* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 41 - Auricht Projects
Survey
Document related concepts
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
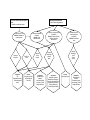
43. Currawinya Lakes Information in the Ecological Character Description (ECD) (BMT WBM, 2008) and the latest version of the RIS for the Currawinya Lakes Ramsar site were reviewed to identify threats to the ecological character of the site. Terminology from these key Ramsar documents was aligned to be consistent with the approach of the Ramsar Rolling Review (see Table 1). The Ramsar Rolling Review uses the IUCN threat classification to standardise terminology across sites. All threat categories identified at the Currawinya Lakes Ramsar site are listed in Table 2. The critical components, processes and services (CPS) specified in the ECD are reproduced in Table 3Error! Reference source not found.. Threats which have the potential to change one or more of the critical CPS within a 10 year timeframe are defined as imminent threats to the ecological character of the site (labelled IMM in Table 3Error! Reference source not found.). Consultation with site managers was undertaken to ensure the correct identification of current and imminent threats (see Table 1). A stressor model is presented to illustrate the major pathways by which imminent threats effect the critical CPS. For clarity, the model does not attempt to show non-imminent threats, weak linkages or feedbacks. Threat, stressor, and indicator terminologies have been standardised for comparison across all Australian Ramsar sites under the Rolling Review. For Queensland Ramsar sites the Queensland Wetlands Program terminology has been cross referenced against the terminology of the Rolling Review for imminent threats (see Table 4Table). Where an appropriate indicator from the QLD program matches the stressors identified in the Rolling Review they have been included in the model. Table 1: Notes regarding alignment of terminology and additional information sourced from site managers to aid in the development of the sites threat conceptual model. Notes: The ECD has focused on critical services and did not seek to identify critical components and process, with the primary approach to describing services has been to articulate Ramsar criteria as the Services. Critical components were not specifically identified in the ECD. The approach taken in this work was to review the ECD and make professional judgments on which Components were critical. Critical Processes were identified in the ECD (Table 4-1 “Summary of critical services/benefits”) and are reproduced in Table 3. Seven critical supporting and two cultural services were identified in the ECD: (S1) Unique diversity of habitats with many different wetland types represented in a ‘natural’ (unmodified) wetland (Supporting service: Near natural wetland ecosystems). (S2) Wildlife refuge in drought conditions for amphibians, fishes, reptiles and birds (Supporting service: Special ecological, physical or geomorphic features). (S3) Supports waterbird diversity, abundance and habitat value (Supporting service: Priority wetland species and ecosystems). (S4) Supports Threatened wetland dependent fauna (painted snipe, grey snake and freckled duck) (Supporting service: Threatened wetland species, habitats and ecosystems). (S5) Supports a notable diversity of native wetland fauna of bioregion (Supporting service: Biodiversity) (S6) Supports Threatened Ecological Community (Artesian mound springs) (Supporting service: Threatened wetland species, habitats and ecosystems). (S7) Supports Threatened plant species (Sclerolaena walkeri and others) (Supporting service: Threatened wetland species, habitats and ecosystems). (C1) Contains indigenous cultural heritage values (Cultural service: Cultural heritage and identity) (C2) Contains research and education values (Cultural service: Science and education) The ECD notes that there are several key threatening processes that were acting before the site was listed. These related to: long term changes to vegetation type and cover reduction in the flow of groundwater from the Great Artesian Basin into the mound springs on the site long term sedimentation of Lake Karatta and Lake Wyara. ECD identifies threats as: Change to existing (hydrological) management regime (7. Natural System Modifications - 7.2. Dams & water management/use) Lake sedimentation (2. Agriculture & Aquaculture - 2.3. Livestock farming & ranching) Climate change (11. Climate Change & Severe Weather - 11.4. Storms & flooding) Non-native fish (8. Invasive & Other Problematic Species & Genes - 8.1. Invasive non-native/alien species) Local expert advice was used to help identify imminent threats. Stressors were identified on the basis of information in the ECD. Table 2: Major categories and subcategories of current threats for the Ramsar site 43. Currawinya Lakes 2. Agriculture & Aquaculture 2.3. Livestock farming & ranching 8. Invasive & Other Problematic Species & Genes 8.1. Invasive non-native/alien species 7. Natural System Modifications 7.2. Dams & water management/use 11. Climate Change & Severe Weather 11.4. Storms & flooding Wetland habitats IMM Waterbirds IMM Fish IMM Threatened species IMM Vegetation IMM Biological processes IMM Geomorphologic processes Hydrological regime Nutrient cycling IMM IMM IMM 11.4. Storms & flooding 8.1. Invasive nonnative/alien species 7.2. Dams & water management/use processes green, services yellow) 2.3. Livestock farming & ranching Table 3: Matrix of all current threats against critical components, processes, and services showing those considered to be an imminent threat to the ecological character of the Ramsar site. Components, Processes and Services (CPS) (components blue, Water quality Supporting Service: Near natural wetland ecosystem IMM Supporting Service: Special ecological, physical or geomorphic features (drought refuge) IMM Supporting Service: Priority wetland IMM species and ecosystems Supporting Service: Threatened wetland species, habitats and ecosystems (various species and artesian mound springs) IMM Supporting Service : Biodiversity IMM Cultural Service: Science and education IMM Cultural Services: Cultural heritage and identity IMM IMM IMM Table 4: Rolling review terminology for imminent threats cross referenced against relevant QLD EPA Wetlands Program indicators (Scheltinga & Moss In Prep). Ramsar Rolling Review (RRR) QLD Wetlands Program equivalent/potentially relevant indicators IUCN Threat Category and Subcategory Stressor and associated indicator Pressure Indicator (PI) Condition indicator (CI) 7. Natural System Modification 7.2 Dams & water management/use Stressor: Reduced base flows to mound springs from groundwater Indicator: Groundwater levels Stressor: Hydrology PI 26: % of median annual flow impounded and extracted (surface and ground water) Stressor: Hydrology CI 9: change in wetland habitat extent CI 10: change in extent of wetland waterbody CI 11: change in composition of wetland ‘wet’ and ‘dry’ species Ramsar Rolling Review (RRR) QLD Wetlands Program equivalent/potentially relevant indicators IUCN Threat Category and Subcategory Stressor and associated indicator Pressure Indicator (PI) Condition indicator (CI) 7. Natural System Modification 7.2 Dams & water management/use Stressor: Frequency, timing and duration of inundation Indicator: Volumes of inflows, changes to the Water Resource Plan Stressor: Hydrology PI 26: % of median annual flow impounded and extracted (surface and ground water) 7. Natural System Modification 7.2 Dams & water management/use Stressor: Increased suspended sediments Indicator: Total suspended solids 8. Invasive & Other Problematic Species & Genes 8.1. Invasive nonnative/alien species Stressor: Invasive species carp Indicator: Abundance of invasive species Stressor: Aquatic sediments PI 1: % of wetland disturbed by livestock and feral pigs PI 8: % difference between pre-European sediment load and current load PI 27: % of catchment modified Stressor: Pest species (carp) PI 33: presence of ‘key’ aquatic pest species (carp) in the site and adjoining areas Stressor: Hydrology CI 9: change in wetland habitat extent CI 10: change in extent of wetland waterbody CI 11: change in composition of wetland ‘wet’ and ‘dry’ species Stressor: Aquatic sediments CI 9: change in wetland habitat extent CI 10: change in extent of wetland waterbody Key to shapes used in conceptual model. Stressor: Pest species (carp) CI 20: presence of key pest (animal, plant) species References: BMT WBM. (2008). Ecological Character Description of the Currawinya Lakes Ramsar Site. Prepared for the Queensland Environmental Protection Agency. Brisbane. Scheltinga, D.M. and Moss, A. (In Prep). A framework for assessing the health of, and risk to, Queensland’s lacustrine (lake) and palustrine (swamp) wetlands. 6th May 2009, Ver. 1.3. WL EPA 17: Queensland Wetland Indicators and Monitoring Tools project report. 43. Currawinya Lakes 8. Invasive & Other Problematic Species & Genes 8.1. Invasive non-native/alien species 7. Natural System Modifications 7.2. Dams & water management/use Increased suspended sediments Indicator: Total suspended solids Invasive species - fish Indicator: Abundance of invasive species Increased competition Mortality of fauna Component: Fish Services: Biodiversity; Cultural heritage and identity Process: Biological processes (bird breeding and food webs) Reduced faunal richness Component: Wetland habitats Service: Near natural wetland ecosystems, Cultural heritage and identity Frequency, timing and duration of inundation Indicator: Volumes of inflows, changes to the Water Resource Plan Reduced base flows to mound springs from groundwater Indicator: Groundwater levels Change in wetland type (loss of mound springs) Change in wetland type (reduced depth) Component: Waterbirds, vegetation Service: Special ecological, physical or geomorphic feature, Threatened spp, Biodiversity, Priority wetland species, Cultural heritage and identity Process: Hydrological regime Component: Wetland habitats Service: Threatened ecosystem (mound springs), Cultural heritage and identity