* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bio Study Guide So I don`t Fail SECTION 1 DEFS Element
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
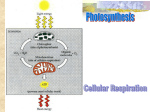
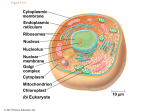
Bio Study Guide So I don’t Fail SECTION 1 DEFS Element-substance composed of atoms Compound-many atoms bonded together Atom Proton-positive Neutron-neutral Electron-negative Isotopes-same number of protons, different neutrons Bonds Ionic bonds-between two oppositely charged ions. Ionic bonds are formed between a cation, and an anion, Polar Covalent bond- H2O bond, not equal sharing Nonpolar covalent bond- equal sharing of electrons Hydrogen bonds-weak, bond using H Peptide bonds- carboxyl/amine group bond Functional groups OH (Alcohol) CO (Carbonyls) COOH (carboxyl) NH2 (Amine) SH (sulfhydryl) PO4 (Phosphates) CH3 (Methyl) Carbohydrates Monosaccharides-glucose, fructose, and galactose 1-4 Glycosidic linkage Functions: o Cell Energy Storage Starch (Amylose, amylopectine) Glycogen o Structural component Cellulose Chitin Lipids Monomer: glycerol+3 fatty acids Ester linkage Types: o Triglyceride Saturated-has all H’s Unsaturated-has double bonds Cis-bends due to H’s Trans-doesn’t bend Proteins Monomer: Amino Acid Peptide bond Primary-amino acid sequence Secondary-pleats and helices Tertiary-bridging Quarternary-interaction between proteins Nucleic Acids Types: o DNA Double Helix Sugar-deoxyribose N-base: Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine Function-genetic code o RNA Multiple structures Sugar-ribose N-base: Adenine, Uracil, C, G Function: genetic code, messenger, transports, structural Monomers: nucleotides Phophodiester bond SECTION 2 Characteristics of life~ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Energy utilization Reproduction Reaction to stimuli Levels of organization Composed of cells Respond/adapt to environment Growth/development Homeostasis Eukaryrote and Prokaryote prokaryotic no nucleus eukaryotic nucleus. prokaryotic cells lack some organelles eukaryotic organelles prokaryotic unicellular eukaryotic cells are often multicellular. prokaryotic cells reproduce/divide by binary fission eukaryotic cells reproduce/divide by mitosis/meiosis Cell Parts and Functions Ribosomes-used in translation, found on rough ER ER: Syn. of proteins. Storage. Mitochondria: Cellular respiration Golgi Body: movement of molecules. Makes proteins more complex Chloroplasts: Photosynthesis Transport through Cell Active transport: o Ion pump-uses ATP to pump ions o Cotransport-molecules moved @same time o Endo/exo cytosis Phagocytosis-cell eating Pinocytosis-cell drinking Recptormediated-uses receptor proteins Faculative Diffusion: uses proteins to aid in diffusion Diffusion: movement of molecules from high conc. to low conc. Osmosis o Hypotonic-less amnt of dissolved mat o Hypertonic-more dissolved mat o Isotonic-equal SECTION 3 Photosynthesis Photosynthesis: converting energy into glucose 6H2O+6CO2- C6H12O6+6O2 Reactions: o Light Dependant: Noncyclic (P680 and P700) E moves down and H enters lumen. H can only exit through ATP synthase, thus ATP is made H is picked up by NADP Photolysis makes more H’s and E’s to repeat Products-ATP, NADPH, O2 Cyclic (P700) Electron moves down, H pulled in H makes ATP E is pulled back to start Products: ATP (to stroma) o Calvin/Bensen cycle CO2 fixed onto RuBP Breaks into PGA (3carb) Add e- to make G3P (uses ATP and NADPH) 1 (of 6) are removed to be used to make glucose 5 G3P are made back into RuBP (uses ATP) C3, C4, CAM Plants C3-uses O2 to make PGA and CO2 (calvin cycle) C4 o Stored CO2 is added to PEP o Makes malate (stored in mesophyll) o When env. improves, CO2 is released into Calvin cycle o PEP is reused CAMo C fixation at night o CO2 binds with PEP o Malate stored until sunlight o CO2 released o Pyruvate becomes PEP again Parts of a leaf Simple: o Midrib, blade, petiole Compound: o Pinnate o palmate Monocot vs. Dicot Monocot o One cotyledon o Multiples of 3 flower parts o Parallel leaf venation o Scattered vascular bundles o Fibrous root system Dicot: o 2 cotyledons o 2, 4, 5 flower parts o Net-like leaf venation o Rings like vascular bundles o Taproot system Cellular Respiration Cell Resp-making Energy out of glucose C6H12O6+6O2 6H2O+6CO2+ATP Glycolysis o Energy investment/return o Products: 4 ATP 2 NADH 2 Pyruvate Intermediate Step o Products: Acetic Acid CO2 2 NADH Krebs cycle: o Products: 4 CO2 6 NADH 2 FADH 2 ATP o CO2 Fixation o Reducing NAD o Regeneration o 3C, 2C, 6C, 5C, 5C, 4C, 4C, 4C, 4C, 4C,REPEAT Oxidative Phosphorylation: o In Matrix o NADH and FADH drop off e- and H o Electrons travel down electron transport chain o H pulled in, exit through ATP synthase o O collects H’s and e’s to make H2O Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration Aerobic-uses O2 Anaerobic-doesn’t use O2 Aerobic is more productive Anaerobic Resp Glycolysis: o Makes 4 ATP 2 NADH 2 Pyruvate Alcoholic Fermentation: o C6H12O6 2CO2+2C2H6O+2ATP o Makes alcohol and CO2 Lactic Acid o C6H12O6 2C3H6O3+2ATP o Makes lactic acid SECTION 4 Cell Cycle Stages: o G1-growth, longest o S-synthesis of genetic material o G2-growth 2 o M-mitosis Mitosis: o Interphase o Prophase o Metaphase o Anaphase o Telaphase o Meiosis: remaking sex cells o Prophase 1,2 o Metaphase 1,2 o Anaphase 1,2 o Telaphase 1,2 o Diploid/Haploid o Diploid-cell contains two sets of DNA Most cells in the body are diploid. o Haploid-cell contains one set of DNA, half of a diploid cell. SECTION 5 Translation Making proteins out of tRNA Initiation-read start codon Elongation-read code and deliver AA Termination-read stop codon Transcription DNA unwinds and unzips Nucleotides bind to antisense strand Once read, RNA drops off and DNA rewinds Introns taken out Exons fused together Made tRNA for translation Replication DNA unwinds and unzips Complementary nucleotides bind 5P-3P direction SECTION 6 Evolution Adapting to changes in environment Natural selection: only the strong survive to reproduce Evidence of evolution: o Fossil record Relative dating Radiometric-uses isotopes AA dating o Comparative anatomy o Comparative embryology o Molecular biology o Biogeography Hardy-Weinberg Showed that gene pool doesn’t change Factors that cause pop to change: o Mutations o Nonrandom mating o Migration o Small population o Harmful genes Factors to prevent interbreeding Prezygotic: o Habitat isolation o Behavioral o Temporal o Gamete isolations (lock/key between sperm and egg) o Mechanical isolation Postzygotic: o Reduced hybrid viability-death of fetus o Reduced hybrid fertility-offspring live but are infertile o Hybrid breakdown-2nd generation are infertile Modes of speciation: o o Allopatric-isolation due to geography Sympatric-isolation due anything else besides geography Darwin’s theory Many offspring produced, not all live due to competition for resources Some have advantages within environments to easier get resources Organisms with advantages have better chance to reproduce Baptist theory Use and disuse-organs that are not used are discarded Inheritance of acquired characteristics-modifications made in a lifetime are passed onto offspring Environment affects evolution SECTION 7 Classification Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species Taxonomy- is the science of identifying and naming species, and arranging them into a classification o Binomial Nomenclature- Kingdom, phylum…. o Phylogenetic classification-connects organisms to a common ancestor Kingdoms: o Plant o Animal o Protist o Eubacteria o Archaebacteria o Fungi Dichotomous key SECTION 8 Genetics: Law of Independent Assortment-homologous genes enter different gametes independently of other gene pairs Incomplete dominance: o No dominant gene o Phenotype is a combination o Ex: R=red, W=white, RW=pink Co-dominance: o Full expression of both genes o Ex: R=red, W=white, RW=red and white Sexlinked traits: o Linked to sex chromosome o Ex: hemophilia Pedigrees: Complete dominance Incomplete dominance Codominance Multiple alleles- more than 2 alleles for a gene (blood type) Polygenetic inheritance- trait controlled by more than one gene locus Pleiotropy- control by a simple gene of several distinct and unrelated phenotypic effects Epistasis- nonallelic genes in which one masks the expression of another SECTION 9~~~LAST ONE Ecology Greenhouse effect-greenhouse gasses are trapped in atmosphere and cause global warming Global warming destroys some environments (such as ice caps) Producer-makes food from sun energy Consumer-eats producer or other consumers 10% rule-each organism gets 10% of the energy that its prey ate o Ex: plant-10% from sun Insect-10% of plant (1%) Mouse-10% of insect (0.1%) Owl-10% of mouse (0.01%) Abiotic factors: nonliving factors of an environment (ex: weather, climate) Biome-type of environment o Mountain o Grassland o Desert o Forests o tundra o rainforests Explain how carbon, oxygen, nitrogen and water is cycled through the ecosystems Explain the J-Curve or exponential curve of population growth