* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Population Sampling Methods Sample Problems
Survey
Document related concepts
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
The Population Bomb wikipedia , lookup
Human overpopulation wikipedia , lookup
World population wikipedia , lookup
Two-child policy wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Human population planning wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
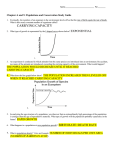
IB Senior Review Chapter 52: Population Ecology Population Ecology Population— A group of individuals of the same species living in a particular geographic area Population Ecology— Concentrates mainly on the factors that affect how many individuals of a particular species live in an area Exponential Growth Species Immigration Density Sigmoid/Logistic Growth Mortality K-Strategy Growth r-Strategy Growth Demographic Emigration Carrying Capacity Exponential Growth Natality Life History Species 1. ____________ A group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Density 2. ____________ Number of individuals per unit area or volume. Ex. White Oak trees per square kilometer in Potter County Pennsylvania 3. Demographic ____________ The study of the rise and fall of population sizes over time Natality 4. ____________ Rate of Birth (# of individuals in a given period of time) Mortality Rate of Death (# of individuals in a given period of time) 5. ____________ Immigration The movement of individuals into a population 6. ____________ Emigration The movement of individuals out of a population 7. ____________ Cap. The maximum population size that can be supported by the 8. Carrying ____________ available resources, symbolized by K. 9. Exponential. ___________ The geometric (larger the quantity gets, the faster it grows) increase of a population as it grows in an ideal, unlimited environment Sigmoid A model describing population growth that levels off as 10. __________ population size approaches carrying capacity HistoryThe series of events from birth through reproduction and death 11. Life __________ r-Strategy The concept that in certain populations, a high reproductive rate 12. __________ is the chief determinant of life history and survival 13. K-Strategy __________The concept that in certain populations, life history is centered around producing relatively few offspring that have a good chance of survival Think back to the Wissahickon Trip. How did we measure avian biodiversity? Simpson’s Biodiversity Index D = Σ(n(n -1) / N(N-1)) … 1-D Where: D = Bias corrected form for Simpson Index n = Number of individuals of one species N = Total number of individuals in community 1-D = Relative biodiversity (the closer to 1, the more diverse the community) Simpson’s Index Sample Problem: Which community is more diverse? Community #1 3 Chickadees 6 Robins 9 Carolina Wrens 2 Blue Jays Total: 20 (3 (3-1) + 6 (6-1) + 9 (9-1) + 2(2-1)) (20 (20-1)) Community #2 3 Downy Woodpeckers 2 Robins 6 Crows 2 Carolina Wrens Total: 13 (3 (3-1) + 2 (2-1) + 6 (6-1) + 2(2-1)) (13 (13-1)) D = 110 / 380 = .29 D = 40 / 156 = .26 1-D = .71 1-D = .74 Define the term random sample. A sample where every member of a population (plant or animal) has an equal chance of being selected Sample selected without bias Why is it important to take random samples? To ensure the data taken for the biodiversity or population size/distribution indices represents the whole population What is one method for estimating animal population sizes? Lincoln Index/Mark-Recapture Method (“hunting forks” activity) Population size = ((n1 x n2) / n3) Where n1 = number of individuals initially caught, marked, and released n2 = total number of individuals caught in the second sample n3 = number of marked individuals in the second sample What is one method for estimating plant distribution? Quadrat Transect Method Transects are distributed evenly across the entire site so all plants may be sampled Each quadrat is spaced evenly along the transects, again so all plants have the chance of being sampled The percent of area covered by each plant species is estimated within each quadrat which 1 meter squared in size Each of these total species percentages is divided by the total quadrat percentages (100% for one quadrat, 200% for two quadrats etc.) to get the relative percentage of each plant species Calculating the yearly change in population Change in population size per year = births – deaths + immigration - emigration Often, immigration and emigration are said to cancel out, so unless otherwise stated, assume immigration – emigration = 0 MC- 1. A population of ground squirrels has an annual per capita birth rate of 0.06 and an annual per capita death rate of 0.02. Estimate the number of individuals add to or lost from a population of 1,000 individuals after one year. a. 120 individuals added b. 40 individuals added c. 20 individuals added d. 400 individuals added e. 20 individuals lost (1000 x 1.06) – (1000 x 1.02) = + 40 individuals Population Growth Curves Exponential Growth K––––––––––––– Unrestricted growth Sigmoid/Logistic Growth Exponential phase natality much higher than mortality Transitional phase natality higher than mortality Plateau phase natality = mortality Plateau Transitional Exponential What is the general ecological feature that limits population growth? Carrying Capacity – The maximum number of individuals of one species the environment can support based on available resources These resources are known as densitydependent factors Means the size of the population is dependent on these factors. MC-2. Which of the following statements correctly describes the carrying capacity of an environment? a. The maximum rate of population growth for a species. b. The area of land that can support a denned population of species. c. The minimum population of a species that can be sustainably supported by a given environment. d. The maximum population of a species that can be sustainably supported by a given environment. MC-3. As N approaches K for a certain population, which of the following is predicted by the logistic equation? a. The growth rate will not change. b. The growth rate will approach zero. c. The population will show an Allee effect. d. The population will increase exponentially. e. The carrying capacity of the environment will increase. Name some density-dependent factors. Food supply Water supply Breeding/nesting sites Habitat/shelter Predator-prey relationship Disease Territory MC-4. Which of the following can contribute to density-dependent regulation of populations? a. the accumulation of toxic waste b. intraspecific competition for nutrients c. predation d. all of the above e. none of the above r- and K-Strategy Growth Only HL kids need to know this in depth r-Strategy Growth high reproductive rate little or no investment in offspring short lives small size can adapt to variable environments K-Strategy Growth low reproductive rate large investment in offspring long lives large size prefer stable environments MC-5. All the following characteristics are typical of an r-selected population except a. occurrence in variable environments b. high intrinsic rate of growth c. onset of reproduction at an early age d. extensive parental care of offspring e. occurrence in open habitats IB Exam Question 1. Describe a method, used by ecologists, for estimating accurately the size of a plant population. (Total 4 marks) divide sample area using transects; use quadrats; position them randomly; count the percentage of coverage of the plant species in each quadrat; count as many quadrats as possible; total (density) = total percentage of one species / total percentage (per meter squared) IB Exam Question 2. The data shows the number of flowers per flower head of a random sample from a white clover (Trifolium repens) population. 36 51 56 62 62 63 65 69 73 83 Mean = 62 Standard deviation = 12.5 What statistical percentage of the population has between 49 and 75 flowers per flower head? A. 5 % B. 32 % C. 68 % D. 95 % IB Exam Question 3. Describe the use of one technique that ecologists use to estimate accurately the size of a population of animals, including details of any calculations that need to be done. (6 marks) capture-mark-release method; capture a sample of population; example of method of capture (cages…); mark each captured individual and release; allow to settle back into the environment/ wait at least 24 hours/ until randomly dispersed; recapture as many individuals as possible; count the marked and unmarked individuals; Lincoln Index calculation: number marked originally x recaptured number marked and recaptured IB Exam Question 4. Discuss why an index of diversity could be useful in monitoring environmental change. (3 marks) an index of diversity is a measure of species diversity; can be used with plant or animal species; index diversity of species is a measure of health / stability / degree of stress of an environment; comparison of two values is a measure of change for better or worse; data can be used for policy decisions regarding the environment; measure of species richness / diversity; low diversity indicates environmental stress; IB Exam Question 5. State three factors that can affect the distribution of animal species. (1 mark) temperature, water, breeding sites, food supply, territory, predation, competition IB Exam Question 6. Explain the reasons for the sizes of animal populations within communities changing and the reasons for them staying the same. (8 marks) Natality/ birth / reproduction increases populations; As long as natality is higher than mortality; Abundant food allows increase / food shortage causes decrease; Low levels of predation allows increase / high level causes decrease; Low level of disease allows increase / high level causes decrease; Immigration increases populations; As long as immigration is higher than emigration; Population rise until a plateau is reached; This is the carrying capacity of the environment when the resources of the environment cannot support any more individuals IB Exam Question 7. Describe with the aid of a diagram the phases of a sigmoid population growth curve. (4 marks) K––––––––––––––––– 2 1. (exponential) – rapid increase in population; 2. (transitional) – slowing of growth; 3. (plateau) – leveling off, birth rate = death rate; carrying capacity labeled; Next Week There will be a short quiz on this chapter, including some IB data-based questions. Please study these notes. If you want me to email them to you, please drop me a note at [email protected] I will try to get the notes on Mr.Herb’s website. Remember, we are not covering everything, just the major topics. You also need to study on your own.