* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy and Design Process - Study Guide - Team 6
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
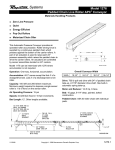
Energy and Design Process - Study Guide Name: __KEY________________________ Period: __________ Date: __________ 1. List the steps in the design process: 1. __Identify the need____ 2. ____Research/Brainstorm___ 3. ____Create Prototype___ 4. ___Test/Redesign___ 5. ___Communicate Results____ 2. List the 3 types of models used during the design process: 1. __Physical____ 2. ___Mathematical_______ 3. __Computer_______ 3. What is kinetic energy? ___Energy of motion__________________________________________ 4. Give 2 examples of kinetic energy: ___Varies – anything that moves__________________________________ 5. What two factors determine the amount of kinetic energy an object has? __Mass___ ___Speed____ 6. What is potential energy? ___Stored energy_________________________________________ 7. Give 2 examples of potential energy: _____Varies __________________________________ 8. Below are 3 types of potential energy. Complete the chart with definitions and examples of each. Type of Potential Energy Gravitational Potential Energy Description/Definition – in your own words Example(s) Stored energy due to height and position Book being held above your head Elastic Potential Energy Energy stored due to being compressed or stretched Stretched rubber band or compressed spring Chemical Potential Energy Energy stored in the chemical bonds of molecules Gasoline, food, firework before exploding 9. What 2 main factors determine the amount of gravitational potential energy an object has? _____Weight___ _____Height_____ 10. How do work and energy relate to each other? ____Energy is the ability to do work. You must have energy to do work.____________________________________________________________________________________ 11. Complete the chart below to describe each form of energy and give examples. Type of Energy Mechanical Energy Description/Definition – in your own words Total amount of PE and KE in a system Example(s) Throwing a ball, a roller coaster system Sound Energy Energy due to vibrating waves Playing a guitar *cannot travel through a vacuum Thermal Energy Heat energy Fire Electric Energy Energy that travels through electrical currents Anything that you plug in – lamp, TV, etc. Radiant Energy Electromagnetic waves / light waves Anything that lights up – lamp, flashlight, Sun * can travel through a vacuum Nuclear Energy Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom and is released when the atom is split Nuclear power plant, Sun 12. Identify the energy transformations occurring in the following situations: making toast in a toaster: ____Electric_______ changes to ____thermal_________ watching television: ___Electric______ changes to __radiant________ and ___sound_____ using a microwave: ___Electric_____ changes to ___radiant________ changes to ___thermal_____ eating an apple: ____Chemical_______ potential energy changes to ___mechanical/thermal/kinetic____ 13. Describe the Law of Conservation of Energy: _______States that energy can’t be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed______________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 14. List the 3 types of energy produced by the Sun: 1. __Radiant_____ 2. ____Thermal_____ 3. ____Nuclear_______ ****Also SOLAR**** 15. Review the picture of the roller coast below: A C B At what point does the roller coaster have the most kinetic energy? ___B__ At what point does the roller coaster have the most potential energy? ___A_____ 16. What is the formula for volume? _____length x width x height = cm3_________________________ 17. What it the formula for density? _____Mass / Volume = g/cm3________________________________ 18. A change of state of matter is an example of a __physical________ change. 19. A old metal swing set left outside in the rain starts to rust. This is an example of a __irreversible chemical___ change. 20. Mr. Smith’s class was trying to determine if the height at which a paper helicopter is dropped affects that speed that it will fall. They made paper helicopters using the same design and the same type of paper. Then, they dropped the helicopters from different heights and recorded the number of seconds it took for the helicopter to fall. Identify the variables in this experiment: Independent Variable: _____Height helicopter is dropped from________ Dependent Variable: __Time it takes to fall / speed of fall_______________ Constants: __Design_________ _______Paper_________ Below is a data table with the results of their experiment. Use the data form the table to create a bar graph. Time of Fall (seconds) 1.5 1.8 2.1 2.5 2.8 Helicopter Drop Test 3.0 2.8 2.6 Time to fall (sec) Height of Drop (meters) 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 2.4 2.2 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.0 .8 .6 .4 .2 0 1 1.5 2 Height of Drop (m) 2.5 3