* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide for Chapter 12, Part 2 – The Heart Terms – know the
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
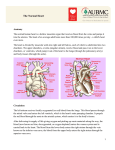
Study Guide for Chapter 12, Part 2 – The Heart Terms – know the definition and anatomical/physiological significance of: aorta, aortic semilunar valve, artery, atrioventricular (AV) bundle, atrioventricular (AV) node, atrium, autorhythmicity, capillary, cardiac cycle, cardiac output, chordae tendineae, coronary sinus, diastole, ECG (P wave, QRS complex, T wave), electrical syncytium, fibrous skeleton, Frank-Starling principle, gap junctions, heart rate, intercalated discs, left AV (bicuspid or mitral) valve, papillary muscle, pericardium, pulmonary semilunar valve, pulmonary trunk and arteries, pulmonary veins, Purkinje fibers, right and left bundle branches, right AV (tricuspid) valve, systole, vein, vena cavae (superior and inferior), vein, venous return Know the path that blood takes through the heart. Know the chambers, major vessels, valves and other structures (e.g. papillary muscle, chordae tendineae, lungs) that blood encounters along this path.) Know the elements of the cardiac conduction system and their functions. The heart is composed of two electrical syncytia. What is an electrical syncytium? How is this concept important to cardiac function? What factors determine cardiac output? How can cardiac output be increased during exercise? What does an ECG record? What do the major waves represent? What directly follows each of the major waves? Practice Questions 1. The normal pacemaker of the heart is the: a. AV bundle of His b. AV node d. Right and left bundle branches c. Purkinje fibers e. SA node 2. The spread of electrical activity between the atria and ventricles is delayed briefly to allow the atria to contract before the ventricles contract. This delay occurs at the: a. AV bundle of His b. AV node c. Purkinje fibers d. Right and left bundle branches e. SA node 3. The innermost layer of the heart is a simple squamous endothelium. This layer lines the atria and ventricles and is continuous with the endothelium of the blood vessels. This layer is known as the: a. endocardium b. epicardium c. myocardium d. parietal pericardium e. visceral pericardium 4. The QRS complex of an electrocardiogram is an actual record of cardiac muscle contraction. a. true b. false 5. The “average person’s” left ventricle pumps about 5 liters of blood per minute. The average person’s right ventricle pumps about ___ liters per minute at rest. a. 1 b. 2.5 c. 5 d. 7.5 e. 10 6. Assuming that all other factors remain constant, if stroke volume increases, then cardiac output will: a. decrease b. increase c. remain the same 7. Assuming that all other factors remain constant, if heart rate increases, then cardiac output will: a. decrease b. increase c. remain the same 8. Oxygenated blood from the lungs returns to the heart via the ___. a. aorta b. inferior vena cava c. pulmonary arteries d. pulmonary veins e. superior vena cava 9. Deoxygenated blood from your head returns to the heart via the ___. a. aorta b. inferior vena cava c. pulmonary arteries d. pulmonary veins e. superior vena cava 10. The chordae tendineae function to open the atrioventricular valves. a. true b. false 11. The openings for the coronary arteries are located in the ___. a. aorta b. left atrium c. left ventricle d. right atrium e. right ventricle 12. Deoxygenated blood returning to the heart from the body’s tissues first enters the ___. a. left atrium b. right atrium c. left ventricle d. right ventricle 13. The aortic semilunar valve closes when ___. a. aortic pressure is greater than left ventricular pressure b. left ventricular pressure is greater than aortic pressure c. papillary muscle contracts and pulls on chordae tendineae 1e 2 b 3 a 4 b 5 c 6 b 7 b 8 d 9 e 10 b 11 a 12 b 13 a