* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Climate Change - WordPress.com
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Myron Ebell wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Canada wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
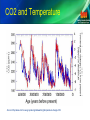
Climate Change: An Overview and Current Scenario Mihir Mathur TERI, New Delhi Presented at Seminar on Climate Change and Global Warming, 21st July 2016 Vishwa Yuvak Kendra, New Delhi Global Warming and Climate Change • What is global warming? – It generally refers to the increase in average surface temperature of Earth. • What is climate change? – It generally refers to long term shifts in climate parameters like precipitation, temperature, rainy days, extreme weather events etc. • They both are similar, but not the same Variation and Change Variation and Change Source: http://www.carbonbrief.org/media/49142/graph_temp_rise.png Climate Change: Background • The earth's climate is naturally variable on all time scales • But current increase in rate of change is also attributed to anthropogenic factors • Mainly due to greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) from human activities • Anthropogenic climate change Global Warming Effect • Rising Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions are the dominant cause of observed warming • The global average surface temperature rose 0.6 to 0.9 degrees Celsius between 1906 and 2005, and the rate of temperature increase has nearly doubled in the last 50 years. • Global Warming Potential of GHGs – – – – – Carbon Dioxide: Methane: Nitrous Oxide: Perfluoro-Methane: Sulfur Hexafluoride: 1 23 296 5700 22200 Source: IPCC AR5 SPM, Earth Observatory NASA, The Science: Carbon Cycle Source: google images The Science • Consensus among the scientific community that the climate is changing • Human influence on the climate system is clear, and recent anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases are the highest in history • The atmosphere and ocean have warmed, the amounts of snow and ice have diminished, and sea level has risen • With continued emissions the likelihood of severe, pervasive and irreversible impacts for people and ecosystems is increasing Source: IPCC SPM 2014 Anthropogenic Emissions • About half of the anthropogenic CO2 emissions between 1750 and 2011 have occurred in the last 40 years • Emissions of CO2 from fossil fuel combustion and industrial processes contributed about 78% of the total GHG emissions increase from 1970 to 2010 • The atmospheric CO2 ppm levels have increased from 275 in year 1800 to current levels of 400 ppm. • Globally each year we add approx. 2 ppm level of CO2-eq to atmosphere • Mitigation actions should target to keep the ppm levels at 450 or lower in order to maintain warming below 2°C Source: IPCC AR5 SPM, Atmospheric CO2 Levels Source: http://www.climatecentral.org/gallery/download/400000-years-of-carbon-dioxide Reference in History CO2 and Temperature • The last time atmosphere had 400 ppm CO2 concentration levels humans were not there • Earth’s average temperature was warmer by 3-4°C • That was around 3.6 million years ago • IPCC suggests 2°C as the safe limit to avoid dangerous climate change Source: http://climate.nasa.gov/climate_resources/7/ CO2 and Temperature Source: http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/paleo/globalwarming/temperature-change.html Climate Risks and Impacts Climate Change Risks • It is very likely that heat waves will occur more often and last longer, and that extreme precipitation events will become more intense and erratic in many regions. • Warming is likely to exceed 2°C • Amplification of existing risks and occurrence of new risks which will be unevenly distributed and greater for disadvantaged people and communities. Source: IPCC SPM 2014 Economic Impacts • 40% of the world's natural disasters occurred in Asia between 1999 and 2008 and accounted for 80% of disaster deaths. • Cost of climate change risks could be equal to 5% of Global GDP every year and could even go upto 20% (Stern review) • Hurricane losses could increase property insurance losses by 30 to 40 percent over the next 20 years • Katrina like storm could result into losses of around $60 billion in future Source: Development Asia March 2011, Insurance Information Institute Climate Change in India Climate Change Impacts • Dry years are expected to be drier and wet years wetter. • A 2°C rise in the world’s average temperatures will make India’s summer monsoon highly unpredictable. • Crop yields are expected to fall significantly because of extreme heat by the 2040s. • Unusual and unprecedented spells of hot weather are expected to occur far more frequently and cover much larger areas. Source: http://www.worldbank.org/en/news/feature/2013/06/19/india-climate-change-impacts The Need • India has diverse landscape and ecosystems - Long Coastline, Arid and Semi Arid Regions, Forests, Mountains • It will face varying impact of climate change – heat waves, floods, storms and cyclone, drought • Has high share of climate dependent livelihood sectors (mainly agriculture and ancillary industries) • Differing vulnerability amongst better off and poor people living in different agro ecological zones having varying developmental needs makes adaptation to climate change a highly complex task • The response capacity has to be built at local level Challenges • Incremental adaptation is not enough, deeper structural changes and social transformations are required (Pelling 2011, O’Brien 2012, Bulkeley 2013, IPCC 2014) • These transformations have to also meet the developmental needs of the people • Thus, there is adaptation deficit and development deficit • Activities should address both and should be in a Continuum (McGray 2007) Climate Actions • Government has established the National Adaptation Fund on Climate Change (NAFCC) with a budget provision of around Rs.500 crores • The focus of the fund is to assist concrete adaptation activities that reduce the effects of climate change facing communities and sectors. • The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) has been appointed as National Implementing Entity (NIE) Source: https://www.nabard.org/english/climate_change.aspx Climate Actions • NABARD is also the National Implementing Entity (NIE) for Adaptation Fund under the Adaptation Fund Board. • It is for the first time that two proposals from India were approved by AFB (US$ 3.2 million). • Project 1: Conservation and Management of Coastal Resources as a Potential Adaptation Strategy for Sea Level Rise (Executing Entity: MSSRF) USD 689,264 (Andhra Pradesh) • Project 2: Enhancing Adaptive Capacity and Increasing Resilience of Small and Marginal Farmers in Purulia and Bankura Districts of West Bengal (Executing Entity: DRCSC) USD 2,510,854 Source: https://www.nabard.org/pdf/AFB_Press_Release.pdf Managing the Unavoidable Mitigation Challenge • Evolving global consensus on mitigation commitments (Paris Agreement), but not fast enough (1992-2016) • If all commitments are met, it would still push the temperature up by 2.7°C • At current rate of emissions we would be reaching 450 ppm levels in next 25 • Mitigation actions require support of technological and infrastructural change but these are long term changes • Shrinking window of opportunity What is required? • Human Systems should be prepared to respond to effects of climate change • But this response has to be in time with the changes • Response Time < Change Time • Responses = Mitigation and Adaptation • If we respond late then we are not responding but reacting Types of Adaptation Response Source: IPCC, 2001 TERI’s Work on Climate Change 1. Coping with Climate: Assessing Policies for Climate Change Adaptation and Transport Sector Mitigation in Indian Cities (CLIMATRANS) – Urban flood modeling and its impact on transport infrastructure in three cities (Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore) 2. The governance of climate services: Improving knowledge networks for resilient and socially just societies (GovClimServices) – Governance of climate services and related risks/uncertainties and conditions for developing innovative, useable and socially just learning networks.(Maharashtra) 3. Heat Island Study: IB-Valley Industrial Cluster, Jharsuguda, Odisha (Heat Island) – Identification of temperature hotspots and adaptation measures for female agricultural labourers to reduce the impact of heat stress. TERI’s Work on Climate Change 4. Himalayan Adaptation, Water and Resilience (HI AWARE) – Will look into the temporal dimension of risks and its matches/mismatches with decision making from the community to public policy with a focus on multiple geographical scales within Indus, Ganga and Brahmaputra river basins. 5. Adapting to climate change impacts on water quantity and quality in the drylands of Maharashtra, India (TOO India) – To understand and asses the impacts of climate change on the hydrological system with respect to water availability and quality in the drylands of Maharashtra 6. Extreme Risks, Vulnerabilities and Community based Adaptation in India: A Pilot Study (EVA) – Identifying adaptation options in a participatory manner, conditions for effective implementation and identification of barriers at different levels. Way Forward • Aggressive mitigation required, immediately • Need for Climate Policy Planning Tools • Improvement in Climate Information Systems • Ecosystems as (low cost) means of Adaptation (EbA) and Mitigation • Widespread actions, led by us! Thank You! Avoid the Unmanageable: Mitigate Manage the Unavoidable: Adapt Visit us at www.teriin.org