* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C11.2 Notes - Destiny High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
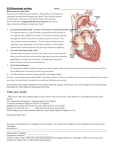
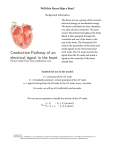
Mr. B: Anatomy & Physiology II Chapter 11 Lesson 2 Notes Today’s Objectives: 1. Describe the mechanisms that regulate the heart. 2. Describe different types of arrhythmia, or abnormal contractility conditions that can be detected via electrocardiogram. 3. Identify the components of the conduction system of the heart. Regulation of the Heart The heart is _________________________ by three different ________________________. One inside the heart; the other two _____________________________ of the heart: _____________________________ control of the heart external control the ________________________________________ system Internal Control of the Heart _____________________________________ node o Known as the “______________________________” or the SA Node o Located at the top of the ___________________________ ___________________________ o sends _________________________ impulse that tells the heart to ________________________________ o tells heart to beat ________ – __________ bpm External Control of the Heart the cardiac center o _________________________ nerve system __________________________ up the heart rate o _________________________ nerve system __________________________ down the heart rate o Parasympathetic dominant branch at ____________________ which is why your heart rate is ________________ at rest. the endocrine system o some _____________________________ speed up the heart _____________________________ o ________________________________ and norepinephrine increases heart rate The Conduction System ________________________ is the process of conveying or _______________________ types of energy, such as _______________________ impulses. Includes two areas of ____________________________ tissue and a network of conduction ________________________. These ______________________________ allow the electrical impulses formed by the ______________ node to travel to the _________________________, telling them to contract. The electrical impulse travels to the ___________________ atrium and goes through the ______________________________ node (AV Node) Once the electrical impulse ________________________ the AV node, it is carried through conducting fibers called the ________________________ of ____________________. Electrocardiogram Known as an ______________________ or ________________________ o _________________________ of the electrical activity of the ____________________________ Mr. B: Anatomy & Physiology II Chapter 11 Lesson 2 Notes o It illustrates what is happening _________________________________ o Depolarize – _______________________________ o ______________________________ – relax Cardiac Arrhythmias normal ___________________________________ condition o ______________________________ rhythm o A normal ________________________________ heart follows a ______________________________ rhythm. __________________________________ contractility condition o arrhythmia ventricle or _______________________________ contraction is not _____________________________ A beat can arrive too _____________________________ or beat in an abnormal way. _____________________________ slow heart beat – less than 60 bpm tachycardia o _____________________________ atrial contraction (PACs) o _____________________________, rather than SA node, cause beat ventricular fibrillation (VF) o ventricles contract too soon ventricular tachycardia (VT) o atria contract faster than ________________________ bpm _____________________________ ventricular contractions (PVCs) o atria contracts before SA node Can be caused by _____________________________ or _____________________________ atrial fibrillation o _____________________________ heart beat – above _________________ bpm ventricles contract faster than _____________________________ bpm heart block o _____________________________ from SA node to AV node are _____________________________ or blocked. _____________________________ – impulse delayed Second – _____________________________ blocked Third - _____________________________ blocked Defibrillators and Life-Threatening Arrhythmias automatic external defibrillator (_____________________________) o Produces an _____________________________ shock o _____________________________ heart and allows the heart to start _____________________________l rhythm o _____________________________ can use one