* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HS 03 Geometry Overview (Prentice Hall)
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Conic section wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
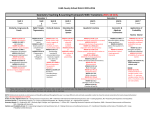
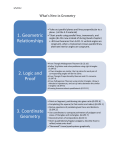
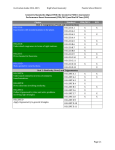
0 HS 03 Geometry Overview (Prentice Hall) Section 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 2.5 12.1 12.2 Topic Points, Lines, and Planes Segments, Rays, Parallel Lines and Planes Measuring Segments and Angles Basic Constructions Proving Angles Congruent Reflections Translations 12.3 12.4 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.5 5.1 5.2 5.3 Supp 6.2 6.3 Rotations Composition of Reflections Properties of Parallel Lines Proving Lines Parallel Triangle Angle Sum Theorems Polygon Angle Sum Theorems Congruence Triangle Congruence by SSS and SAS Triangle Congruence by ASA and AAS Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles Midsegments in Triangles Bisectors in Triangles Medians Constructions Properties of Parallelograms Proving Parallelograms 6.4 Special Parallelograms Domain Cluster Experiment with Transformations in the Plane (G.CO.1, G.CO.2, G.CO.3, G.CO.4, G.CO.5) Understanding Congruence in terms of rigid motion (G.CO.6, G.CO.7, G.CO.8) Prove Geometric Theorems (G.CO.9, G.CO.10, G.CO.11) Congruence (12 weeks) Unit 1 Make Geometric Constructions (G.CO.12, G.CO.13) supp 9.5 Supp 3 1.7 10.2 supp 10.5 10.6 10.7 ?Application: Minimizing Cost (Trigonometry and Area) (Law of Sines and Cosines) Perimeter, Circumference, and Area Cross Sections of 3-d Figures Rotating 2-d Objects Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders Volumes of Pyramids and Cones Volume of Spheres Geometric Measurement and Dimension* (3 weeks) supp Dilations Similar Polygons Proving Triangles Similar Similarity in Right Triangles Proportions in Triangles The Tangent Ratio Sine and Cosine Ratios Proving Trig Ratios Equal Trig and Complementary Angles Angles of Elevation and Depression Indirect Measurement ? Density Similarity, Right Triangles and Trigonometry* (5 weeks) 12.7 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 9.1 9.2 supp supp 9.3 4 1.6 3.5 3.6 supp supp 6.6 6.7 11.5 Distance and Midpoint Lines in the Coordinate Plane Slopes of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Partitioning Segments into a Given Ratio Equations of Parabolas Using the Focus and Directrix Figures in the Coordinate Plane Proof in Coordinate Geometry Circles in the Coordinate Plane Express Geometric Properties with Equations* (4 weeks) 2 Understand similarity in terms of similarity transformations. (G.SRT.1a, G.SRT.1b, G.SRT.2, G.SRT.3) Prove theorems involving similarity (G.SRT.4, G.SRT.5) Define Trigonometric Ratios and solve problems involving triangles (G.SRT.6, G.SRT.7, G.SRT.8) Apply geometric concepts in modeling situations (G.MG.1, G.MG.2, G.MG.3) Apply trigonometry to general triangles (G.SRT.9, G.SRT.10, G.SRT.11) Explain volume formulas and use them to solve problems (G.GMD.1, G.GMD3) Visualize the relationship between 2- and 3-dimensional objects (G.GMD.4) Apply geometric concepts in modeling situations (G.MG.1, G.MG.2, G.MG.3) Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically (G.GPE.4, G.GPE.5, G.GPE.6, G.GPE.7) Translate between the geometric description and the equation of a conic section (G.GPE.1, G.GPE.2) Angle Bisectors and Perpendicular Bisectors Relationships in the Inscribed Quadrilateral Arc Length and Sector Area Tangent Lines Chords and Arcs Inscribed Angles Angle Measures and Segment Lengths Circles and Completing the Square Radii and Intercepted Arcs Introduction to Radian Measure Circles* (4 weeks) 5 5.3 supp 7.7 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 supp supp Conditional Probability and the Rules of Probability; Using Probability to Make Decisions (6 weeks) 6 *Includes Modeling with Geometry Understand and apply theorems about circles (G.C.1, G.C.2, G.C.4, G.C.4(+)) Find arc lengths and area of sectors (G.C.5) Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically (G.GPE.4) Translate between the geometric description and the equation of a conic section (G.GPE.1) Apply geometric concepts in modeling situations (G.MG.1, G.MG.2, G.MG.3) Understand independence and conditional probability and use them to interpret data (S.CP.1, S.CP.2, S.CP.3, S.CP.4, S.CP.5) Use the rules of probability to compute probabilities of compound events in a uniform probability model (S.CP.6, S.CP.7, (+)S.CP.8, (+)S.CP.9) Use probability to evaluate outcomes of decisions ((+) S.MD.6, S.MD.7)