* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The First Crusade
Survey
Document related concepts
Church of the Holy Sepulchre wikipedia , lookup
Savoyard crusade wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Nicopolis wikipedia , lookup
Kingdom of Jerusalem wikipedia , lookup
Third Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Despenser's Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Albigensian Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1189–1191) wikipedia , lookup
Rhineland massacres wikipedia , lookup
Fourth Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Second Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1291) wikipedia , lookup
Northern Crusades wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
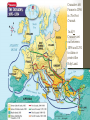
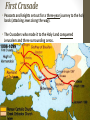
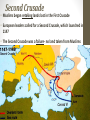
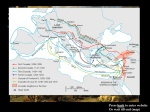
The Crusades What areas are Roman Catholic Christian? What areas are Eastern Orthodox Christian? What areas are Muslim lands? The Crusades • What were the Crusades? • A bunch of religious wars where the Western Christians tried to conquer the Holy Land and Jerusalem. • Three questions to answer: • Why did the Europeans launch the Crusades? • What happened during the Crusades? • What were the effects of the Crusades? Why did the Europeans launch the Crusades? Goal: For Christians to gain control of the holy lands The Crusades Jerusalem was controlled by the Fatimids, a Muslim empire. Muslims in Turkey took control of Persia and attacked the Christian Byzantine Empire. The Crusades The Byzantine Emperor turned to Western Europe for help. Pope Urban II responded by gathering church leaders at Clermont and calling them to arms “God wills it”. The Council of Clermont Pope Urban II called a meeting (council) in Clermont, France • The Pope described dangers faced by Byzantines • He called on Christian warriors to join together against their common enemy: the Muslims Crusaders left France in 1096 in The First Crusade. In all, 9 Crusades set out between 1096 and 1291 to claim or protect the Holy Land. First Crusade • Peasants and knights set out for a three-year journey to the holy lands (attacking Jews along the way). • The Crusaders who made it to the Holy Land conquered Jerusalem and three surrounding areas. Second Crusade • Muslims began retaking lands lost in the First Crusade • European leaders called for a Second Crusade, which launched in 1147 • The Second Crusade was a failure- no land taken from Muslims Third Crusade • 1177 – A new leader arose in Muslim world, Salah al-Din (Saladin) • Saladin set out to take back Crusader states and successfully drove European Christians out of Jerusalem • Three European Kings - Richard, Philip, Frederick set out from Europe to retake Jerusalem • Only King Richard the Lion-Hearted of England fought in Holy Land and despite winning several battles he could not retake Jerusalem Fourth and Later Crusades • After the failure of the Third Crusade, Jerusalem was still in Muslim hands. A Fourth Crusade set out in 1201 to retake Jerusalem. • Due to disorganization and poor leadership, Crusaders ended up attacking the Christian areas of Zara and Constantinople. • This crusade and the five later crusades all failed to recapture the Christian Holy Lands (most were complete disasters). What were the effects of the Crusades? Economic Changes • Crusades enhanced existing trade between Muslims, Byzantines, and Europeans (Returning Crusaders brought more goods, spices, and textiles, to Europe) • Increase in trade added to changing European economy during Middle Ages (Where does trade fit into the Manor system?) Political Changes • Crusades led to deaths of many knights, nobles • Lands of these nobles were taken over by Kings and other ambitious nobles Religious Changes • Many Christians viewed nonChristians as enemies, persecuted Jews • Holy Land Jews saw Crusaders as cruel invaders • Anti-Semitism continued for centuries