* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NIS Space Diagnostic
Survey
Document related concepts
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Mirror symmetry (string theory) wikipedia , lookup
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Rule of marteloio wikipedia , lookup
Event symmetry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
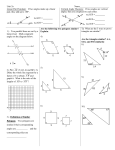
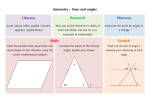
NIS Space Diagnostic Test Name/draw geometric shapes (square, triangle, rectangle, circle) Q1 Draw a triangle Name/draw 3D shapes (prism, pyramid, cone, cylinder, sphere) Q2 Name these 3D shapes Describe movement in terms of ¼, ½, ¾, full turn, more/less than ¼ turn, anti/clockwise Q3 Using the clock face supplied. On which number would the second hand be pointing after a: a) Half Turn, b) Three quarter turn clockwise? Construct/sketch a simple map Q4 My house has a shed to the west of it in the back yard and a water tank along it's North side. Draw a simple map to show my house, shed and water tank. Name/draw geometric shapes (quadrilaterals) Q5 Name these three quadrilaterals Q6 What 3D shape could be made from the net below? Tessellating properties of triangles and squares – flips, slides, turns, keeping symmetry Q7 Which of these shapes will tessellate? A B C Uses mapping conventions (alpha-numeric grid, symbols, legends) Q8 Give the grid reference for the Queen Victoria Market D Distinguish between polygon and not polygon Q9 Circle the shapes which are polygons. Name 4 main triangles (equilateral, isosceles, scalene, right-angled) Q10 Draw a representation of the following triangles. On each diagram label any equal angles and sides of equal length. Scalene Right-angled Isosceles Equilateral Name angles (acute, obtuse, reflex, straight, right, revolution) Q11 Name these types of angles using acute, obtuse, reflex, straight, right, revolution Distinguish between regular and irregular polygons Q12 Which of these are regular polygons? (one or more) A B C D Naming polygons – 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 sided Q13 Name these polygons. Identify lines, planes and points of symmetry in shapes and objects Q14 Draw all lines of symmetry in this shape Relates rotational symmetry and angle of rotation to transformations and tessellations Q15 Which of these has rotational symmetry greater then order 1? Circle one or more Naming non-polygons (circles, ellipses) Q16 Draw an ellipse Naming features of circle (radius, diameter, centre, circumference, chord, tangent) Q17 Name the following parts of the circle labelled above A _________________ B _________________ C _________________ D _________________ E _________________ Construct 3D objects from plans, nets, isometric drawings Q18 Draw the isometric drawing for the following net Sum of interior angles (triangle, quadrilateral) Q19 Find the value of A Measure and construct angles (acute, obtuse, reflex, straight, right, revolution) Q20 Using a protractor, construct a 60 degree angle. Recognise congruent shapes can be super-imposed Q20 Which of the following shapes are congruent A B C Estimates and calculates distance between grid references (horiz. and vert.) Q21 Michael walks along the edge of a paddock 5 km west followed by 5 km North. a) Draw a picture to represent his movement. b) How far has Michael walked? Interpret movements using 8 compass points Q22 If Michael were able to cut across the paddock is what direction would he travel and estimate the distance he would have to travel to get to the same end point. Uses co-ordinates to describe the location of a point on a Cartesian plane Q23 Write the coordinates of the two points shown below A _______ B _______ B A Visualise cross-section of prisms and pyramids Q24 What shape is the horizontal cross-section of the following prisms Identify parts of a composite shape Q25 Draw a hexagon using two or more shapes Properties of exterior angles (triangles, polygons) Q26 What is the value of angle A Calculate complimentary, supplementary, opposite angles Q27 Determine the value of the missing angles. Distinguish between properties of similarity and congruence Q28 Explain why these two triangles are similar. Uses ratio scale to calculate distance between grid references Q29 Using the scale of 1 cm = 250 m find the distance Kelly has to travel from Flinders St Station to Victoria St. Describes locations using longitude and latitude Q30 Which country is located at Longitude 20 E and latitude 20 N Cross-sections of shape (circle – sector, segment) Q31 Match the terms with the labels shown on the diagrams. a) Minor segment b) Major segment c) Minor arc d) Major arc e) Minor sector f) Major sector g) Chord Sum of interior angles (polygons - rule) Q32 a) What is the sum of the internal angles of a pentagon? b) What is the value of one internal angle in a regular pentagon? Calculate vert. opposite, co-interior, corresponding, alternate angles Q33 Calculate the values of the pronumerals giving reasons for your answers. a= g= b= f= c= h= Describes a sequence of transformations Q34 Describe how shape A could be transformed into shape C. If B is a reflection of C then draw in the line of reflection Describes location using distance and bearings in whole degrees Q35 Use a ruler and protractor to describe the distance and bearing from the post office to the shop if 1cm = 1km. Uses mapping conventions (angles, bearings, keys, annotations)