* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download c - Fsusd
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
First observation of gravitational waves wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
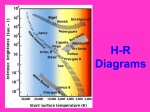
Student Name: _________________________________ Mrs. Lee – 8th Grade Physical Science Period #: ______ Page 1 Chapter 15 Practice Test – Answer Key ______ c 1) What is light? a) electrical energy from the sun c) energy that travels in the form of waves b) matter that travels as waves d) matter that allows us to see things ______ d 2) As the result of nuclear fusion, the sun gives off ______. a) mechanical & electrical energy b) chemical energy & sound c) electrical energy & light d) heat & light ______ a 3) How many stars are in our solar system? a) one b) hundreds c) thousands d) millions ______ d 4) The planets and moons in our solar system are visible because they ______. a) emit their own light b) undergo nuclear fusion c) absorb light from the sun d) reflect light from the sun ______ b 5) Patterns of stars in the sky are called ______. a) galaxies b) constellations c) star systems d) observatories ______ b 6) Which of the following is not part of the electromagnetic spectrum? a) radio waves b) sound waves c) X-rays d) infrared radiation ______ d 7) A neutron star that appears to produce pulses of radio waves is called a ______. a) quasar b) binary system c) black hole d) pulsar ______ a 8) The earliest stage of a star’s “life” is called a ______. a) protostar b) giant star c) quasar d) white dwarf ______ a 9) The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram graphs stars’ ______. a) absolute brightness & temperature b) apparent brightness & absolute brightness c) distance & absolute brightness d) diameter & apparent brightness ______ b 10) How long a star “lives” depends on ______. a) its color b) its mass c) whether it is single or binary ______ c 11) Parallax can’t be used on a star if the star is too ______. a) close b) bright c) far away d) large ______ b 12) A light-year is a unit of ______. a) time b) distance c) mass Ch 15 Practice Test Answer Key d) its temperature d) absolute brightness 1 Student Name: _________________________________ Mrs. Lee – 8th Grade Physical Science Period #: ______ Page 2 Chapter 15 Practice Test – Answer Key ______ b 13) The distance between the crest of one wave of electromagnetic radiation and the crest of the next one is its ______. a) frequency b) wavelength c) color d) spectrum ______ a 14) When a star runs out of fuel, it cannot become a ______. a) protostar b) neutron star c) white dwarf d) black hole ______ a 15) A star is born when nuclear fusion begins inside a protostar. a) True b) False ______ b (galaxy) 16) A quasar is a type of globular cluster. a) True b) False ______ a 17) A star system containing two stars is called a binary star. a) True b) False ______ b (apparent brightness) 18) A star’s absolute brightness is its brightness as seen from Earth. a) True b) False ______ b (red or reddish) a) True 19) The coolest stars are blue-white in color. b) False ______ a 20) What is a building that has one or more telescopes? a) observatory b) radio telescope c) planetesimal ______ b 21) What do astronomers use to measure distances to nearby stars? a) galaxies b) parallax c) sound waves ______ c 22) The earliest stage in a star’s life is called a ______. a) quasar b) pulsar c) protostar ______ b 23) What is a huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters, dust, and gas? a) nebula b) galaxy c) black hole ______ a 24) Young galaxies with giant black holes at their centers are ______. a) quasars b) pulsars c) supernovas ______ c 25) According to Hubble’s law, the farther away a galaxy is, ______. a) the slower it is moving away from Earth b) the sooner it will stop moving c) the faster it is moving away from Earth Ch 15 Practice Test Answer Key 2 Student Name: _________________________________ Mrs. Lee – 8th Grade Physical Science Period #: ______ Page 3 Chapter 15 Practice Test – Answer Key ______ b 26) Astronomers think that in the future the universe will continue to ______. a) shrink b) expand c) explode ______ b (refracting)27) A reflecting telescope focuses light through lenses. a) True b) False ______ a 28) A device used by astronomers to discover the elements found in stars is a spectrograph. a) True b) False ______ b (black hole) bang. a) True 29) An object with gravity so strong that no light can escape is a big b) False ______ a 30) Earth is in the Milky Way Galaxy a) True b) False ______ a 31) An elliptical galaxy looks like a round or flattened ball. a) True b) False ______ b (big bang) 32) The universe began with an explosion called the black hole. a) True b) False ______ a 33) The light you can see is called visible light. a) True b) False ______ b 34) A star’s absolute brightness is the star’s brightness as seen from Earth. a) True b) False ______ b 35) Spinning neutron stars are called supernovas. a) True b) False ______ a 36) The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy. a) True b) False ______ a 37) Astronomers think that most of the universe is made of dark energy and dark matter. a) True b) False Ch 15 Practice Test Answer Key 3 Student Name: _________________________________ Mrs. Lee – 8th Grade Physical Science Period #: ______ Page 4 Chapter 15 Practice Test – Answer Key The diagram below is used by astronomers to classify stars. Use the diagram to answer the following 5 questions: ______ a 38) Interpreting Graphs: What is the name for the kind of diagram shown in the picture? a) H-R diagram b) universal diagram c) spectrograph ______ a 39) Interpreting Graphs: Which group of stars in the diagram has the greatest absolute brightness? a) group D b) group B c) group C ______ c 40) Interpreting Graphs: In which group of stars could a very bright red star or a very bright yellow star be found? a) group B b) group C c) group D ______ c 41) Applying Concepts: Which group of stars represents white dwarfs? a) group A b) group B c) group C ______ b 42) Applying Concepts: In which group of stars would a main-sequence star be found? a) group A b) group B c) group C Ch 15 Practice Test Answer Key 4