* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download L1 Energy - Don`t Trust Atoms
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
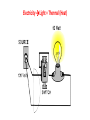
Energy L1: Introduction to Energy Learning Objectives: 1. Recall the different forms of energy. 2. Understand the law of conservation of energy. 3. Describe energy transfers. Task • Can you think of all the different forms of energy? • Write down as many types of energy as you can think of – HINT: there are 9. Types of energy • • • • • • • • • Light Sound Thermal (heat) Electricity Chemical Elastic or Strain Kinetic (movement) Gravitational Potential Nuclear (from nucleus of atoms) Types of energy • • • • • • • • • Light Sound Thermal (heat) Electricity Chemical Elastic or Strain Kinetic (movement) Gravitational Potential Nuclear • Which types are stored energy? Types of energy • • • • • • • • • Light Sound Thermal (heat) Electricity Chemical Elastic or Strain Kinetic (movement) Gravitational Potential Nuclear • Fuels store chemical energy • Stretched objects store elastic energy. • Gravitational potential energy is the energy stored in objects above the ground. Energy changes Instructions: For each demonstrated action describe: a) What happens b) Draw energy changes as in the example. e.g. A book hitting the floor: Kinetic energy Sound + thermal (heat). Electricity Light + Thermal (Heat) Gravitational Potential Kinetic + Elastic + GP Elastic (Strain) + Gravitational Potential Gravitational Kinetic Sound + Thermal Chemical Light + Thermal (Heat) Chemical Kinetic + Thermal (Heat) + Sound Electricity Kinetic + Sound + Heat Law of Conservation of Energy • Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only change form. • We say that energy is transferred from one type to another. • This means that in an energy transfer, the amount of energy going in must be the same as the amount of energy coming out (only the type of energy is different). Energy Transfers • Energy is measured in joules (J). • Example: Light bulb 100 J Electrical energy 70 J light energy + 30 J heat energy Video • https://www.brainpop.com/science/energy/formsofenergy/