* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mechanics and Properties of Matter Revision Questions Multiple
Survey
Document related concepts
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic mass wikipedia , lookup
Variable speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
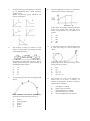
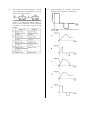
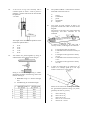
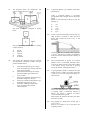
Mechanics and Properties of Matter Revision Questions Multiple Choice and Short Answer Please Note: These questions come from an earlier version of the syllabus. Use g = 10 ms-2. Some of these questions represent very difficult problem solving. Not all areas of the course are covered, for example there are no questions on buoyancy. Answers are at the end. 5. 1. A boy drops a stone down a dry well. If he sees the stone strike the bottom after 3 seconds, how deep is the well? A B C D E 2. A mass of 1 kg hangs from a spring balance which is suspended on the inside of a small rocket. 15 m 30 m 45 m 60 m 90 m A trolley is given a sharp push along a rough horizontal bench. Which distance—time graph represents its subsequent motion if distance is measured from the starting-point of the trolley? What will the balance read when the rocket is accelerating upwards from the earth’s surface at a constant rate of 2 ms-2 ? A B C D E 6. 3. A lunar module package is designed to withstand an impact of 10 m s-1. The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is 1/6 of that on the earth. The heights that the package can be safely dropped from on the earth and moon are 4. A parachutist of mass 50 kg descends towards the Earth at a constant velocity of 2 ms-1. The upward force acting on him is A B C D E 10 N 25N l00 N 200 N 500 N Zero 2N 8N 10 N 12 N A 20 N force acts on a box as shown below. Which line of the following table correctly shows the horizontal and vertical components of the force? 7. An object moving in a straight line is acted on by an unbalanced force which decreases steadily to zero. Which velocity-time graph represents the motion of the object? 10. The force applied to a block on a frictionless surface varies as shown in the graph. If the block was initially stationary and then moves in a straight line, what will be its kinetic energy after it covers a distance of 4 metres? A B C D E 11. 8. 9. Two trolleys, P and Q, are held on a level surface as shown below. The trolleys are then released simultaneously. 30 J 40 J 60 J 70 J 80 J A steel ball of mass m is released from point P, and rolls along the curved curtain rail shown. Neglecting any effects due to friction, what is the ratio speed of trolley P: speed of trolley Q immediately before impact? Neglecting friction, the kinetic energy of the ball at point Q is given by A B C D E A B C D E 1:4 1:2 1:1 2:1 4:1 A projectile moves from P to T along the path shown. 12. A B C D E point P point Q point R point S point T. point P mg √(x2 + y2). The pressure of a gas can be affected by factors such as its mass, its density, its volume, its temperature. Pressure is inversely proportional to volume if A B C D E If air resistance can not be ignored, the projectile has maximum kinetic energy at mgX mgy mg(x + y) mg(y — x) mass alone is constant density alone is constant temperature alone is constant mass and density are constant mass and temperature are constant. 13. A sample of oxygen gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure occupies a volume of 1 X 105 litres. The temperature and pressure are now altered until all the gas has been liquefied. The volume of liquid oxygen produced is approximately A B C D E 14. 1 X 102 litres 1 X 103 litres 1 X 104 litres 1 X 105 litres 1 X 108 litres 15. A car driver presses the accelerator sharply when the traffic lights go green. The unbalanced force on the car varies with time as shown. The graphs I to III below attempt to show the variation with time of I II III A man weighs 800 N and stands on an accurate weighing-machine in a lift. The reading on this weighing-machine is 820 N. This indicates that the lift is A B C D E the car’s displacement; the car s speed; the car’s acceleration. stationary moving upwards at a steady speed moving downwards at a steady speed accelerating upwards accelerating downwards. Which of these graphs is/are correct? A B C D E I only II only I and III only II and III only I,II and III 16. A block X of mass 3 kg is accelerated from rest by a force of 5 N for 2s. An identical block Y is accelerated from rest by a force of 5 N for 4s. The ratio of the kinetic energy of X to the kinetic energy of Y after acceleration is A B C D E 17. 20. 5:3 3:4 2:1 1:2 1:4. Assuming that the temperature changes are negligible, the pressures in atmospheres in flask Y become respectively The diagram below shows a block moving down a 30O slope, at a constant speed. The weight of the block is 20 N. 21. From the above information, which entry in the table is correct? 18. Flasks X, Y and Z have the same volumes. Y contains air at a pressure of 6 atmospheres. X and Z have been evacuated and the taps are closed. Tap 1 is now opened, followed a short time later by Tap 2. The kelvin temperature of a gas varies directly as A B C D E the average momentum of the molecules the average inertia of the molecules the average velocity of the molecules the average kinetic energy of the molecules the average potential energy of the molecules. 22. During an experiment involving a fixed mass of gas, the kelvin temperature is trebled and the volume is doubled. Due to these changes, the pressure is 23. A car is travelling at 15 ms-1 It accelerates uniformly for 5 s to a speed of 25 ms-1 Calculate the distance gone by the car during the acceleration. 24. A tractor of mass 1000 kg pulls a trailer of mass 1000 kg along a horizontal road. The total resistance to motion has a constant value of 4000 N. One quarter of this resistance acts on the trailer. When the acceleration is 2 ms-2, what is the force exerted on the tractor by the tow-bar? Two trolleys are travelling in the same direction, as shown below. The trolleys collide. After impact they move off together. The amount of kinetic energy lost is A B C D E 19. 4J 6J 12 J 14 J 18 J. The equation s = ut + ½at2 can be derived from A B C D E the area under a velocity—time graph the area under an acceleration—time graph the slope of a velocity—time graph the slope of a displacement—time graph the slope of an acceleration—time graph. 25. The graph below shows the force acting on a body over a period of 6 seconds. 29. Two trolleys are joined together by a thread and are pulled along a level bench by a force of 12 N, as shown. One second after starting from rest, the thread breaks at X. Neglecting possible effects of friction, which pair of statements correctly describes the motion of each trolley after the thread breaks? What is the momentum gained by the body in this time? 26. A trolley of mass 1 kg travelling at 3 ms-1 collides with, and remains attached to, a stationary trolley of mass 2kg. What is the change in momentum of the 1 kg trolley? 27. Which one of the following pairs contains one vector and one scalar quantity? 30. A B C D E 28. displacement; acceleration power; speed work; potential energy force; kinetic energy momentum; velocity A wheel nut falls straight down from a helicopter which is descending vertically at a constant speed of 5 ms-1. The wheel nut strikes the ground 5 s later. Assuming that the effect of air resistance on the nut is negligible, how far does the nut drop? A B C D E 50 m 55 m l00 m 125 m 150 m A block of mass 3 kg is held at rest on a friction-free surface inclined at 300 to the horizontal. Two seconds after the block is released, the component of the weight (F) acting down the slope, and the distance (d) travelled are 31. An inelastic collision takes place between a moving object and a stationary object of equal mass. Which of the following quantities is/are conserved for this system in this situation? I II III A B C D E 32. I and II only I and III only II and III only III only I,II and III The pressure exerted on the table by the cylinder resting in the position shown is 33. 34. 2 Pa 20 Pa 200 Pa 2000 Pa 20 000 Pa.. Specific heat capacity can be found from the experimental results given below. Which one of the following measurements creates most uncertainty in the calculated value of the specific heat capacity? A B C D E A girl on a bicycle is cycling at a constant speed. The combined kinetic energy of the girl and her bicycle is 1600J. She then slows down. What is the new combined kinetic energy of the girl and her bicycle when their COMBINED MOMENTUM is half its previous value? 36. The volume of a certain mass of air at 270C is 3m3. If the temperature is increased to 127 0C without changing the pressure, what will the new volume of the air be? 37. A car is accelerating uniformly in a straight line. Which of the following displacement— time graphs could represent its motion? Momentum Total energy Kinetic energy A solid cylinder of mass 20kg has a flat base of area 0.1 m2 in contact with the level table on which it rests. A B C D E 35. Power = 2000 + l0 W Time = 300 + 1 s Mass = 5.0 + 0.2kg Final temperature — 50 + 0.5 0C Change in temperature = 30 + 1 0C In the diagram, a force of 10 N is pulling a trolley along a level surface. If the trolley moves 3 m against a frictional force of 2 N, what is the work done against friction? 38. The acceleration due to gravity is 10 ms-2 on Earth and 26 ms-2 on another planet. On Earth, a ball released from rest takes 0.5 s to drop through a certain height. Assuming that the resistance of the atmospheres can be neglected in both cases, the time for the ball to drop from rest through the same height on the other planet would be 39. The forces shown below act on the trolley of mass 2kg which is originally at rest on a level surface. The velocity—time graph for the trolley is 40. An object of mass 2kg, initially at rest, is acted upon by the changing force shown on the graph. 42. Two vehicles moving along a linear air track collide with each other. After impact, they stick together and continue to move along the track. Which of the following statements is/are correct? I II III What is the change in momentum produced by the force? 80 kgms -1 40 kgms -1 20 kgms -1 10 kgms -1 5 kgms -1 A B C D E 41. Ball P is projected vertically upwards with a velocity v, while an identical ball Q is projected at the same time with velocity 2v at an angle of 30o to the horizontal. In the absence of air resistance, which of the following statements is/are true? I II III P and Q will hit the ground at the same instant. The vertical deceleration of P is greater than that of Q. P will rise to a greater vertical height than Q. A B C D E I only I and III only II only II and III only I, II and III A B C D E The collision is inelastic. The total change in momentum is zero. The total change in kinetic energy is zero. None of these I only II only I and II only I, II and III 43. Which of the following graphs shows the relationship between the volume of an enclosed mass of ideal gas and its temperature when the pressure is kept constant? 44. Graphs X and Y show the pressure, volume and temperature of a fixed mass of gas during an experiment in which the gas starts with the conditions shown at point 1 and undergoes changes to the conditions shown at point 2. Which of the following statements is/are correct? I II III A B C D E 45. The gas expands according to Boyle’s Law. The gas is compressed at constant temperature. The pressure decreases at constant temperature. I only III only I and II only I and III only II and III only A ball is projected horizontally with a velocity of 30ms-1 from the top of a high tower. After what time will its velocity be in the direction 45o to the horizontal, if air resistance can be neglected? 46. The diagram shows a collision between two trolleys X and Y. The momentum of trolley X before and after collision, and the momentum of Y before the collision are as indicated. Both trolleys are travelling to the right after they collide. What is the momentum of trolley Y after the collision? 47. In the diagram shown below, the pendulum bob, of mass 2kg, is released from position B, 80cm above the lowest position of the bob at A. 50. A motocross rider takes a jump which is 1.25 m high. He lands l0 m from the base of the jump. Assuming that he was travelling horizontally when he left the edge and that air resistance can be ignored, at what speed did he approach the jump? A B C D E Assuming no air resistance, what is the speed of the bob when it reaches A? 51. 48. The graph below represents the motion of a body falling freely in a vacuum. 5 ms-1 10 ms-1 15 ms-1 20 ms-1 25 ms-1 Figure 1 shows a trolley of mass 2kg moving to the right with a constant velocity of 10ms-1. The quantity y plotted along the vertical axis is A B C D E 49. speed distance acceleration force kinetic energy A car is travelling at 25ms-1. The brakes are applied for 5 s and the speed is reduced to 15ms-1. How far does the car travel in this time if the deceleration is uniform? A B C D E 25 m 50 m 75 m l00 m 175 m At a certain instant, a constant force of 6 N is suddenly applied to the trolley in a direction to the left as shown in Figure 2. The acceleration of the trolley while this force acts is A B C D E 3 ms-2 to the right 3 ms-2 to the left 7 ms-2 to the right 12 ms-2 to the right 12 ms-2 to the left. 52. A car of mass m is travelling with a constant velocity up a hill at an angle to the horizontal, as indicated. 55. 53. m g cos + F m g cos — F m g sin + F m g sin — F mg + F sin. 56. A projectile is fired at an angle to the horizontal. The vertical and horizontal components of velocity at the instant of firing are as shown. What will be the vertical and horizontal components of velocity after 5 s, if air resistance is negligible? 0.14 kgm-3 1.4 kgm-3 14 kgm-3 140 kgm-3 1400 kgm-3 A B C D E If F is the resultant resistive force acting on the car, the effective engine force needed to maintain this constant velocity must be A B C D E The pressure gauge on an oxygen cylinder of capacity 0.1 m3 reads 1.0x 107 Pa. The density of oxygen at atmospheric pressure (1.0xl05 Pa) is 1.4 kgm-3. Assuming that the temperature remains constant, what is the density of the oxygen in the cylinder? The acceleration-time graph of an object starting from rest is shown below. What is the velocity after 6 s? 57. A ball X of mass 1 kg travelling at 5 ms-1strikes a stationary ball Y of mass 2kg. If ball X bounces back along its original path at 1 ms-1, what will be the speed of ball Y? 58. The statements below were found in a pupil’s notebook. I II III Acceleration, velocity and displacement are all vector quantities. Force and weight are vector quantities but mass is a scalar quantity. Time, distance and speed are all scalar quantities. Which of these statements is/are correct? A B C D E 54. A motorcycle safety helmet has a soft inner lining which is compressed on impact with the skull. This design protects the skull because it A B C D E decreases the impulse applied to the skull increases the time of impact of the skull decreases the time of impact of the skull decreases the change in momentum of the skull increases the change in momentum of the skull. I only II only III only II and III only I, II and III 59. A mass of 0.060 kg is suspended from a spring balance inside a lift. The lift accelerates downwards at 4.0 ms-2. What is the reading on the spring balance during this acceleration? A B C D E 0.60N 0.24N 0.36N 0.84N 24N 60. The graph below shows how the acceleration of a rocket, in outer space, changed during a l0s period. The rocket motors produced a constant thrust of 4.0 x 104N. How much fuel was used in the l0s period? A B C D E 0.4 x l03 kg 1.6 x l03 kg 2.0 x l03 kg 2.4 x l03 kg 4.0 x l03 kg 61. The speed-time graph below represents the motion of an object moving along a straight line with an initial speed u and a speed v after time t. The average speed during this time interval t is given by 62. A steel ball of mass m is released from point P and it moves along a track which is bent into a loop, as shown. Neglecting friction, the kinetic energy of the ball at point Q is given by A B C D E mgx mgy mg(x + y) mg(y-x) mg√( x2 + y2) 63. A shell is fired from a gun at an angle to the horizontal. Graphs are drawn of its horizontal component of velocity Vh and its vertical component of velocity Vv , against time t, up to the time when the shell reaches its maximum height. Assuming air resistance to be negligible, which pair of the following graphs is correct? 64. The motion of an object of mass 2 kg over a 6 s period is described on the following velocity-time graph. There are no opposing forces acting on the object which is moving in a straight line along a horizontal surface. Which of the following can be calculated from the information given? I II III A B C D E 65. 66. The average acceleration over the 6 s period The kinetic energy of the object after 3 s The work done on the object during the 6s period 67. One million kilograms of water per minute flow through the turbines of a hydroelectric power station, after falling through a height of 50 m. The turbines develop a useful power output of 5MW. Calculate the percentage efficiency of the energy conversion. 68. A bicycle pump has its barrel full of air at a pressure of 1.0 x l05 Pa. The pressure in the tyre which is to be inflated is 1.5 x l05 Pa. If the original volume of air in the barrel is 600 cm3 and there is no temperature change during the movement of the piston, what will be the new volume of air in the pump when the tyre valve is just beginning to open? 69. The velocity—time graph for the vertical component of the velocity of an object thrown upwards and falling onto the roof of a building is shown below. I only I and II only I and III only II and III only I,II and III A fixed mass of gas condenses at atmospheric pressure to form a liquid. By how much does its density increase and by how much does the spacing between its molecules decrease? In a Test Match, a cricket ball follows the path shown from X to V. A fielder at Z starts running when the ball is directly overhead at H. What is the average speed of the fielder during his run from Z to Y, where he catches the ball just before it touches the ground? The height of the building is A B C D E l0 m 40 m 45 m 50 m 80 m. 70. Two trolleys are joined together by a thread and are pulled by a horizontal force of 12 N along a level track as shown. 71. The acceleration of an object which starts from rest varies with time as shown below. One second after starting from rest, the thread breaks at X. Neglecting possible effects of friction, which statements correctly describe the motion of both trolleys after the thread breaks? Which graph is the corresponding velocity— time graph? 72. For an inelastic collision, between two linear air track vehicles, which of the following statements is/are true? I II III A B C D E 73. 74. The graph below shows the variation with time of the force exerted on a body of mass 2 kg. The total momentum of the vehicles is conserved. The total kinetic energy of the vehicles is conserved. The total energy remains constant. I only II only III only I and II only I and III only During the four seconds, the momentum of the body changes by The graphs below show the horizontal and vertical components of velocity of a projectile, from the moment it is fired until it lands 8 s later. A B C D E 75. 1.5 kg ms -1 3 kg ms -1 10 kg ms -1 20 kg ms -1 32 kg ms -1 A pendulum bob of mass 2kg is released from P. Its speed at the lowest point Q is v. The mass of the bob is reduced to 1 kg and it is released again from the same point, P. Assuming that frictional effects can be neglected, its speed at Q will now be What is the speed of the projectile 2s after firing? A B C D E 15 ms-1 17.5 ms-1 20 ms-1 25 ms-1 35 ms-1 76. An object moves from rest and travels with a constant acceleration. The correct kinetic energy—time graph of its motion is 77. Gas in a cylinder is at room temperature and us pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure. Some of the gas is released into the atmosphere and the cylinder is then re-sealed. What would a graph of pressure/volume for the gas in the cylinder look like while the gas is being released? 78. A balloonist, rising at a constant speed of 15ms-1, drops a sandbag overboard. Assuming that the air resistance on the sandbag is negligible, how long does it take to return to the height at which it was released? 79. An object of mass 10kg is moving down a slope, as shown in the diagram, with a constant acceleration of 10ms-2. An applied force of 200 N acts down the plane. The component of weight down the plane is 50 N. What is the value of the friction force opposing the motion? 80. A projectile fired at an angle of 45o to the horizontal has an initial vertical component of velocity of 30ms -1. What is the maximum height reached by the projectile, assuming that air resistance is negligible? 81. The following graph shows how the force applied to an object of mass 5 kg varies with time. The object is initially at rest. The corresponding displacement-time velocity-time graphs are shown by and 82. A lift on an oil rig rises vertically with a constant speed of 2.0ms-1. After it passes a platform, a spanner falls from the lift and hits the platform 3.0 s later. 84. The product FORCE x VELOCITY could be measured in the same units as A B C D E 85. energy acceleration power momentum impulse. Two linear air track vehicles, P and Q, are projected towards each other as shown in the diagram. The masses of P and Q are 0.4kg and 0.2kg respectively and their velocities are as indicated. The height of the lift above the platform at the instant the spanner falls is A B C D E If vehicle Q rebounds to the right with a velocity of 2ms-1, what happens to vehicle P? 30 m 39 m 45 m 51 m 90 m. A B C 83. Two masses are joined together by string Y and then hung from a beam using string X. D E 86. It is stationary after the collision. It rebounds to the left with a velocity of 1 ins-1. It continues to the right with a velocity of 1 ins-1. It rebounds to the left with a velocity of 7 ms-1. It continues to the right with a velocity of 7 ms-1. A skier of weight 700 N is pulled up a 20o incline at a constant speed by a tow rope which is acting at 35o to the incline. String X is burned through using a candle. Neglecting the mass of each string, what is the tension in string Y I II BEFORE string X is burned through, and AFTER string X is burned through? When he has moved 20 m along the incline, the gravitational potential energy (in joules) gained by the skier is given by A B C D E 700 x 20 sin 20o 500 x 20 cos 35o 700 x 20 cos 20o 500 cos 35o x 20 sin 20o 700 sin 20o x sin 55o 87. When a substance changes from liquid to gas at atmospheric pressure, its density changes by a factor of the order of A B C D E 88. 92. 10-5 10-4 10-3 10-2 10-1 A B C D E The speed—time graph for a vehicle moving in a straight line is shown below. 93. 12 000 N 14 400 N 24 000 N 26 400 N 48 000N A competitor completes the following sequence of displacements in 10 minutes during part of an orienteering event. Which entry in the following table gives the competitor’s total displacement, average speed and average velocity for this part of the event? What is the average speed of the vehicle during the 25 seconds? 89. A rocket of mass 1200 kg rises vertically from a planet which has a gravitational field strength of 20Nkg-1. The rocket accelerates away from the surface of the planet at 2 ms-2. What force must the rocket motors produce to give this acceleration? A ball is projected horizontally from the top of a cliff with a speed of 40ms-1. Assuming no air resistance, what is the speed of the ball 3 seconds after it leaves the edge of the cliff? 90. Two trolleys are moving in the same direction as shown below. The trolleys collide and move off coupled together after impact. How much kinetic energy does the system lose during the impact? 91. The pressure of a fixed mass of gas is 200 kPa. What is the new pressure of the gas after its kelvin temperature has been trebled and its volume has been doubled? 94. An object travelling at 20ms-1 has 500J of kinetic energy. After undergoing an acceleration, the value of its kinetic energy is increased to 2000J. What is the new speed of the object? A B C D E 40 ms-1 60 ms-1 80 ms-1 160 ms-1 320 ms-1 95. The speed—time graph for a train on a straight, level track is shown below. Which of the following shows the corresponding displacement—time graph for the train? 96. The diagram shows the view from above a level, frictionless table, where a 1 kg mass is being accelerated by a horizontal force acting along direction OP. Which of the following arrangements would produce the same component of acceleration along direction OP if the forces act horizontally on the masses shown? 97. The diagram shows the dimensions and masses of three cubes P, Q and R. 99. A physical quantity y is related to three other quantities by where represents density, g represents gravitational field strength and h represents height. Which of the following could be a unit for quantity y? A B C D E The three blocks are arranged as shown below. 100. Nm Nm-2 N kg-1 kg m-3 kg m-2 A ball is thrown horizontally from the top of a cliff. It takes 2 seconds to strike the water below and it enters the water at 45o to the horizontal. The pressure at the surface where Q makes contact with R is A B C D E 98. 833 Pa 2222 Pa 3750 Pa 7500 Pa 20 000 Pa The volume of a fixed mass of gas is halved, the temperature remaining constant. The gas pressure doubles due to A B C D E each molecule delivering on average twice the impulse per collision with the walls of the container each molecule delivering on average the same impulse per collision but twice as often the forces of repulsion between the gas molecules being twice as great the forces of attraction between the gas molecules being twice as great molecules colliding with the walls twice as often because of their increased speed. Assuming that the acceleration due to gravity is 10 ms-2 and that air resistance is negligible, what must be the initial horizontal velocity of the ball? 101. The acceleration due to gravity on a certain planet is 2 ms-2. An astronaut, who has a mass of 50 kg on Earth, travels to this planet. What is her kinetic energy when she is moving across the surface of the planet at l0ms-1? 102. A spring-loaded cylinder is mounted at right angles to the top surface of a trolley and a ball is laid on top of the compressed spring, as shown below. The mass of the ball is exactly the same as the mass of the adapted trolley. When the trolley is moving along a horizontal runway at 20cms-1 the spring is released by remote control and the ball is ejected. What will be the speed of the trolley Just after the ball is ejected? 103. The volume of a fixed mass of ideal gas is 12 m3 at 270C. What is the volume at 127 0C and twice the original pressure? Answers 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 C E A E E E C D A D D E A D B E E B A C D C 100 m 3000 N 20 kg ms-1 2 kg ms-1 D E C A A D C 6J 400 J 4 m3 B C A B A D D D 3s 8 kg ms-1 4 ms-1 A C A B C D B D 10 ms-1 3 ms-1 E C B A 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 D A E C 12 ms-1 60 % 400 cm3 B C D E D D C E E 3s 150 N 45 m A B B C A C C 10 ms-1 50 ms-1 15 J 300 kPa D C A A C B B B 20 ms-1 2500 J 10 cms-1 8 m3