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Theory of everything wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
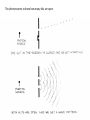
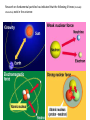
The Concepts of Quantum Reality Wave Complimentarity, Bosons, Fermions and Miscellaneous (50 slides) creatively compiled by dr. michael farnworth The purpose of this lesson is simply to make us more familiar with the concepts of Quantum theory. You don’t have to do anything with the information than just allowing it to register in the memory files of your mind. 1. The wave and particle compound of complimentarity The Dual Nature of Light • To understand the dual nature of light, the Complementarity Principle of Niels Bohr, illustrates that light has both properties (of wave and particle) but will exhibit which ever property the observer is testing/looking for. Janus is a good metaphor for the nature of light…It shows us what ever face we are looking for. Roman God Janus. He has two faces, looking in opposite directions. Roman God Janus The classic two slit experiment: • To illustrate the wave-particle duality of light an experiment was set up where photons were shot through a plate with two slits in it and on to a photo (light) sensitive screen. • If the photons were particles there would be patterns of random hits. • If the photons were waves there would be wave like patterns of interference on the screen. The photon seems to know how many slits are open. If the light source were particles they would leave a pattern similar to… Particle like patterns… If the light source were waves they would leave a pattern similar to… Wave like patterns… A Normal Wave… A wave energy Packet… For a demonstration of the particle-wave duality two split experiment click on the below: http://www.colorado.edu/physics/2000/schroedinger/two-slit2.html The reason this is important • It seems everything on the Quantum level of reality has this dual nature which lives in potentiality and is only brought into actuality when the quantum state collapses when it is observed or acted upon. • More about this later. 3. Fermions and Bosons… The ancients believed that the world was made up of basic materials or elements… like: Air Water Fire Earth We now know that the basic elements are much more elemental and sub-atomically small… Molecule Atom Proton Quark Now, at this point in time, we have labeled the smallest building components of reality as: fermions and bosons. fermions and bosons Fermions are Individuals A fermion is any particle that has an odd half-integer (like 1/2, 3/2, and so forth) spin. Quarks and leptons, as well as most composite particles, like protons and neutrons, are fermions. (For reasons we do not fully understand, a consequence of the odd halfinteger spin is that fermions obey the Pauli Exclusion Principle and therefore cannot co-exist in the same state at same location at the same time.) “Fermions are highly territorial individualists. If one fermion is in a particular quantum state, then all other fermions are excluded from that state, resulting in the Pauli exclusion principle. In a universe where electrons were bosons rather than fermions, no life would be there to worry about it. Bosonic electrons around atoms, instead of forming into "shells" providing the outer valence electrons that make chemistry work, would pile up together in the most tightly bound inner atomic orbit, making chemistry and also life impossible. We owe our very existence to the Fermi-Dirac statistics of electrons.” John G. Cramer Bosons are ‘groupies’… Bosons are those particles which have an integer spin (0, 1, 2...). All the force carrier particles are bosons. “Bosons are gregarious groupies. If one boson is in a particular quantum state, all other bosons are "invited in" to share the same state. The more bosons that pile into the state, the stronger becomes the tendency for others to join them. In such a state, a very large number of particle will have a single quantum wave function. This is what is called a Bose-Einstein condensate. It is a new state of matter because, although predicted, it has never before been observed in an atomic system.” John G. Cramer The Pauli Exclusion Principle • At one time, physicists thought that no two particles in the same quantum state could exist in the same place at the same time. This is called the Pauli Exclusion Principle, and it explains why there is chemistry. • But it has been since discovered that a certain group of particles do not obey this principle. Particles that do obey the Pauli Exclusion Principle are called fermions, and those that do not are called bosons. • Imagine there is a large family of identical fermion siblings spending the night at the Fermion Motel, and there is another large family of identical boson siblings spending the night at the Boson Inn. Fermions behave like squabbling siblings, and not only refuse to share a room but also insist on rooms as far as possible from each other. On the other hand, boson siblings prefer to share the same room. (Since fermions rent more rooms than bosons, motel owners prefer doing business with fermions. Some motels even refuse to rent rooms to bosons!) We have answered the questions, What is the world made of And What holds it together? The world is made of six quarks and six leptons (called fermions). Everything we see is a conglomeration of quarks and leptons. There are four fundamental forces and there are force carrier particles (called bosons) associated with each force. 3. Miscellaneous Concepts The Bose Einstein Condensate. These two men are the ones responsible for The creation of the Bose-Einstein Condensate. In the 1920s they collaborated in their work. Satyendra Nath Bose Albert Einstein Bose-Einstein Condensate… • In some special conditions boson atoms coalesce with other boson atoms to become identical with, and to them. • In other words they overlap, coalesce and absorb each other into one large quantum boson atom sharing the same qualities and nature. • The Bose-Einstein Condensate is created when the multiple atoms unify into one. A ‘visual’ of atoms coalescing… into In a Bose -Einstein Condensate the atoms join together and lose their individual particle like characteristics and become wave like. Another way to picture the dynamics of Bose-Einstein condensates… • Another way to picture the dynamics of the atoms in a BoseEinstein Condensate is vibrationally. • Tuning forks, singing voices, sounds that are oscillating at the same frequency and becoming one and the same wave length. The brain as a Bose-Einstein Condensate: • Danah Zohar and Ian Marshall in their book Spiritual Intelligence suggest that consciousness may be the product of the coherent alignment and oscillations of electrons in proteins in the neurons’ membranes or of electrons in the water of the neurons. • These neurons are so overlapped and coalesced that they become one big quantum molecule and this is the basis for the unitary consciousness and sense of self. Brain Waves • We all are probably familiar with brain waves. • The brain wave oscillations change according to the different mental activities that are going on: • Gamma, Beta, Alpha, Theta or Delta. • What if the brain/spirit were a Bose-Einstein condensate? • More about this later. The four forces of the universe. The four fundamental forces of the Universe are made of Bosons • 1. Gravitation • 2. Electromagnetism • 3. Strong nuclear forces • 4. Weak nuclear forces Research on fundamental particles has indicated that the following 4 forces (mutually interactive) exist in the universe: Superstring Theory The Superstring theory • Scientists are working to find a theory linking all of the 4 forces. • This theory postulates that the smallest piece of matter is not a fundamental particle, but rather an infinitesimally small, vibrating string. • The theory is gaining attention as a result of its ability to contribute to understanding mystifying phenomena such as the big bang and black holes. The Superstring Theory The superstring theory explains everything about space, matter and space-time and has been called the ultimate theory. It fulfills Einstein's dream of combining quantum mechanics and the general theory of relativity. The Superstring theory, first proposed in 1974 by John Schwarz, a Hungarianborn theoretical physicist from the California Institute of Technology, works using a principle measurement unit of strings that are 10 to the power of minus 33 cm in length. When the strings vibrate or are subjected to an enormous burst of energy they break and rejoin to create elementary particles. String Theory is the hope of making General Relativity consistent with Quantum Theory. This would be the theory that unifies our understanding of the world we have created via the two theories. Black Holes Black Holes • The general theory of relativity could be regarded as the law that confirms the development of time in bent three dimensional space. • But having bent space to a certain point it must inevitably reach a singular point (where time and space become indefinable). • This is known as the Penrose-Hawking singularity theorem. • It explains the destruction of space-time by gravity, and black holes are singular points enclosed by event horizon. continued… When objects are sucked into black holes, they continue falling for an unlimited period of space and time. At a central point, gravity becomes infinite, time and space are bent, and concepts of time and space, as we know them, become irrelevant. Such an occurrence happened when the Universe was formed, and this is also known as a singular point. Objects sucked into singular points disappear from our Universe without a trace. Can you ‘see’ the black hole? Even though Quantum Theory is difficult to understand it has the power to change how we see the world and the paradigms we choose to live in. The Newtonian paradigm is ego centric and strokes the ego with a cause and effect world that it can attempt to control. The Quantum paradigm is foreign and strange inviting the ego to surrender its assumptions from the Newtonian world and start reconstructing a world marinating in mystery and awe. It will take effort and work. "In light of knowledge attained, the happy achievement seems almost a matter of course, and any intelligent student can grasp it without too much trouble. But the years of anxious searching in the dark, with their intense longing, their alterations of confidence and exhaustion and the final emergence into the light, only those who have experienced it can understand it.” Albert Einstein the end