* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exp-10 - WordPress.com
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Capacitor discharge ignition wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
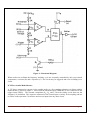
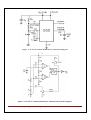
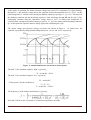
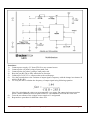
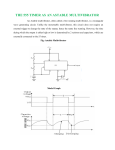
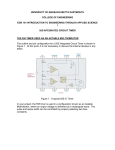
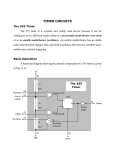
SUBJECT: ANALOG ELECTRONICS (2130902) TITLE: TO DESIGN/BUILD ASTABLE MULTIVIBRATORS USING 555 IC AND VERIFY THEIR OPERATION USING MEASUREMENTS BY OBSERVING WAVEFORMS. DOC. CODE : DIET/EE/3rd SEM EXPERIMENT NO. 10 DATE : REV. NO. : 1.00/JUNE-2015 AIM: To design/build astable multivibrators using 555 IC and verify their operation using measurements by observing waveforms. APPARATUS: Analog board of AB28. DC power supplies + 5V, from external source or ST2612 Analog Lab. 2 mm patch cords. Ohm meter. Function generator THEORY: Basically, 555 timers is a highly stable circuit capable of functioning as an accurate time-delay generator and as a free running multivibrator. The 555 timer is highly stable device for generating accurate time delay or oscillation. The device consists of two comparators that drive the set (S) and reset (R) terminals of a flip-flop, which in turn controls the 'on' and 'off cycles of the discharge transistor Q1. The comparator reference voltages are fixed at 2/3 Vcc for comparator C1 and Vcc/3 for comparator C2 by means of the voltage divider made up of three series resistors (R). These reference voltages are required to control the timing. The timing can be controlled externally by applying voltage to the control voltage terminal. Pin configuration: Figure.1: IC 555 Pin Out Darshan Institute of Engineering And Technologies, Rajkot Page 36 Figure. 2: Functional Diagram When used as an oscillator the frequency and duty cycle are accurately controlled by only two external components, a resistor (R) and a capacitor (C). The circuit may be triggered and reset on falling wave forms. IC 555 as Astable Multivibrator : A 555 timer connected to operate in the astable mode as a free-running relaxation oscillator (astable multivibrator) is shown in Figure 3. Notice that the threshold input (THRESH) is now connected to the trigger input (TRIG). The external components RA, RB and C form the timing circuit that sets the frequency of oscillation. The capacitor connected to the control input is strictly for decoupling and has no effect on the operation. Circuit does not have an input from any other circuit. Darshan Institute of Engineering And Technologies, Rajkot Page 37 Figure. 3: IC 555 as Astable multivibrator Functional Diagram Figure. 4: IC 555 as Astable multivibrator with internal structure diagram. Darshan Institute of Engineering And Technologies, Rajkot Page 38 In this mode of operation, the timing capacitor charges up toward Vcc (assuming VO is high initially) through (RA + RB) until the voltage across the capacitor reaches the threshold level of 2 Vcc/3. At this point comparator C1 switches state causing the flipflop output Q to go high i.e., Q = V(1). This turns on the discharge transistor Q1 and the timing capacitor C then discharges through RB and Q1 (pin 7). The discharging continues until the capacitance voltage drops to Vcc/3, at which point comparator C2 switches states causing the flip-flop output Q to go low, i.e., Q=V(0), turning off the discharge transistor Q1. At this point the capacitor starts to charge again, thus completing the cycle. The output voltage and capacitor voltage waveforms are shown in Figure 5. As shown here, the capacitor is periodically charged and discharged between 2 Vcc/3 and Vcc/3, respectively.. Figure. 5: Astable multivibrator waveform at various points The time T1 for which the output is ‘high’ is given by ; T1 = 0.694 (R1 + R2) C The time T2 for which the output is ‘low’ is given by; T2 = 0.694 R2C ∴ Total period T for the oscillation is; T = T1 + T2 T = 0.694 (R1 + 2 R2) C The frequency f of the astable multivibrator is given by ; Note that f will be in Hz if resistance is in ohms and capacitance in farads. Darshan Institute of Engineering And Technologies, Rajkot Page 39 Procedure: 1) Connect power supply +5V from ST2612 or any external source. 2) Connect point a to point b using a 2mm patch cord. 3) Connect point d to point f/g using a 2mm patch cord. 4) Keep the pot (R2 1M) to fully anticlockwise direction. 5) Connect pin 3 of IC55 i.e. output socket to the oscilloscope. 6) Vary the pot and observe the variation of output signal’s frequency with the change in resistance R (where, R=R1+R2). 7) To verify the above calculate the frequency of output signal using following equation 8) 9) Note: For calculating the value of R, disconnect the +5V supply and connection between point a and b. Connect ohmmeter between point a and TP1. The ohmmeter will read the value of R. Trace the waveforms of the voltage across capacitor C1 and ground. Repeat above procedure for different values of R. Darshan Institute of Engineering And Technologies, Rajkot Page 40 OBSERVATION TABLE: Sr. No. R1 R2 C T1 T2 T f CALCULATION: CONCLUSION: LAB-INCHARGE Darshan Institute of Engineering And Technologies, Rajkot H.O.D Page 41