* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT IntroGenetics
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
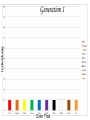
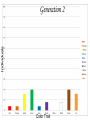
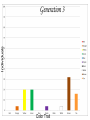
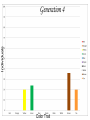
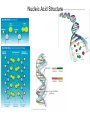
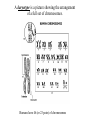
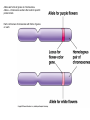
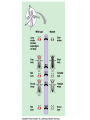
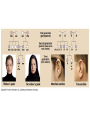
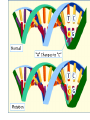
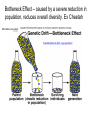
Evolution The change in life forms over time http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php Natural Selection Lab Individuals Generation 1 Color Trait Individuals Generation 2 Color Trait Individuals Generation 3 Color Trait Individuals Generation 4 Color Trait Variations Among Individuals Struggle for Survival Survival of Fittest Must Survive Eaten by predators Fittest Pass Their Traits to Their Offspring Industrial Melanism •Shift in phenotype frequencies •Light colored moths were reduced and dark color became predominant •Birds preyed on the light colored moths Natural selection – the peppered moth Peppered moths on tree trunk Natural selection – the peppered moth Dark coloured peppered moth Natural selection – the peppered moth Pale coloured, speckled peppered moth Five Tenets of Evolution by Natural Selection Variations among individuals, Large numbers of offspring, Struggle for survival, Survival of fittest must reproduce Fittest pass on their traits to their offspring SOOO What are traits?????? Population- group of organisms of the SAME species; and occupies certain area at the same time Species- organisms that can INTERBREED and produce FERTILE offspring What is a Species? • A group of actually or potentially interbreeding populations (isolated from other groups) • Gene flow can occur between populations of the same species CO 13 Chap 13 DNA Nucleic acids DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) RNA (ribonucleic acid) NUCLEOTIDES (found in nuclein) Contain a sugar, phosphate and a nitrogen base Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine Nucleic Acid Structure DNA: THE DOUBLE HELIX •Steps of ladder are • • bases (A, T, G, C) Sides of ladder are sugar & phosphate Both sides held together by hydrogen bonds Some interesting facts: A sequence of bases (A’s, C’s, G’s, and T’s) that code for a protein is called a gene All of the base pairs along all the chromosomes in an organisms are that organisms genome 95% of the A’s, C’s, G’s and T’s do not code for any proteins – only 5% of DNA sequence in a genome are genes. Genome Sizes vary from species to species. The human genome contains over 3 Billion bases (A’s, C’s, G’s, and T’s). The Human genome contains about 35,000 different genes each consisting of about 27,000 base pairs. When a cell is dividing, DNA winds up tightly and forms chromosomes in the nucleus of the cell. The genes are contained within the chromosome. A karyotype is a picture showing the arrangement of a full set of chromosomes. Humans have 46 (or 23 pairs) of chromosomes Alleles are forms of genes on chromosomesAlleles – chromosome sections that code for specific proteins traits Each cell has two chromosomes with forms of genes on each. Examples of alleles: Humans have alleles for blue eyes / brown eyes /green eyes curly/straight hair blood type A / B / O / AB The gene pool is the set of all genes, or genetic information, in any population, usually of a particular species . This also proves to be the basic level at which evolution occurs. Populations have alleles Gene pool – total of all the allele in the population Gene pool – total of all the allele in the population 18.1 MICROEVOLUTION Population -- all the members of a single species Evolution that occurs within a population = microevolution Population genetics – studies variations in gene pools Code is responsible for the phenotype- expression of the gene Evolution Changes in genetic makeup of a population The basic mechanisms of evolution Natural selection, mutation, and migration- Along with Genetic Drift A. Causes of Evolution of Populations… 1. Genetic Mutations a ) Polymorphism (two or more distinct phenotypes) b) blood types, eye color..etc c) Mutations (can be harmful or beneficial) d) Some mutations may at first appear harmful, but give an advantage if the environment changes. -- this is referred to as RELATIVE FITNESS Figure 18.3 Example of GENE FLOW •Each rat snake represents a separate population of snakes •These snake remain similar and can interbreed •This keeps their gene pools somewhat similar •They are considered subspecies . Genetic Drift In each generation, some individuals may, just by chance, leave behind a few more descendents (and genes, of course!) than other individuals. The genes of the next generation will be the genes of the “lucky” individuals, not necessarily the healthier or “better” individuals. That, in a nutshell, is genetic drift. It happens to ALL populations—there’s no avoiding the vagaries of chance. How is this different from Natural Selection? What will the next generation look like? More Brown beetles, not because they are better adapted but by chance… GENETIC DRIFT Refers to changes in allele frequencies, usually in small populations Occurs when founders start a new population or after a bottleneck Bottleneck Effect – caused by a severe reduction in population, reduces overall diversity. Ex Cheetah Most alleles are yellow! Youtubebottleneck effect –lego population FOUNDER EFFECT The founder effect is an example of genetic drift where rare alleles or combinations occur in higher frequency in a population isolated from the general population. Dwarfism in Amish communities Due to few German founders Investigating Bottleneck Effect Trying to identify if a population is going through genetic drift is quite tough because it is such a slow procedure. Once the population that has survived the bottleneck reproduces the allele frequency compared to the parent population will be completely different. Look at some case studies to investigate whether an event in the 1860s that limited genetic variation among Navajos may have led to both children of a modern-day Navajo couple being born with a rare genetic disease called XP (the abbreviation for xeroderma pigmentosum).