* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the solar system
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Discovery of Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
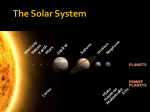
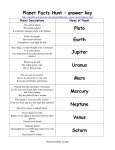
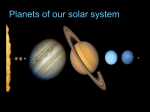
THE SOLAR SYSTEM Solar system – the sun, the planets, and many smaller objects that travel around the sun Planet- a body of matter that travels around a star in a path called an orbit I) Terrestrial planet- one of the highly dense planets (earth-like) nearest the sun A) Mercury- 1st planet (Roman god of speed) 1) Temperature range from -173 c to 427c (very hot and very cold) 2) Long day –(59 earth days) rotation 3) Short year- (88 earth days) revolution 4) 2nd smallest so very little atmosphere (small amount of gravity) 5) cant burn up meteors, so many craters B) Venus – 2nd planet (Roman goddess of beauty) 1) Carbon dioxide atmosphere causes major global warming (464 c) 2) Hottest planet 3) Atmosphere 90x greater than earth 4) Sulphuric acid clouds and rain 5) “twin planet” 6) retrograde (clockwise from north pole) rotation 7) spins SLOW so a day (243 days) is longer than a year (224 days) C) Earth- 3rd planet 1) 1 moon- LUNA 2) has atmosphere of nitrogen and oxygen 3) 75% water on surface 4) tectonic plate movement 5) 23.5* tilt of axis (allows for 4 seasons and plenty of food) 6) prograde rotation D) Mars- 4th planet (Roman god of war) 1) “Red” planet from iron oxide (rust) 2) polar ice caps of water and carbon dioxide 3) river channels (once flowing water?) 4) inactive volcanoes and rift valleys showing tectonic plate movement 5) Olympus Mons (largest volcano in solar system) 6) 70 degrees F at equator 7) axis wobbles (if in “warm cycle” of wobble, may melt ice caps) 8) plans to send humans in 2010 9) has 2 moons Phobos and Deimos II) Gaseous Giants—large low density planet composed mainly of gas A) Jupiter- 5th planet (Roman King of the gods) 1) Greatest volume (1 ½ times greater than others) 2) Greatest mass (2x greater than all others combined) 3) Made of helium and hydrogen [why not a star? Not big enough yet.. sun is 1000x bigger than jupiter] 4) 62 moons (a) Io-most volcanically active object in the solar system (b) Callisto- has water (c) Ganymede- largest moon in the solar system and has frozen water (d)Europa- has underground oceans (maybe life?) 5) Red spot-giant hurricane B) Saturn- 6th planet (Roman god of harvest) 1) 2nd largest, but least dense (would float in water) 2) 37 moons 3) Titan – largest moon (a) has atmosphere with nitrogen on it and maybe life? (b) Visited by Huygens probe (European) 4) Spectacular rings of dust and rock 5) Made of helium and hydrogen 6) giant lightning storms the size of the US C) Uranus- 7th planet (Roman father of the Titans) 1) Tilt of axis 98 degrees (“sideways” planet) 2) Rotates backwards (retrograde) 3) Methane gas gives it its blue/green color 4) 27 moons- none of interest D) Neptune-8th planet [since 1999 now the 8th again] (Roman god of sea) 1) Frozen methane gas gives it a whitish blue green color 2) System of faint rings 3) Great dark spot—massive tornado 4) Winds blow at 1200 mph, almost twice the speed of sound 5) 13 moons 6) Triton-largest moon (a) Nitrogen geisers and water/ammonia eruptions (b) Coldest body in the solar system III) Planetisimals or dwarf planets A) Pluto- 8th sometimes 9th planet [as of 1999 it is 8th] (Roman god of underworld) 1) Composed of rock and ice (frozen gas) 2) Charon – moon that is ½ size of the planet [largest ratio of moon to planet] 3) Very little atmosphere 4) Is it really a planet? (a) Used to be called a double planet (b) Ancient comet? [due to orbit path and composition] (c) Old moon of Neptune? IV) Other objects in the solar system A) Comets – large chunk of ice, dust, frozen gas, and rock moving through space (dirty snowball) 1) Nucleus—center of a comet 2) Coma—cloud of vaporized (turned to gas) ice that surrounds the nucleus 3) Tail—the coma of a comet that is being blown back by solar winds 4) Oort cloud—birthplace of comets found beyond Pluto (a) Objects are dislodged by the gravity of a planet passing by 5) Halley’s Comet—short period comet (has an orbit of less than 200 years) that returns every 76 years (2061) nucleus coma tail B) Asteroids—large rocks in space 1) Asteroid belt—zone between mars and Jupiter where most asteroids are found 2) Origin of asteroid belt (a) a planet formed and Jupiter pulled it apart (b) Jupiter’s gravity kept the pieces from forming in the first place (c) a planet formed but then a large object hit it and broke it into pieces C) meteoroids—small rocks in space 1) made of broken asteroids or 2) broken comets D) meteors—a meteoroid that has entered a planet’s atmosphere (making a streak of light) 1) friction with the atmosphere wears off tiny pieces of the meteor causing it to heat up, glow, and eventually disintegrate 2) most are sand-sized E) meteorite—a meteor that strikes a planet’s surface 1) the meteor is big enough to not completely disintegrate before making contact 2) baseball/softball sized *These are all the same rock but are renamed based on WHERE they are located