* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Physical Science
Electromigration wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Residual-current device wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
National Electrical Code wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
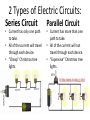
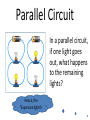
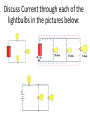
Physical Science Goal 4 Electricity and Magnetism Static Electricity • Static Electricity—electricity that is not moving. • Basic Law of Electrostatics – Like charges repel, opposite charges attract!! • How do objects become “charged”???? – Objects become charged by gaining or losing electrons!! Protons will not move!!! 3 ways to charge an object: 1. Conduction—direct contact • No contact, no conduction 2. Friction—Rubbing together 3. Induction—Rearrangement of charge of a neutral object caused by a nearby charged object! Current Electricity • Voltage will determine whether electricity will or will not flow!!!! • Resistance determines how much current flows!! – Low resistance, high current – High resistance, low current Electricity Symbols and Units Quantity Symbol in Equation Unit Symbol Unit Current I Amperes A Resistance R Ohms Voltage V Volts W V Power P Watts W Electricity Equations 2 Types of Electric Circuits: Series Circuit Parallel Circuit • Current has only one path to take. • All of the current will travel through each device. • “Cheap” Christmas tree lights. • Current has more than one path to take. • All of the current will not travel through each device. • “Expensive” Christmas tree lights. Series Circuit: In a series circuit, if one of the lights goes out, what happens to the remaining light(s)? Hence, the “Cheap lights”! Parallel Circuit In a parallel circuit, if one light goes out, what happens to the remaining lights? Hence, the “Expensive lights!! Discuss Current through each of the lightbulbs in the pictures below: Magnetism • Like Poles repel, opposite Poles attract!! Lines of Repulsion Lines of Attraction • Magnetic Field Lines always move out of the north pole and into the south pole!!! • Magnets are strongest at the poles!! • If you break a bar magnet in half, you get 2 bar magnets both with a north and a south pole!! Magnetic Domains • In a permanent magnet, the “Domains” are aligned. In a normal piece of metal, the domains are not aligned!! • You can only make a magnet from Iron, cobalt and Nickel(Iron Triad) Electromagnetism • Oersted—If a current moves through a wire, there will be a magnetic field produced around the wire. • Faraday—If you move a wire through a magnetic field, or a magnetic field through a wire, there will be a current induced in the wire!! Electromagnet • A temporary magnet. Will quit working when the current is turned off. • 3 requirements: 1. Iron Core 2. Turns of Wire(conductor) 3. Current 2 ways to strengthen Electromagnet: 1. Increase the current 2. Increase the # of turns of wire Motor vs. Generator • Motor—converts electrical energy into mechanical energy(something turns) • Generator—converts mechanical energy into electrical energy(you get electricity)