* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Modern theory of evolution o Bottleneck Mutation
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
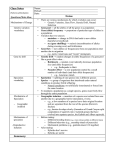
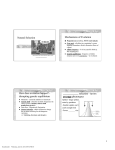
Modern theory of evolution r Changes in gene pool as a result of natural selection. Natural selection leads to changes over time, changes in allelic frequency. u Gene - paft of the chromosome containing a trait o Alleles - alternate forms of a trait u Gene pool - all of the genes in a population u Allelic frequency - propoftion of specific genes in a gene pool Population size r If population is large, then free gene flow a Migration - immigration or emigration out of an area r If population is localized or fragmented then genetic drift occurs r Genetic drift- any change in genetic make up due to chance. It is a non random change in gene frequency, In small populations ceftain alleles, present in the larger population, may not be present. o o Founder effect Bottleneck Founder effect r when a small pop gets isolated from their place of origin, rare alleles may be enhanced. Some alleles may be eliminated. Bottleneck n If a pop is reduced in size due to flood etc. the survivors may have only a paft of the total alleles causing a reduction in genetic variability of the population (A sharp reduction in the gene pool) r cheetah Mutation r Random; onlysource of new alleles u Can be lethal, neutralor beneficial u Caused by Mistakes made when DNA replicates Environmental factors such as gamma rays, chemicals, temperature r r What are the results of Natural Selection? r Natural selection causes deviations from Hardy Weinberg by changing allele frequenry. o Adaptations to living and physical conditions enables organisms to survive under a given set of conditions and live to reproduce Natural selection is a main cause of evolution r The environment imposes the conditions that result in selection and thus the direction of r r evolution. Natural selection acts on the phenotype of the organisms; this in turn affects the genotype. Natural selection on single genes can affect allelic frequency of that gene. Fitness depends on the effect of that one gene. r r When polygenic traits are involved there is a range of phenotypes that may be fit. Natural selection acts upon variation in the population Three main types of selection o Stabilizing selection a Disruptive selection Directional selection o Stabilizing selection r Selects against extremes. Acts to eliminate both extremes from the phenotypes; individuals at the center of the curve show highest fitness. q Ex: babies born to humans tend to be around the same size and birth weight. Larger and smaller infants are not as fit. In ducks and chickens eggs those with intermediate weights have highest fitness.., s Disruptive selection r Selects for extremes, acts to eliminate the intermediate type. a In a bird population where large and small seeds are more common than medium seeds, birds at the extremes have highest fitness, Directional selection r Shift in population; acts to eliminate one extreme from an array of phenotypes. o Ex: beak size when only large seeds are available, those birds with larger beaks are more fit. Speciation r Speciation - formation of new species r Gradualism (Phyletic evolution) - gradual changes take place through time. I Allopatric speciation - Divergent evolution - ancestral species gives rise to others. Punctuated equi Iibrium. o Geographic isolation leads to reproductive isolation. Genetic drift o Adaptive radiation - organisms evolve to fill unoccupied niches especially after major extinction. Key brea kthroug hs. a Lineages may remain unchanged for long periods of time F Name * Variation in P€)pulations with Chapter Use 15, Section 15.2 Stabilizing Selection Directiona! Selection Selection N*rrna! for variation longer beaks = ? o O + > (, F o o 6 ,: '; Disruptive Selection o o @ 'i o U * UNIT 5 CHAPTER 1 5 The Theory of Evolution Name Variation in Populations Use with Chapter lS, Section lS.2 1. Study the_graph for stabilizing selection. Explain the effect of this qrpe of natural selection. 2. use the transparency to explain the effect of directional selection. 3. use the tra,sparency to explain the effect of disruptive selection. a. why might average-sized spiders be favored in a given environment? d 5' Why mirhl woodpeckers with longer shorter beaks? beaks have a selective advantage over those 6 with 'E o E (,c z o E F c 6. Limpets are marine organisms that attach themselves to rocks. Under what environmental conditions_might intermediate forms of limpets-those that are tan, rather than white or dark brown-be at a disadvantage? o 's ; > g E 7. what do the three gpes of natural serection have in common? o @ b e a U CHAPTER 15 The Theorv of Evolution UNIT 5