* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 08 SFT2841 connected..
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
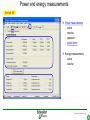
Current source wikipedia , lookup
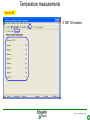
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
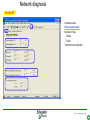
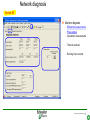
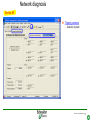
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
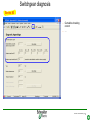
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
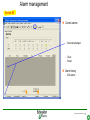
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
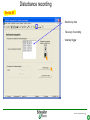
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
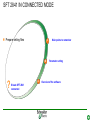
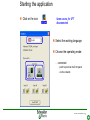
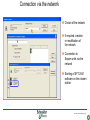
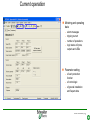
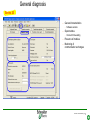
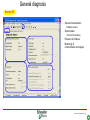
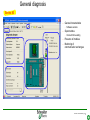
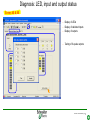
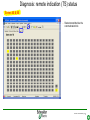
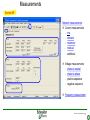
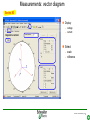
SFT 2841 IN CONNECTED MODE Prepare setting files C B ? A Situate SFT 2841 connected Main points to remember Parameter setting Overview of the software Starting the application Click on the icon Same access for SFT disconnected Select the working language Choose the operating mode: – connected – point to point via the front panel – via the network SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 2 Connection via the network Choice of the network If required: creation or modification of the network Connection to Sepam units via the network Starting of SFT 2841 software on the chosen station SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 3 SFT 2841 expert UMI The protection and parameter setting data may be saved. Reports may be edited. SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 4 PARAMETER SETTING C B ? A Situate SFT 2841 connected Main points to remember Parameter setting Overview of the software Current operation Metering and operating data – – – – alarm messages tripping current number of operations logic status of inputs, outputs and LEDs Parameter setting – of each protection function – of control logic – of general installation and Sepam data SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 6 Logipam – – – – Selection Choice in the list Apply Activate – Delete – Download onto the PC – Automatic updating SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 7 Logipam internal resources LOGIPAM: – – – – internal bits counters clocks delays SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 8 General information on connected mode – – – – – – Connection Sepam type Sepam name Code operating mode Remote control Internal clock SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 9 General diagnosis Series 20 – General characteristics – Software versions – Sepam status – Clock with time-setting – Presence of modules – Monitoring of communication exchanges SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 10 General diagnosis Series 40 – General characteristics – Software versions – Sepam status – Clock with time-setting – Presence of modules – Monitoring of communication exchanges SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 11 General diagnosis Series 80 – General characteristics – Software versions – Sepam status – Clock with time-setting – Presence of modules – Monitoring of communication exchanges SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 12 Diagnosis: LED, input and output status Series 40 & 80 – Display of LEDs – Display of validated inputs – Display of outputs – Testing of 3s pulse outputs SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 13 Diagnosis: remote indication (TS) status Series 40 & 80 – Status transmitted via the communication link SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 14 Measurements Series 80 Network measurements: Current measurements – rms – demand – maximum – residual – additional Voltage measurements – phase-to-neutral – phase-to-phase – positive-sequence – negative-sequence Frequency measurement SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 15 Measurements: vector diagram Series 80 Display – voltage – current Select – scale – référence SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 16 Power and energy measurements Series 80 Power measurements – active – reactive – apparent – power factor Energy measurements – active – reactive SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 17 Temperature measurements Series 80 MET 148 modules SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 18 Network diagnosis Series 80 – Unbalance ratio – Phase displacement – Number of trips – Phase – Earth – Total Harmonic Distortion SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 19 Network diagnosis Series 80 Machine diagnosis – Differential measurements – Phase angles – Impedance measurements – Thermal overload – Running hours counter SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 20 Network diagnosis Series 80 Tripping contexts – Selection by date SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 21 Switchgear diagnosis Series 80 – Cumulative breaking current – … SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 22 Alarm management Series 80 Current alarms – Not acknowledged – Clear – Reset Alarm history – 200 alarms SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 23 Disturbance recording Series 80 – Selection by date – Recovery of recording – Voluntary trigger SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 24 On-line help Series 80 On-line help SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 25 MAIN POINTS TO REMEMBER C B ? A Situate SFT 2841 connected Main points to remember Parameter setting Overview of the software Network diagnosis functions Tripping current This function gives the RMS values of the phase currents and residual currents at time of the last trip. The measurement is defined as the maximum RMS value measured during a 30 ms interval after the activation of the O1 output. Acquisition of tripping current TRIPI1. RETURN SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 27 Machine operating assistance functions Current phase displacement Current phase displacement between the main phase currents (I) and additional phase currents (I') (1, 2, 3) is calculated for each phase. The angle is measured in the clockwise direction. The information is used to check Sepam wiring when 87T protection functions are implemented. I I’1 RETURN SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 28 Metering functions Power factor (Cos) This function gives the phase displacement between the phase currents and the phase-to-neutral voltages. The + and - signs and the IND (inductive) and CAP (capacitive) indications give the direction of power flow and the type of load. Q V -CAP +IND I P -IND +CAP RETURN SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 29 Network diagnosis functions Phase displacement This function gives: Io 0 Vo – phase displacement measured between the residual voltage and residual current in the trigonometric direction – phase displacement between the V1, V2, V3 voltages and I1, I2, I3 currents respectively, in the trigonometric direction I V The measurements are used during Sepam commissioning to check that the voltage and current inputs are wired correctly. The angle is positive when the current is leading compared to the voltage (trigonometric direction). the angle is modified by 180° by the setting incomer / feeder. RETURN SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 30 Machine operating assistance Differential / through current Differential / through current is calculated for the implementation of the differential protection functions 87T and 87M. It is calculated for each phase by: I diff I I I I It 2 When a transformer is used (87T), the Idiff / It calculation takes into account the vector shift and transformation ratio.. The Idiff / It value is expressed with respect to In, the rated current of the main channels. Idiff = Iadjusted + I’adjusted It = max ( Iadjusted , I’adjusted ) RETURN SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 31 Metering functions Physical values measured Sepam measures the following physical values: – – – – phase current (3I) residual current (Io) phase voltage (3V) residual voltage (Vo) Each measured signal is processed by Sepam to produce all the values necessary for the metering, diagnosis and protection functions. RETURN SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 32 Metering functions RMS measurement RMS measurement is only used by the phase current metering function and for the thermal overload protection function (49). The RMS values take into account harmonics up the the 13th. For all other metering and diagnosis functions, the H1 fundamental 50 Hz or 60 Hz component is used. RETURN SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 33 Metering functions Residual current This function gives the RMS value of the residual current obtained by: – measurement: Io – calculation of the sum of the phase currents: Io Accuracy at Ino: ±1%. Accuracy ± 2% from 0.3 to 1.5 Ino Accuracy ± 3% from 0.1 to 0.3 Ino The measurement range extends to 40 Ino when Io measurement is used. In the other cases, the range extends to 20 Ino. RETURN SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 34 Metering functions Demand phase current A Demand current 5mn 5mn 5mn 5mn 5mn 100A 55A 63A 89A 78A 59A t Resetting to zero: – by the clear key on the display unit if one of the two screens is displayed, – by the clear command in the SFT2841 software, – via the communication link (remote control order TC4). RETURN SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 35 Metering functions Peak demand current At the end of each integration period, i.e. once the new demand current values are available, the function determines the greatest demand current value obtained since the last reset. A Peak demand current 5mn 5mn 5mn 5mn 5mn 100A 55A 63A 89A 89A 89A t RETURN SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 36 Metering functions Phase-to-phase voltage This function gives the RMS value of the 50 or 60 Hz component of the phase-to-phase voltages. U21 voltage between phases 2 and 1 (U21=V1-V2) U32 voltage between phases 3 and 2 (U32=V2-V3) U13 voltage between phases 1 and 3 (U13=V3-V1) – by calculation when 3 phase-to-earth VTs are connected, – by measurement (U21 and U32) and by calculation (U13) when 2 phase-to-phase VTs are connected, – by measurement (U21) when only one phase-to-phase VT is connected, in which case the U32 and U13 voltages are not available. RETURN SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 37 Metering functions Frequency This measurement is based on: – U21 if only one phase-to-phase voltage is available, – positive sequence voltage if the U21 and U32 measurements are available. The frequency is not displayed (replaced by ****) if: – U21 or Vd is less than 40% of Un. – frequency is out of range. Accuracy at Unp: ±0.01Hz 25 to 65 Hz range Sepam series40 and 80 45 to 55 Hz if 50Hz Sepam series 20 55 to 65 Hz if 60Hz Sepam series 20 RETURN SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 38 Metering functions Power factor (Cos) Capacitive/inductive circuit: If V is leading compared to I, in the trigonometric (counter-clockwise) direction, then is positive. A capacitive (CAP) circuit is one in which the current is leading compared to the voltage ( <0). An inductive (IND) circuit is one in which the current is lagging compared to the voltage ( >0). V I I V RETURN SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 39 Metering functions Active, reactive and apparent power For an incoming circuit: – Power supplied to the busbars is positive. – Power supplied by the busbars is negative. Direction of power flow For an outgoing circuit: – Power supplied to the busbars is negative. – Power supplied by the busbars is positive. Direction of power flow RETURN SFT2841 connected EN 2007_01.ppt 40