* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circuit Breaker Box – Main Panel
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical connector wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Crossbar switch wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Light switch wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Residual-current device wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
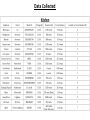
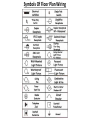
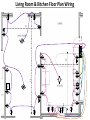
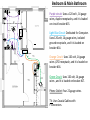
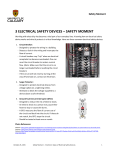
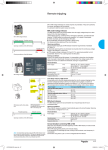
Group Formally Known As the Team Physics 211- Final Project Monday, 26 July 2010 Anthony Tanios Thai Pham Matthew Buras Jason Preston Julian Moore Background Information Does Sharon and Stanley need some 240 V lines as well as 120 V ? Sharon and Stanley need both the 120 volt and 240 volt wiring in their household. Some examples of 240 volt appliances are air conditioning unit, clothes dryer, and water heater, but in our project we are only going to be dealing with the range(oven/stove). It is the only appliance that we are going to wire that uses 240 volt. What voltage are the electrical lines coming into the house? The voltage of the electrical lines coming into the house is 120 volt per hot wire. To produce 240 volt needed for certain appliances, we use a dipole switch breaker in the breaker box that allows 2-120 volt wires to combine that produce 240 volt. How are the ratings on the circuit breakers determined? A circuit breaker is rated by the voltage and the current. The ratings on the circuit breakers signify the total load capacity of wattage that the circuit breakers can handle without breaking. They are designed to carry 100% of their rated current but as a safety measure, The National Electrical Code (NEC) determined that the safety capacity should only be 80% of that rated load capacity of wattage. How are houses wired? All the wiring in the house is done in parallel because in series, the voltage splits between the different types of small-appliances running in a closed circuit. Is there a minimum number of outlets that must be wired for each room? There is no minimum or maximum number of receptacles requirement by the NEC but there are specific rules for their placement such as: include receptacles on all walls 24 inches wide or greater, include receptacles so a 6-ft. cord can be plugged in from any point along a wall or every 12-ft. along a wall or more, and include a switch-controlled receptacle in rooms without a built-in light fixture operated by a wall switch. How are overhead light switches wired into the circuit? An overhead light is wired in parallel with the rest of the circuit running in the wall, but its switch is wired in series with it. It is placed on the hot wire before it connects back to the overhead light and after it leaves the main circuit. What questions should you ask Sharon and Stan in order to determine their wiring needs? To be able to wire the house for Sharon and Stan we need to ask them about the different types and location of appliances they will be using (120 or 240 volt), and their simultaneous uses. Data Collected Symbols Of Floor Plan Wiring Living Room & Kitchen Floor Plan Wiring S 15’ Main panel S 12’ GFCI GFCI 15’ S GFCI GFCI 25’ GFCI TV GFCI GFCI GFCI S GFCI GFCI GFCI GFCI S Living Room Purple circuit: Uses a 120 volt , 14 gauge wires, duplex receptacles, and its loaded on circuit breaker #3. TV: Uses Coaxial Cables with F-connectors. Phone Outlet: Four 22 gauge wires. Kitchen Pink circuit: Uses 120-volt, 12 gauge wires, GFCI Receptacles, and it is loaded on circuit breaker #7. Yellow Circuit: Dedicated for Microwave. Uses 120 volt, 12 gauge wires , GFCI receptacle, and it is loaded on breaker #6. Orange Circuit: Dedicated for Dishwasher. Uses 120 volt, 14 gauge wires ,a duplex receptacle, and it is loaded on breaker #9. Blue Circuit: Dedicated for Garbage Disposal. Uses 120 volt, 14 gauge wires, GFCI receptacle, and it is loaded on breaker #8. Light Blue Circuit: Dedicated for Range (Oven/Stove). Uses 240/120 volt, 8 gauge wires, 50 Amp. receptacle, and it is loaded on breaker #4. Black Circuit: Dedicated for Wok/Fry Pan/Toaster Oven/Toaster. Uses 120 volt, 12 gauge wires, GFCI receptacles, and it is loaded on breaker #5(Note: Only two appliances can be used at the same time). Phone Outlet: Four 22 gauge wires. Bedroom & Main Bathroom Purple circuit: Uses a 120 volt , 14 gauge wires, duplex receptacles, and it is loaded on circuit breaker #15. 10’ TV 1 2’ * Light Blue Circuit: Dedicated for Computer. Uses 120 volt, 14 gauge wires, isolated ground receptacle, and it is loaded on breaker #14. S Subpan el Orange Circuit: Uses 120 volt, 14 gauge wires ,GFCI receptacle, and it is loaded on breaker #16. GFCI SS Green Circuit: Uses 120 volt, 14 gauge wires , and it is loaded on breaker #17. GFCI 8’ 1 2’ VF Phone Outlet: Four 22 gauge wires. TV: Uses Coaxial Cables with F-connectors. Circuit Breakers & Panels Types, Benefits and Uses: Circuit Breaker Box – Main Panel (1): Main Breaker switch of Main Panel. (2): Breaker switch of hot wires(black and red) going to Sub Panel. (3): Breaker switch of Living Room. (4): Breaker switch of Range(oven/stove). (5): Breaker switch of Toaster/Toaster Oven/Electric Wok/Electric Fry Pan. (6): Breaker switch of Microwave. (7): Breaker switch of Kitchen. (8): Breaker switch of Garbage Disposal. (9): Breaker switch of Dishwasher. (10): Neutral Bus Bar(Main Panel). (11): Ground Bus Bar(Main Panel). (12): Outside Grounding Rod. Note: Black and Red Wires= Hot Wires White Wires = Neutral Wires Green Wires= Ground Wires Circuit Breaker Box - Sub Panel (13): Main Breaker switch of sub panel. (14): Breaker switch of the computer. (15): Breaker switch of the spare bedroom. (16): Breaker switch of the main bathroom receptacles (17): Breaker switch of the main bathroom. (18): Neutral Bus Bar(Sub Panel). (19): Ground Bus Bar(Sub Panel). Note: Black and Red Wires= Hot Wires White Wires = Neutral Wires Green Wires= Ground Wires Work Cited Page “Circuit Breakers.” Buying Guide: Circuit Breakers. 2000-2010. < http://www.homedepot.com/webapp/wcs/stores/servlet/ContentView?pn=Bre akers&langId=-1&storeId=10051&catalogId=10053>. Black & Decker. The Complete Guide To Wiring. Ed. Jennifer Gehihar. Minnesota: Creative Publishing Int. Inc., 2008.