* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 10.2 ppt
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Salafi jihadism wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Medieval Muslim Algeria wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic extremism in the 20th-century Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Iran wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
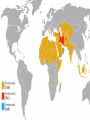
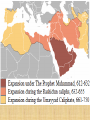
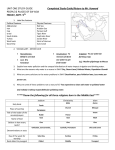
Chapter 10.2 Building a Muslim Empire OBJECTIVE • To learn about where Islam spread— Middle East and North Africa—after Mohammad’s death and • About the 2 main sects of Islam: Sunni and Shia This is important b/c…. 1. As it grew, Islam became more influential. 2. There is conflict btwn the branches of Islam, Sunni and Shiites, today. Chapter 10 vocab Kaaba 1 mosque 1 jihad 1 caliph 2 Calligraphy 3 Quran 1 Hajj 1 Sharia 1 Minarets 2 Taj Mahal 4 Focus Q: Nov. 30 • Are family Holiday gatherings fun? • What are the best/worst things about them? • How will you organize them when you are an adult? Focus Q: Nov. 17 What are the 5 pillars of Islam? Which would be the easiest for you to comply with? The hardest? Why? 1. Abu Bakr—Mohammad’s father-in-law 2. 1st ***Caliph: successor to Mohammad*** Main leader of Muslims 3. “if you worship Mohammad, Mohammad is dead. If you worship God, God is alive” Arabs Unite Under Islam 1. After several battles, Abu Bakr unites many Arab tribes based on their loyalty to Islam, not a person, leader, etc. 2. Are united under 1 leader, the Caliph • convert the remaining Arab tribes to Islam • This ends fighting among Arabs • Conquer much of Byzantine Empire and Persian (Iran) Empire entirely The Spread of Islam Easy to learn and practice. No priesthood. Teaches equality. Non-Muslims, who were “Peoples of the Book,” were allowed religious freedom, but paid additional taxes. Easily “portable” nomads & trade routes. Jihad (“Holy War”) against pagans and other non-believers (“infidels”). The Dome of the Rock Mosque in Jerusalem Mount Moriah Rock where Muhammad ascended into heaven. Divisions: Sunnis and Shias Who will be the Muslim leader? 1. Shiites: must be a descendant of Ali (son-in-law) and Fatima 2. Sunnis: any pious Muslim male from Mohammad’s tribe Shiites—10% 1. Leader must be a ***descendant of Ali (son-in-law)*** and Fatima 2. These people, called Imams, are divinely inspired religious leaders 3. Can interpret the Quran and Mohammad’s actions 4. Iran, Iraq, Lebanon, Yemen Sunnis—90% 1. Leader can be any pious Muslim male from Mohammad’s tribe 2. Called a Caliph (successor) –Is a political leader of the religious community 3. Not divine, inspiration comes from Mohammad’s example Sunni and Shiite • Conflict continues btwn them today • 90% of Muslims are Sunni • Most Shiites live in Iran, Lebanon, Iraq, Yemen How do you read this map? Laugh with me…… • What do you call the soft tissue between a shark's teeth? • The slow swimmer. • What are mixed feelings? • Watching your mother-in-law backing up towards the edge of a cliff in your new BMW. Sufis ***mystics who sought communion w/God through meditation and fasting*** 1. Iike Christian Monks or Nuns, help spread Islam 2. In both Sunni and Shiite branches Sufis dancing • form of Sama, physically form of Sama, • active meditation physically active meditation Whirling Dervish Umayyads (Sunni) 1. After Ali dies, Umayyad Caliphate rules until 750 2. ***Capital is in Damascus, Syria*** 3. Extend Arab rule to Spain, North Africa, India 4. Moved into France, defeated at the Battle of Tours—no further European advancement Umayyads (Sunni) 1. ***Reasons for success: Persians, Byzantines are weak*** 2. Also, camel and horse cavalry— aggressive, mobile—hard to stop Conquered people treated fairly 1. ***Muslim leaders impose a tax on nonMuslims*** 2. Allow Christians, Jews and others to practice their religion and follow their own laws 3. Prohibit looting, destruction of conquered lands—Why is this wise? –Will have $ for tribute, taxes Conquered people treated fairly 1. Many non-Muslims convert for a variety of reasons 2. Islam has no hierarchy or class of priests 3. ***In theory, it emphasizes the equality of all people*** –Can you think of exceptions to this? Decline of Umayyads 1. Difficult to manage a larger empire 2. Lots of $ flows in—when conquests stop— economic tensions begin 3. ***many Muslims criticize the luxurious lifestyle of Caliphs at Damascus***, different that earlier Caliphs 4. Non-Arab converts have fewer rights than Arabs 10.2 Left Side • Make a Venn diagram comparing Sunni and Shiite Muslims • Then draw 1 picture that represents Sunni’s and 1 picture that represents Shiite’s. • Color