* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Mr. Buffa
Survey
Document related concepts
Acropolis of Athens wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek religion wikipedia , lookup
Spartan army wikipedia , lookup
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
List of oracular statements from Delphi wikipedia , lookup
Ionian Revolt wikipedia , lookup
Second Persian invasion of Greece wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Eurymedon wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Corinthian War wikipedia , lookup
Peloponnesian War wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
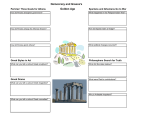
Group 1: Persian Wars 1. Map of Ancient Persian Empire 2. When did the Persian Wars begin & with who? a. 499 B.C. Ionian Greeks vs. Persia 3. Who was Darius I and how was he defeated by the Greeks in 490 B.C.E.? a. Persian ruler. Set out to punish Athens for defending Ionia. Caught off guard by relentless Athenian foot assault. 4. Who was Xerxes? Describe the legend of King Leonidas & the Spartan 300. How did the Greeks ultimately defeat the Persians? a. Son of Darius I. b. Agreed to help the Athenians & defended the passage of Thermopylae. Eventually defeated but held off Persians long enough for Athenians to evacuate & re-group. Greeks had built a fleet of warships in preparation that had battering rams underneath & destroyed the Persian fleet. This ultimately led to the defeat of the Persians in less than another year. Group 2: Pericles & Direct Democracy 1. Image of Pericles 2. Who was Pericles? a. Athenean ruler from 460 B.C.E. to 429 B.C.E. 3. How did Periclean Athens government look? How does it compare to the U.S. today? a. Direct democracy; U.S. indirect b. Council of 500; U.S. has legislature of 565 c. All citizens had right to serve in government; same in U.S. d. Paid salary to members of Assembly & Council; politicians in U.S. get salary e. Created a jury system that could include hundreds/thousands; U.S. jury only 12 for trials f. Could banish political figures; can impeach/remove from office in U.S. 4. How did culture thrive under Pericles? a. Encouraged arts, festivals, dramatic competitions, construction Group 3: Peloponnesian War 1. Map of Sparta & image of Spartan Warrior 2. What were the Delian & Peloponnesian Leagues? a. Delian = alliance of Greek nations for common defense b. Peloponnesian = Sparta & enemies of Athens 3. When did the Peloponnesian War begin & how long did it last? a. 431 B.C.E. & lasted 27 yrs 4. Why did Sparta have the geographic advantage during the war? a. Inland so Athens couldn’t use its’ mighty navy 5. What decision did Pericles make that helped lead to the fall of Athens? a. He let people outside the walls come in for protection. Overcrowding = plague 6. Who did Sparta ally with to help defeat Athens? a. Persia 7. When did Athens officially fall? a. 404 B.C.E. Group 4: Philosophers 1. Image of Socrates, Plato, & Aristotle. 2. What does “philosopher” & “logic” mean? a. Philosopher = lover of wisdom b. Logic = rational thinking 3. How did philosophers view the cause of events? a. Not by gods but by natural forces 4. Who was Socrates? a. Athenian stonemason & philosopher 5. What was the Socratic Method? a. Pose a series of questions & examine implications of responses he received 6. What was the purpose of the Socratic Method? a. Explore truth/self-knowledge 7. What happened to Socrates? a. 70 yrs old put on trial in front of 501 citizens & condemned to death. Forced to drink poison. 8. Who was Plato? a. Student of Socrates. 9. What was Plato’s vision of the ideal government? a. Government should regulate citizen’s lives to provide for their best interests b. 3 classes: workers to provide necessities, soldiers to defend, philosophers to rule c. Philosopher-king to have final authority 10. What was Plato’s view of women? a. Generally men better but that some women were better. Talented women should be educated/trained to serve in government 11. Who was Aristotle? a. Student of Plato 12. What form of government did Plato say was ideal? a. Rule by 1 virtuous leader 13. How did Aristotle’s teachings influence universities 1,500 years later? a. They derived many courses based on his teachings Group 5: Architecture, Art, & Literature 1. Image of the Parthenon & Greek Theatre Masks 2. What was the Parthenon designed as? a. Temple for goddess Athena 3. How has Greek architecture influenced architecture today? a. Have incorporated elements such as columns in designs today 4. How did Greek art change around 450 B.C.E.? a. Started painting natural/idealistic style – perfect human form 5. What did Greek drama develop from? a. Religious festivals dedicated to god of fertility & wine, Dionysus 6. What is a tragedy? a. Play telling of human suffering usually ending in disaster 7. What is a comedy? a. Play that mocked people/customs 8. How did comedies differ from tragedies? a. Focused more on individuals of the day 9. Who is the “Father of History”? Why is he given this title? a. Herodotus b. Began to collect information from people who were at events & recorded it.