* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2·QUIZLET VOCABULARY: Quantum Numbers Study online at
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electron-beam lithography wikipedia , lookup
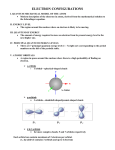
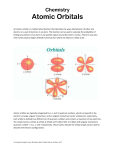
2·QUIZLET VOCABULARY: Quantum Numbers Study online at quizlet.com/_k43od 1. Angular Momentum Quantum Number: l Indicates sublevel that electron is in. s - shape: spherical max 2 e p -shape: dumbbell max 6 e d -shape: 4 leaf clover max 10 e f - shape: flower max 14 e 2. Aufbau principal: states that each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available 3. electron configuration: the arrangement of electrons around nucleus in an atom 4. Hunds rule: orbitals of equal energy are each occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by a second electron, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals must have the same spin 5. Magnetic (orbital) quantum Number: ml Indicates orientation of orbital in space S- 1 orbital P- 3 orbitals D- 5 orbitals F- 7 orbitals 6. orbital: A 3-D space around the nucleus where an electron is likely (high probability) to be found. 7. pauli exclusion principle: An atomic orbital may describe at most two electrons, each with opposite spin 8. Principle Quantum Number: n Indicates the energy level that electron is located in 9. valence electrons: Electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element's atoms; determines the chemical properties of an element. To find, look at group # for main group elements. Usually the only electrons involved in chemical reactions. 10. valence shell: Outermost energy level occupied by electrons of an atom.