* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Database Systems - School of Computer Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Data center wikipedia , lookup
Data analysis wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Expense and cost recovery system (ECRS) wikipedia , lookup
Information privacy law wikipedia , lookup
Data vault modeling wikipedia , lookup
Open data in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Business intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Versant Object Database wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
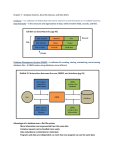
G64DBS Database Systems Tim Brailsford G64DBS Module • • • • Assessment • Exam - 75% • Coursework - 25% Recommended Textbook Date, C.J. (1999). An Introduction to Database Systems. 7th Edition. Addison Wesley. Lectures • • Mondays, 3pm in LT2 Fridays, 4pm in LT3 Labs - TBA • • Will NOT start until approximately Week 4 Wednesdays, 2-4pm in A32 Tim Brailsford ([email protected]) James Goulding Recommended Textbook Connolly, T. & Begg, C. (2009). Database Systems: A practical approach to design, implementation and management. 5th Edition. Addison Wesley. Recommended Textbook Rob, P. Coronel, C. & Crockett, K. (2008). Database Systems: design, implementation & management. 7th Edition. Thompson Learning. Recommended Textbook Mana Takahashi. (2008). The Manga Guide to Databases. English Edition. No Starch Press. What is a Database? • “A set of information held in a computer” Oxford English Dictionary • “One or more large structured sets of persistent data, usually associated with software to update and query the data” Free On-Line Dictionary of Computing • • • “A collection of data arranged for ease and speed of search and retrieval by a computer. ” American Heritage Science Dictionary • Uses of Databases • Library catalogues • Medical records • Bank accounts • Stock market data • Personnel systems • Product catalogues • Telephone directories • Train timetables • Airline bookings • Credit card details • Student records • Customer histories • Stock market prices • Discussion boards • and many more... Why Study Databases? • • Almost everything we see on a computer uses a DBMS. Philosophy - the nature of reality that we are trying to model. • no entities, just statements of communicated fact. • relation rather than object oriented programming • This could well be the next trend in programming • MONEY and JOBS! Why Study Databases? • Many computing applications deal with large amounts of information. • Database systems give a set of tools for • • storing, searching and managing this information. Databases are a ‘core topic’ in computer science and IT. Basic concepts and skills with database systems are part of the skill set you will be assumed to have as a CS and IT graduate. File Based Systems • File based systems • Data is stored in files • Each file has a specific format • Programs that use these files depend on knowledge about that format •Problems: • No standards • Data duplication • Data dependence • No way to generate complex queries • No provision for concurrency, security, recovery, etc. An Example • From the Manga Guide to Databases • The Kingdom of Kod exports apples • Price is 100G per container of apples • Departments: • Merchandise • Overseas Business • Export An Example An Example • From the Manga Guide to Databases • The Kingdom of Kod exports apples • Price is 100G per container of apples • Departments: • Merchandise • Overseas Business An Example • Mistakes get made, the overseas business department didn’t get the message... • What if the price changes? • Redundant Data Storing the same data several times in different places (redundancy) is errorprone! Database Systems • A DATABASE is a system to allow multiple users to share the SAME information. Any item of data should only be stored once Any changes to this data is thus available to all users A Database Management System (DBMS) is the software that implements a database • • • • Oracle • DB2 • MySQL • Ingres • PostgreSQL • Microsoft SQL Server • [MS Access] What a DBMS Does • • Allows users to: store data manage change (updates) organise data retrieve data retain privacy (security) Provides: Data Definition Language (DDL) Data Manipulation Language (DML) Data Control Language (DCL) These may be the same language! • • • • • Where is the DBMS? web pages HTML custom client AJAX web server DMBS tools public API DBMS (server) • • • • File System / OS DBMS Components • Data dictionary • stores information about database objects • Data dictionary compiler • extracts database information and store it in data dictionary • Query processor • interprets and optimises user queries • Transaction manager • communicates with recovery manager and • scheduler to ensure data consistency in multi-user environments Storage manager ANSI / SPARC Architecture Interaction of DBMS Components User Query (via client) Query Processor Database Administrator interp rets q uerie optim s izes q uerie s Transaction Manager Storage Manager concurrency control recovery control ent nagem ce ma a file sp Database • DD Compiler Data Dictionary • Proposed a framework for DBMS in 1975 • • Standards Planning Requirements Committee • Internal level American National Standards Institute Three tier architecture • • • for systems designers • for database designers • for database users Conceptual level External level Types of Database Users • • • • Database systems programmers • writes the DBMS software • designs and manages the database system • write the client software that allows end users to interface with the DBMS Conceptual Level • Deals with the organisation of the entire database content • Abstractions are used to remove Database administrators (DBA) unnecessary details of the internal level • Used by DBAs and application Applications developers End users • programmers • Conceptual Schema: • For example: CREATE TABLE Employee ( Name VARCHAR(25), Salary REAL, Department VARCHAR(10) ) use the information provided by the database to achieve a personal or organisational goal External Level • Provides a view of the database tailored to Internal Level • a user • Parts of the data may be hidden • Used by end users and application programmers • External Schema: • For example: Create View myView as { SELECT Name FROM Employee } • Deals with physical storage of data • • • Structure of records on disk - files, pages, blocks Indexes and ordering of records Used by database system programmers Internal Schema: • For example: RECORD EMP LENGTH=44 HEADER: BYTE(5) OFFSET=0 NAME: BYTE(25) OFFSET=5 SALARY: FULLWORD OFFSET=30 DEPT: BYTE(10) OFFSET=34