* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Marketing Begins with Customers
Survey
Document related concepts
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Targeted advertising wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Brand loyalty wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Music industry wikipedia , lookup
Emotional branding wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
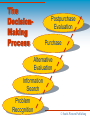
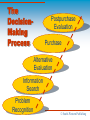
MARKETING BEGINS WITH CUSTOMERS 6.1 Understanding Consumer Behavior 6.2 What Motivates Buyers? 6.3 Types Of Decision-Making © South-Western Publishing UNDERSTANDING CONSUMER BEHAVIOR GOALS for Lesson 6.1 Describe the importance of understanding consumer behavior. Demonstrate and understanding of consumer wants and needs. © South-Western Publishing Consumer Behavior Important for marketers to understand consumers (needs and wants) and their buying behavior Final Consumers – buys a product or service for personal use Business Consumers – buys goods and services to produce and market other goods and services or for resale © South-Western Publishing Consumers’ Wants and Needs A want is an unfulfilled desire. A need is anything you require to live. Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Different People, Different Levels © South-Western Publishing Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs identified five areas of needs and the progression people follow in satisfying needs. Five Areas - physiological, security, social, esteem, self-actualization © South-Western Publishing Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Self-Actualization (to realize your potential) Esteem (respect and recognition) Social (friends, love, belonging) Security (physical safety and economic security) Physiological (food, sleep, water, shelter, air) © South-Western Publishing Different People, Different Levels Marketers must understand each individuals need no matter what level House – provides shelter from weather House – safe neighborhood provides security House – in a neighborhood with lots of families might satisfy social needs House – well maintained could provide self-esteem House – designed and built by the owner might provide self-actualization © South-Western Publishing Group Activity Illustrate Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, then label, explain and provide examples for each level. Then explain why it is important for marketing firms and businesses to understand the levels of consumer’s needs and wants. © South-Western Publishing WHAT MOTIVATES BUYERS? GOALS for Lesson 6.2 Distinguish between different buying motives. Describe the five steps of the consumer decision-making process. © South-Western Publishing Buying Motives Emotional motives Rational motives Patronage motives © South-Western Publishing Emotional Motives Reasons to purchase based on feelings, beliefs, or attitudes (love and affection, guilt, fear, passion) Hallmark Cards – love and affection Security Systems – fear of being robbed © South-Western Publishing Rational Motives Reasons to buy based on facts or logic saving money durability saving time © South-Western Publishing Patronage Motives Reasons to buy based on loyalty low prices, high quality, friendly staff, great customer service, convenient location people become loyal to a product or service business encourage patronage motives, helps lower competition © South-Western Publishing Buying Behavior The decision processes and actions of consumers as they buy and use services and products Consumer Decision Making Process Problem Recognition Information Search Evaluation of Alternatives Purchase Post Purchase Evaluation © South-Western Publishing The DecisionMaking Process Postpurchase Evaluation Purchase Alternative Evaluation Information Search Problem Recognition © South-Western Publishing Problem Recognition The consumer must recognize a need, want or desire Example – You want to be able to play golf, so you recognize the need to find an instructor © South-Western Publishing Information Search The consumer must then gather information Example – ask friends or family, go to the local golf course, check the newspaper © South-Western Publishing Alternative Evaluation Evaluate the various alternatives to determine which is best. (summarize, compare, rank) Example – who can you afford or what hours are available © South-Western Publishing Purchase Decide and make the purchase Example – You decide to take lessons at the local driving range, instead of the golf course. You call and schedule a lesson. © South-Western Publishing Post Purchase Evaluation The consumer judges the satisfaction or dissatisfaction with the product or service. Example – You have had a few lessons and you can consistently hit the ball in the air with all your clubs, so you are satisfied with your improvement. © South-Western Publishing TYPES OF DECISION-MAKING GOALS for Lesson 6.3 Describe the influences on the consumer decision-making process. Explain how consumers and businesses use routine, limited, and extensive decision-making. © South-Western Publishing Influences on the Consumer Decision-Making Process Personality Social class Cultural environment Reference groups © South-Western Publishing Personality A well defined, enduring pattern of behavior that influences buying decisions, everyone has their own preferences. Sports car vs. pick up truck vs. sedan © South-Western Publishing Social Class The lifestyle, values, and beliefs that are common to a group of people. Income level Neighborhood Examples – brand differences (Rolex vs. Fossil) © South-Western Publishing Cultural Environment A set of beliefs or attitudes that are passed on from generation to generation. Examples - © South-Western Publishing Reference Groups Groups or organizations from which you take your values and attitudes. Strong influence on buying behavior Church groups, fraternities, work groups, civic organizations, peer groups Examples - clothes © South-Western Publishing Types of Decision-Making Routine decision-making Limited decision-making Extensive decision-making © South-Western Publishing Routine Decision-Making Used for purchases that are made frequently and do not require much thought Familiar with the product Same brand Easy substitution Final Consumers and Business Consumers use Routine Decision-Making © South-Western Publishing Limited Decision-Making Takes more time, often is associated with a product that is more expensive or purchased less frequently. Jeans – try on, color, compare price, styles Office equipment, furniture © South-Western Publishing Extensive Decision-Making Happens when the consumer methodically goes through all five-steps of the decision-making process New car New mainframe computer system New delivery trucks © South-Western Publishing The DecisionMaking Process Postpurchase Evaluation Purchase Alternative Evaluation Information Search Problem Recognition © South-Western Publishing Marketers’ Response If the consumer considers alternatives The opportunity to explain the benefits of their product or service If the consumer is brand-loyal Will work to insure the product is always available and at the price you expect © South-Western Publishing