* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4.5 Topic Checklist Carbonyl Compounds
Survey
Document related concepts
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
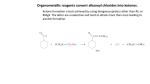
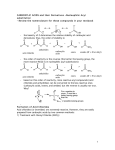
Topic Checklist Compounds containing the carbonyl group 4.5 In Section 4.4 (Nomenclature and isomerism in Organic chemistry), you should gain a series of practical skills associated with organic tests, including purification and a test of purity. an understanding of how carbonyl compounds may react at the molecular level. a recognition of the properties and uses of acids and esters. an appreciation of the use of acid chlorides in organic synthesis. an appreciation of how acid chlorides may react at a molecular level. a series of practical skills associated with the synthesis and analysis of organic compounds. know that aldehydes are readily oxidised to carboxylic acids and that this forms the basis of a simple chemical test to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones (e.g. Fehling’s solution and Tollens’ reagent) appreciate the hazards of synthesis using HCN/KCN know that aldehydes can be reduced to primary alcohols and ketones to secondary alcohols using reducing agents such as NaBH4. Mechanisms showing H– are required (equations showing [H] as reductant are acceptable) understand the mechanism of the reaction of carbonyl compounds with HCN as a further example of nucleophilic addition producing hydroxynitriles know that carboxylic acids are weak acids but will liberate CO2 from carbonates know that carboxylic acids and alcohols react, in the presence of a strong acid catalyst, to give esters know that esters can have pleasant smells know the common uses of esters (e.g. in solvents, plasticizers, perfumes and food flavourings) know that vegetable oils and animal fats are esters of propane-1,2,3-triol (glycerol) know that esters can be hydrolysed understand that vegetable oils and animal fats can be hydrolysed to give soap, glycerol and long chain carboxylic (fatty) acids know that biodiesel is a mixture of methyl esters of long chain carboxylic acids know that vegetable oils can be converted into biodiesel by reaction with methanol in the presence of a catalyst know the reaction with ammonia and primary amines with acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides know the reactions of water, alcohols, ammonia and primary amines with acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides understand the mechanism of nucleophilic addition– elimination reactions between water, alcohols, ammonia and primary amines with acyl chlorides understand the industrial advantages of ethanoic anhydride over ethanoyl chloride in the manufacture of the drug aspirin