* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II - The Northwest School
Survey
Document related concepts
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
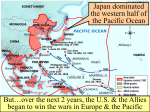
World War II And how it ended. The war in Europe ends • 1944 – Allied forces begin to take the upper hand on the European Front. • 1945 - Allies (mostly US troops) take control of Fascist Italy (parts of Italy were more w/Allies by then) - Allies (mostly Soviet and Polish troops) capture Berlin, the capitol of Germany - Mussolini is killed; Hitler commits suicide - Germany surrenders; European war is over Yalta Conference – February 1945 • The “Big 3” – Churchill, Roosevelt, Stalin • Focus was on Post-War Europe – how to handle it? • Differing agendas - Churchill wanted democratic elections in Europe - Roosevelt wanted Soviet support against Japan - Stalin wanted increased land and power Yalta Conference • The Big 3 agreed on several things, including the decision to split Berlin into 4 sectors, each to be controlled by a different Allied power • Breakdown around some of the agreements made occurred later, increasing tensions between the US/UK and the USSR Divided Germany Potsdam Conference – July 1945 • The Big 3 meet again, but: - Churchill is accompanied by Clement Atlee, who is soon to become the leader of the UK - Truman represents the US, following the death of Roosevelt (and he doesn’t trust Stalin) - The USSR now occupies much of Eastern Europe - The US has developed the Atomic Bomb Potsdam Conference – general focus • • • • How to deal with Post-War Germany How to re-allocate land in Europe How to handle reparations Alerting Japan to the need to surrender, which it does in August of 1945, following the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki • Tensions between the leaders continue The Aftermath • Europe is devastated, but the US economy benefits greatly from the war • US institutes the European Recovery Plan (also called The Marshall Plan) - Many billions of $$$ go toward rebuilding/ upgrading infrastructure/technology/ industry in Europe - Soviets/Soviet allies do not participate, increasing political/economic divisions in Europe More aftermath • The United Nations is formed • The balance of world power is massively altered • US/USSR emerge as world powers with conflicting ideologies • The era of European colonization begins to end, leaving questions and concerns – what forms of government will the newly independent nations take?