* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7 Notes Chapter 7 Notes
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
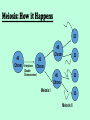
Dominance and Punnett Practice Complete Dominance Gray fur is dominant (G) to orange fur (g). Just like the Punnett squares we have been practicing. Incomplete Dominance The two alleles “blend” together to create a combination of the traits Co-Dominance Both alleles are shown in the phenotype. One is NOT dominant over the other. Sex Linked Traits Because the gene controlling the trait is located on the sex chromosome, It is linked to the gender of the individual. Usually found on the X chromosome. The result is that females will have two copies of the sex-linked gene while males will only have one copy of this gene. If the gene is recessive, then males only need one recessive gene to have a sex-link trait. Examples of Sex-linked Traits: Red-green colorblindness Male Pattern Baldness Hemophilia Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Dominant vs. Recessive • Genotype= the alleles that you have for a trait • Phenotype= the physical expression of those alleles • A person with a dimpled chin can have the genotype DD or Dd • A person with a non-dimpled chin can only have the genotype dd More Definitions •Homozygous= two of same allele (DD or dd) •Heterozygous= two different alleles (Dd- also called hybrid) Human Chromosomes •46 total chromosomes, 23 pairs •23rd pair = sex chromosomes (female = XX , male = XY) • The other 22 pairs are called autosomes • ALL egg cells carry a single X; sperm carry either an X or a Y • This means a woman can ONLY give an X chromosome, a man has a 50/50 chance of giving an X or a Y Meiosis • Meiosis is the process of making gametes (sperm and eggs) • Gametes have half the number (23) of chromosomes of the original cells (46) • Meiosis turns one 46 chromosome cell into four 23 chromosome cells Meiosis: How it Happens 23 46 Chrom 46 Chrom 23 92 Chrom Interphase (Double Chromosomes) 46 Chrom 23 Meiosis I 23 Meiosis II After Meiosis A sperm cell and egg cell, each with 23 chrom., fertilize to form a zygote. + 23 = 23 The cell of the zygote divides/grows to become an embryo, and eventually a baby! The zygote has 46 chromosomes! Muy Importante! Meiosis is necessary because if you merged two cells with 46 chromosomes each to make a baby, you would get a 92 chromosome mutant! You must half the number of chromosomes to get sperm + egg = 46! Why Meiosis? Evolutionary Advantage • Sexual reproduction increases the genetic variety in a population • Greater variety = stronger population • Sexual reproduction always involves the combining of genes from two different organisms to form a zygote • Plants, animals, fungi, protists… Asexual Reproduction • Asexual reproduction also exists in simple organisms, but makes a clone of the parent • This DOES NOT increase genetic variety • Some organisms do both types of reproduction • Potatoes form sprouts that are clones of themselves. • They can also make seeds/sperm to reproduce with neighboring plants.